| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Our unique approach to visuals is designed to emphasize only the components most important in any given illustration. The art style is particularly aimed at focusing student learning through a powerful blend of traditional depictions and instructional innovations.
Much of the art in this book consists of black line illustrations. The strongest line is used to highlight the most important structures, and shading is used to show dimension and shape. Color is used sparingly to highlight and clarify the primary anatomical or functional point of the illustration. This technique is intended to draw students’ attention to the critical learning point in the illustration, without distraction from excessive gradients, shadows, and highlights. Full color is used when the structure or process requires it (for example, muscle diagrams and cardiovascular system illustrations).
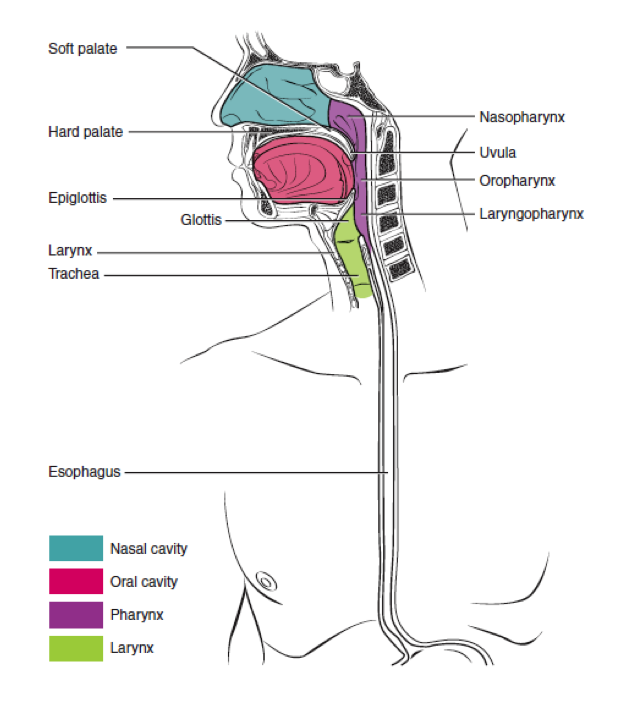
The pharynx
Micrograph magnifications have been calculated based on the objective provided with the image. If a micrograph was recorded at 40×, and the image was magnified an additional 2×, we calculated the final magnification of the micrograph to be 80×.
Please note that, when viewing the textbook electronically, the micrograph magnification provided in the text does not take into account the size and magnification of the screen on your electronic device. There may be some variation.
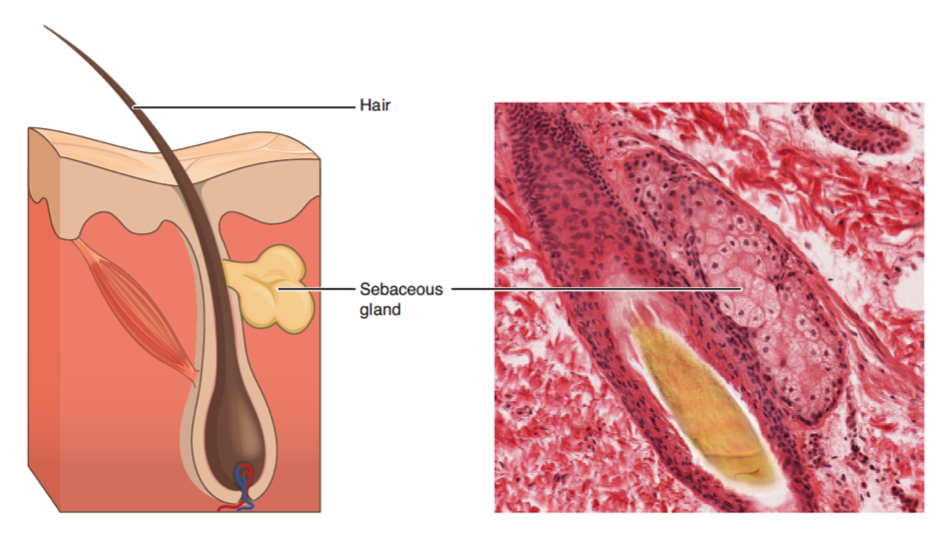
Sebaceous glands
The following resources are (or will be) available in addition to main text:
| J. Gordon Betts | Tyler Junior College |
| Peter Desaix | University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill |
| Eddie Johnson | Central Oregon Community College |
| Jody E. Johnson | Arapahoe Community College |
| Oksana Korol | Aims Community College |
| Dean Kruse | Portland Community College |
| Brandon Poe | Springfield Technical Community College |
| James A. Wise | Hampton University |
| Mark Womble | Youngstown State University |
| Kelly A. Young | California State University, Long Beach |
Robin J. Heyden
| Kim Aaronson | Aquarius Institute; Triton College |
| Lopamudra Agarwal | Augusta Technical College |
| Gary Allen | Dalhousie University |
| Robert Allison | McLennan Community College |
| Heather Armbruster | Southern Union State Community College |
| Timothy Ballard | University of North Carolina Wilmington |
| Matthew Barlow | Eastern New Mexico University |
| William Blaker | Furman University |
| Julie Bowers | East Tennessee State University |
| Emily Bradshaw | Florida Southern College |
| Nishi Bryska | University of North Carolina, Charlotte |
| Susan Caley Opsal | Illinois Valley Community College |
| Boyd Campbell | Southwest College of Naturopathic Medicine and Health Sciences |
| Ann Caplea | Walsh University |
| Marnie Chapman | University of Alaska, Sitka |
| Barbara Christie-Pope | Cornell College |
| Kenneth Crane | Texarkana College |
| Maurice Culver | Florida State College at Jacksonville |
| Heather Cushman | Tacoma Community College |
| Noelle Cutter | Molloy College |
| Lynnette Danzl-Tauer | Rock Valley College |
| Jane Davis | Aurora University |
| AnnMarie DelliPizzi | Dominican College |
| Susan Dentel | Washtenaw Community College |
| Pamela Dobbins | Shelton State Community College |
| Patty Dolan | Pacific Lutheran University |
| Sondra Dubowsky | McLennan Community College |
| Peter Dukehart | Three Rivers Community College |
| Ellen DuPré | Central College |
| Elizabeth DuPriest | Warner Pacific College |
