| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
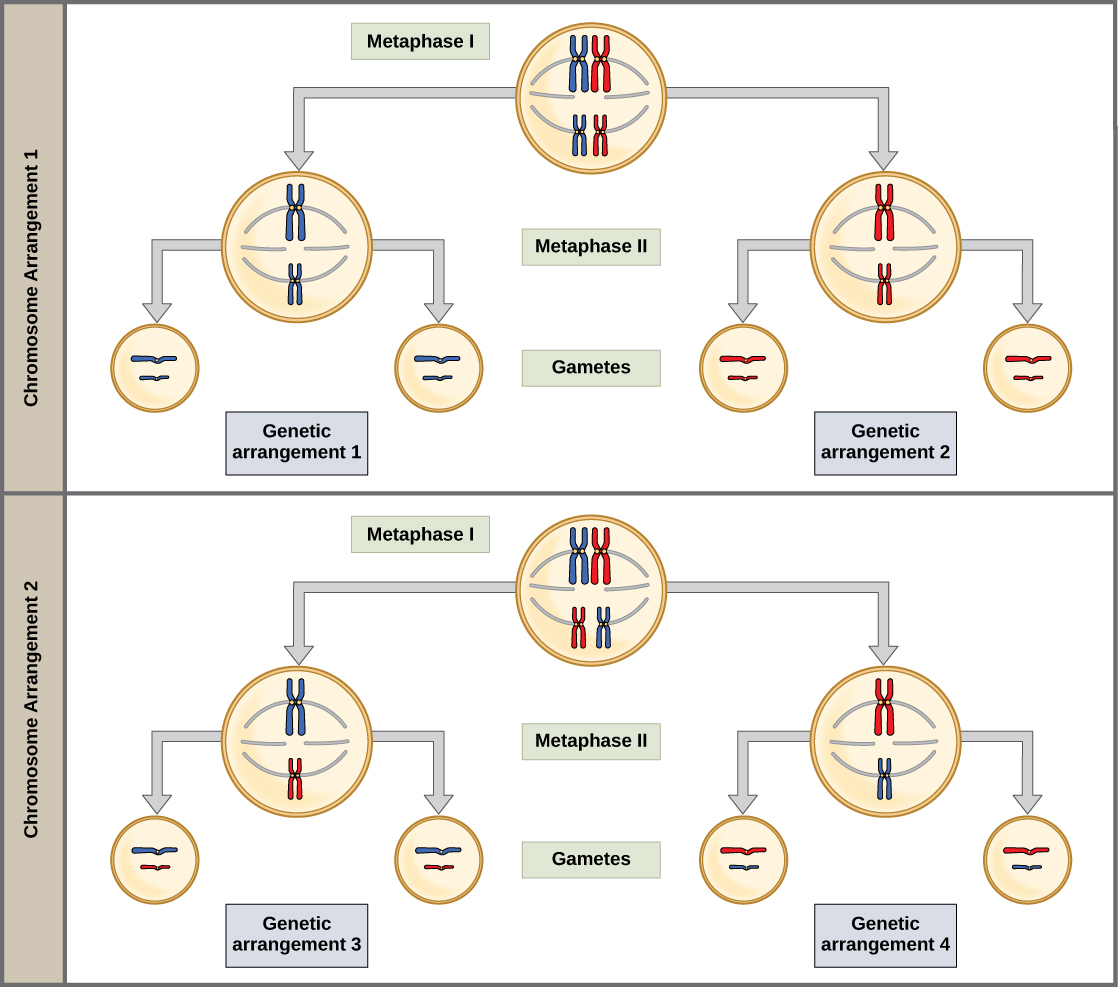
This event—the random (or independent) assortment of homologous chromosomes at the metaphase plate—is the second mechanism that introduces variation into the gametes or spores. In each cell that undergoes meiosis, the arrangement of the tetrads is different. The number of variations is dependent on the number of chromosomes making up a set. There are two possibilities for orientation at the metaphase plate; the possible number of alignments therefore equals 2 n , where n is the number of chromosomes per set. Humans have 23 chromosome pairs, which results in over eight million (2 23 ) possible genetically-distinct gametes. This number does not include the variability that was previously created in the sister chromatids by crossover. Given these two mechanisms, it is highly unlikely that any two haploid cells resulting from meiosis will have the same genetic composition ( [link] ).
To summarize the genetic consequences of meiosis I, the maternal and paternal genes are recombined by crossover events that occur between each homologous pair during prophase I. In addition, the random assortment of tetrads on the metaphase plate produces a unique combination of maternal and paternal chromosomes that will make their way into the gametes.
In anaphase I, the microtubules pull the linked chromosomes apart. The sister chromatids remain tightly bound together at the centromere. The chiasmata are broken in anaphase I as the microtubules attached to the fused kinetochores pull the homologous chromosomes apart ( [link] ).
In telophase, the separated chromosomes arrive at opposite poles. The remainder of the typical telophase events may or may not occur, depending on the species. In some organisms, the chromosomes decondense and nuclear envelopes form around the chromatids in telophase I. In other organisms, cytokinesis—the physical separation of the cytoplasmic components into two daughter cells—occurs without reformation of the nuclei. In nearly all species of animals and some fungi, cytokinesis separates the cell contents via a cleavage furrow (constriction of the actin ring that leads to cytoplasmic division). In plants, a cell plate is formed during cell cytokinesis by Golgi vesicles fusing at the metaphase plate. This cell plate will ultimately lead to the formation of cell walls that separate the two daughter cells.
Two haploid cells are the end result of the first meiotic division. The cells are haploid because at each pole, there is just one of each pair of the homologous chromosomes. Therefore, only one full set of the chromosomes is present. This is why the cells are considered haploid—there is only one chromosome set, even though each homolog still consists of two sister chromatids. Recall that sister chromatids are merely duplicates of one of the two homologous chromosomes (except for changes that occurred during crossing over). In meiosis II, these two sister chromatids will separate, creating four haploid daughter cells.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?