| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Like proto-oncogenes, many of the negative cell cycle regulatory proteins were discovered in cells that had become cancerous. Tumor suppressor genes are segments of DNA that code for negative regulator proteins, the type of regulators that, when activated, can prevent the cell from undergoing uncontrolled division. The collective function of the best-understood tumor suppressor gene proteins, Rb, p53, and p21, is to put up a roadblock to cell cycle progression until certain events are completed. A cell that carries a mutated form of a negative regulator might not be able to halt the cell cycle if there is a problem. Tumor suppressors are similar to brakes in a vehicle: Malfunctioning brakes can contribute to a car crash.
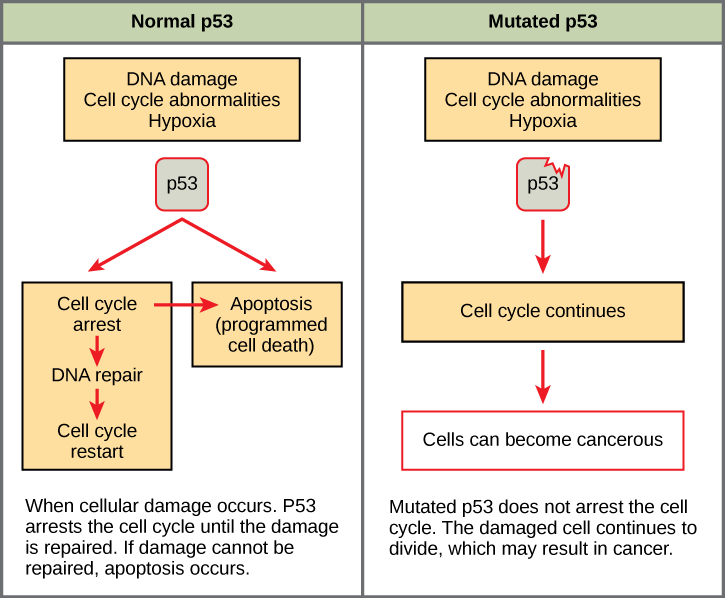
Mutated p53 genes have been identified in more than one-half of all human tumor cells. This discovery is not surprising in light of the multiple roles that the p53 protein plays at the G 1 checkpoint. A cell with a faulty p53 may fail to detect errors present in the genomic DNA ( [link] ). Even if a partially functional p53 does identify the mutations, it may no longer be able to signal the necessary DNA repair enzymes. Either way, damaged DNA will remain uncorrected. At this point, a functional p53 will deem the cell unsalvageable and trigger programmed cell death (apoptosis). The damaged version of p53 found in cancer cells, however, cannot trigger apoptosis.
Human papillomavirus can cause cervical cancer. The virus encodes E6, a protein that binds p53. Based on this fact and what you know about p53, what effect do you think E6 binding has on p53 activity?
The loss of p53 function has other repercussions for the cell cycle. Mutated p53 might lose its ability to trigger p21 production. Without adequate levels of p21, there is no effective block on cell cycle progression. Essentially, without a fully functional p53, the G 1 checkpoint is severely compromised and the cell proceeds directly from G 1 to S regardless of internal and external conditions. At the completion of this shortened cell cycle, two daughter cells are produced that have inherited the mutated p53 gene. Given the non-optimal conditions under which the parent cell reproduced, it is likely that the daughter cells will have acquired other mutations in addition to the faulty tumor suppressor gene. Cells such as these daughter cells quickly accumulate both oncogenes and non-functional tumor suppressor genes. Again, the result is tumor growth.
Go to this website to watch an animation of how cancer results from errors in the cell cycle.
Cancer is the result of unchecked cell division caused by a breakdown of the mechanisms that regulate the cell cycle. The loss of control begins with a change in the DNA sequence of a gene that codes for one of the regulatory molecules. Faulty instructions lead to a protein that does not function as it should. Any disruption of the monitoring system can allow other mistakes to be passed on to the daughter cells. Each successive cell division will give rise to daughter cells with even more accumulated damage. Eventually, all checkpoints become nonfunctional, and rapidly reproducing cells crowd out normal cells, resulting in a tumor or leukemia (blood cancer).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'General biology part i - mixed majors' conversation and receive update notifications?