| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
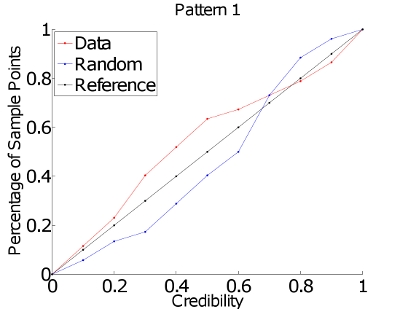
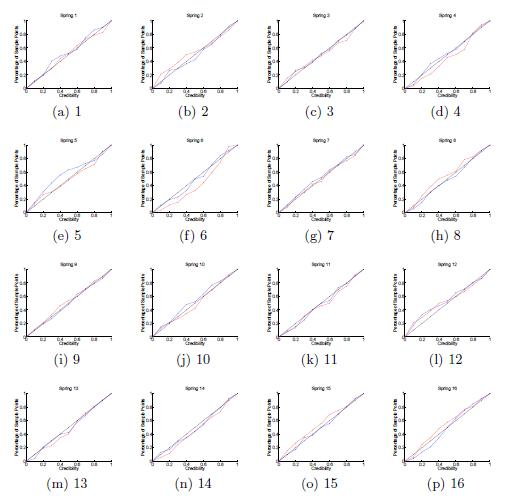
Next we look at the calculated spring constants. First, we look at them individually, drawing from Data Set A. We take experiments pairwise, one from each load, and calculate the spring constants. This gives us 16 samples in R of 52 points each. [link] plots the normality of each spring constant: all seem to be fairly normal. Because of this, we believe that the spring constants are normally distributed.
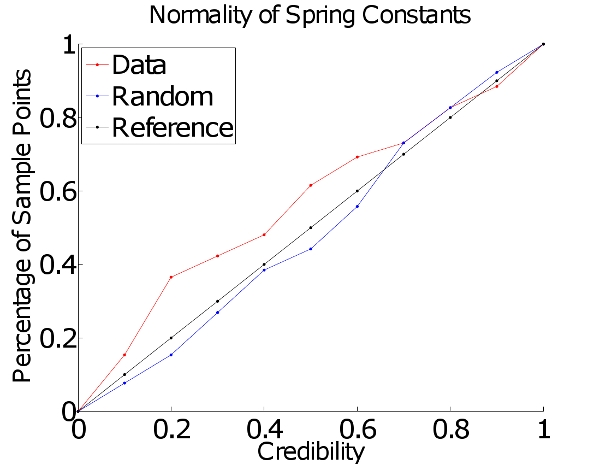
Next we look at the spring constants collectively, with one sample in R 16 . Because we believe that each individual spring constant is normally distributed, we expect the combined spring constants to be normally distributed. [link] is the plot from this sample, suggesting that the spring constants are indeed normally distributed.
When we look at our equation, , this makes sense. If A and f are fixed, then the relationship between x and k is simply linear, with no worries about the distributions of A and f . To be sure, A and f are not entirely accurate, but they are close enough to constant that we can expect k to come from the same kind of distribution as x .
Note that this criteria is fairly subjective. Plotting the random distribution helps us to get a feel for how much deviation from the reference line we can expect, but these in no way prove that the samples are from normal distributions. Rather, it suggests that, if they are not normally distributed, they can probably be reasonably approximated by a normal distribution.
In our original approach to use statistical inference to solve the inverse problem (see "Our Question" ) our problem reduced to the equation , where has the elongation of each spring along the diagonal. If we consider the experimental error as well as the error in the model the equation becomes
where α , ϵ , κ , and γ are error due to either the measurements or the model. The error ϵ is the easiest error that we can describe with all our experimental data, specifically Data Set A (see "Notes: Our Data Sets, Measuring Spring Constants, and Error" ). The error of and κ we either have no description or very little description from our experimental data. The problem that we can then study using our observed error is
Because ϵ is in the middle of the equation, it is very hard to deal with. We wish our problem to take the form
where z is the unknown variable, y is the observed variable with error ϵ , and .
To reach an equation of this form we begin by looking at our original problem (see "An Inverse Problem" ). If A T is invertible, then our equation becomes , where
Because is a vector and is a diagonal matrix, we see that our equation can be rewritten to
where , , and c is the compliance, or the vector of inverses of spring constants. Now if we include error of the observed data, e , we obtain a model for the system of the form

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'The art of the pfug' conversation and receive update notifications?