| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Microorganisms grown in closed culture (also known as a batch culture ), in which no nutrients are added and most waste is not removed, follow a reproducible growth pattern referred to as the growth curve . An example of a batch culture in nature is a pond in which a small number of cells grow in a closed environment. The culture density is defined as the number of cells per unit volume. In a closed environment, the culture density is also a measure of the number of cells in the population. Infections of the body do not always follow the growth curve, but correlations can exist depending upon the site and type of infection. When the number of live cells is plotted against time, distinct phases can be observed in the curve ( [link] ).
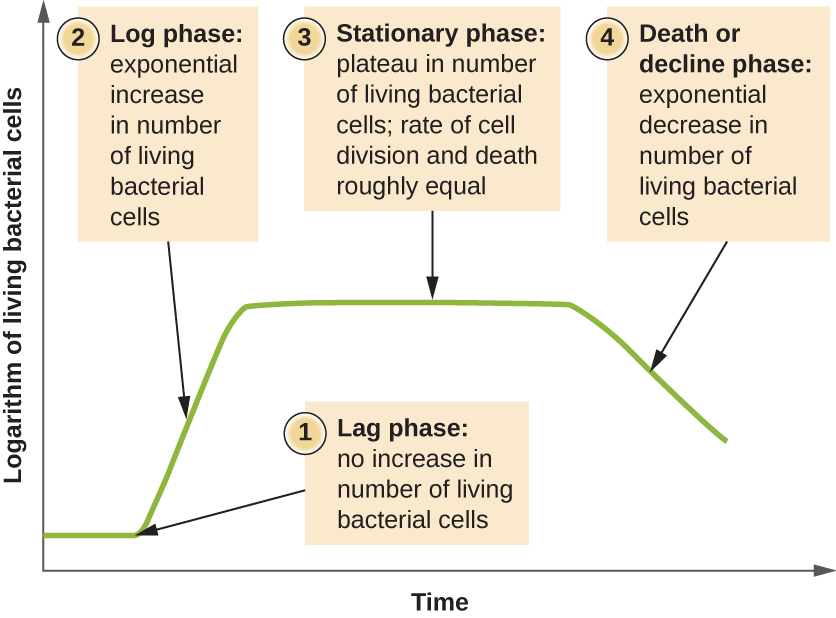
The beginning of the growth curve represents a small number of cells, referred to as an inoculum , that are added to a fresh culture medium , a nutritional broth that supports growth. The initial phase of the growth curve is called the lag phase , during which cells are gearing up for the next phase of growth. The number of cells does not change during the lag phase; however, cells grow larger and are metabolically active, synthesizing proteins needed to grow within the medium. If any cells were damaged or shocked during the transfer to the new medium, repair takes place during the lag phase. The duration of the lag phase is determined by many factors, including the species and genetic make-up of the cells, the composition of the medium, and the size of the original inoculum.
In the logarithmic (log) growth phase , sometimes called exponential growth phase , the cells are actively dividing by binary fission and their number increases exponentially. For any given bacterial species, the generation time under specific growth conditions (nutrients, temperature, pH, and so forth) is genetically determined, and this generation time is called the intrinsic growth rate . During the log phase, the relationship between time and number of cells is not linear but exponential; however, the growth curve is often plotted on a semilogarithmic graph, as shown in [link] , which gives the appearance of a linear relationship.
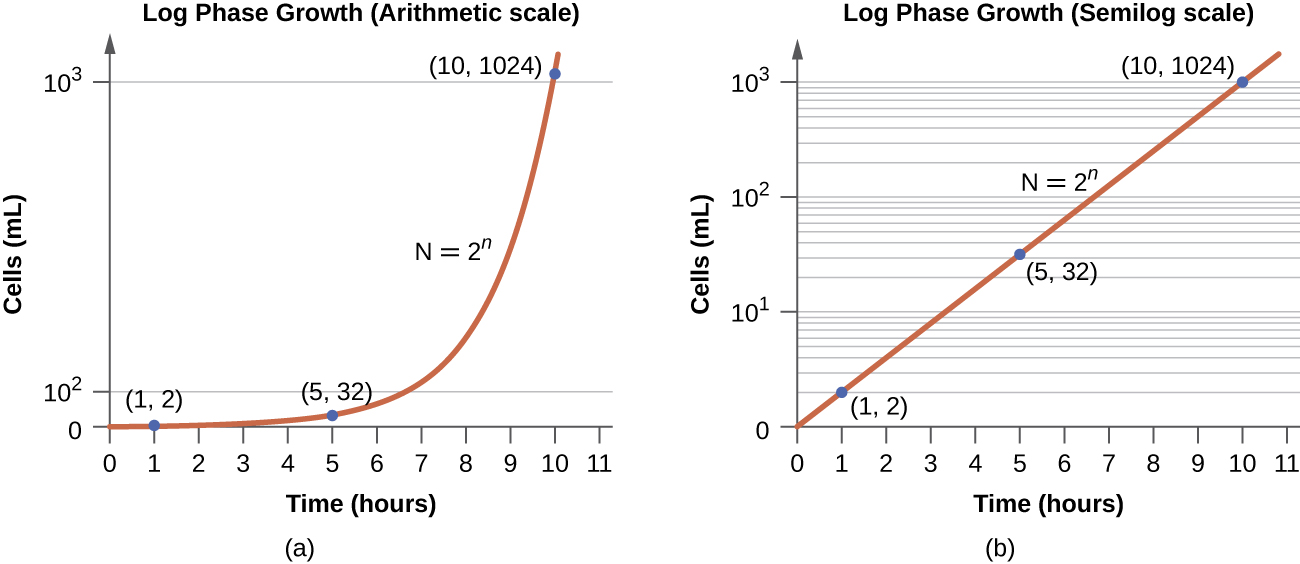
Cells in the log phase show constant growth rate and uniform metabolic activity. For this reason, cells in the log phase are preferentially used for industrial applications and research work. The log phase is also the stage where bacteria are the most susceptible to the action of disinfectants and common antibiotics that affect protein, DNA, and cell-wall synthesis.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?