| Pam Elf | University of Minnesota |
| Sharon Ellerton | Queensborough Community College |
| Carla Endres | Utah State University - College of Eastern Utah: San Juan Campus |
| Myriam Feldman | Lake Washington Institute of Technology; Cascadia Community College |
| Greg Fitch | Avila University |
| Lynn Gargan | Tarant County College |
| Michael Giangrande | Oakland Community College |
| Chaya Gopalan | St. Louis College of Pharmacy |
| Victor Greco | Chattahoochee Technical College |
| Susanna Heinze | Skagit Valley College |
| Ann Henninger | Wartburg College |
| Dale Horeth | Tidewater Community College |
| Michael Hortsch | University of Michigan |
| Rosemary Hubbard | Marymount University |
| Mark Hubley | Prince George's Community College |
| Branko Jablanovic | College of Lake County |
| Norman Johnson | University of Massachusetts Amherst |
| Mark Jonasson | North Arkansas College |
| Jeff Keyte | College of Saint Mary |
| William Kleinelp | Middlesex County College |
| Leigh Kleinert | Grand Rapids Community College |
| Brenda Leady | University of Toledo |
| John Lepri | University of North Carolina, Greensboro |
| Sarah Leupen | University of Maryland, Baltimore County |
| Lihua Liang | Johns Hopkins University |
| Robert Mallet | University of North Texas Health Science Center |
| Bruce Maring | Daytona State College |
| Elisabeth Martin | College of Lake County |
| Natalie Maxwell | Carl Albert State College, Sallisaw |
| Julie May | William Carey University |
| Debra McLaughlin | University of Maryland University College |
| Nicholas Mitchell | St. Bonaventure University |
| Shobhana Natarajan | Brookhaven College |
| Phillip Nicotera | St. Petersburg College |
| Mary Jane Niles | University of San Francisco |
| Ikemefuna Nwosu | Parkland College; Lake Land College |
| Betsy Ott | Tyler Junior College |
| Ivan Paul | John Wood Community College |
| Aaron Payette | College of Southern Nevada |
| Scott Payne | Kentucky Wesleyan College |
| Cameron Perkins | South Georgia College |
| David Pfeiffer | University of Alaska, Anchorage |
| Thomas Pilat | Illinois Central College |
| Eileen Preston | Tarrant County College |
| Mike Pyle | Olivet Nazarene University |
| Robert Rawding | Gannon University |
| Jason Schreer | State University of New York at Potsdam |
| Laird Sheldahl | Mt. Hood Community College |
| Brian Shmaefsky | Lone Star College System |
| Douglas Sizemore | Bevill State Community College |
| Susan Spencer | Mount Hood Community College |
| Cynthia Standley | University of Arizona |
| Robert Sullivan | Marist College |
| Eric Sun | Middle Georgia State College |
| Tom Swenson | Ithaca College |
| Kathleen Tallman | Azusa Pacific University |
| Rohinton Tarapore | University of Pennsylvania |
| Elizabeth Tattersall | Western Nevada College |
| Mark Thomas | University of Northern Colorado |
| Janis Thompson | Lorain County Community College |
| Rita Thrasher | Pensacola State College |
| David Van Wylen | St. Olaf College |
| Lynn Wandrey | Mott Community College |
| Margaret Weck | St. Louis College of Pharmacy |
| Kathleen Weiss | George Fox University |
| Neil Westergaard | Williston State College |
| David Wortham | West Georgia Technical College |
| Umesh Yadav | University of Texas Medical Branch |
| Tony Yates | Oklahoma Baptist University |
| Justin York | Glendale Community College |
| Cheri Zao | North Idaho College |
| Elena Zoubina | Bridgewater State University; Massasoit Community College |
| Shobhana Natarajan | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. |
OpenStax wishes to thank the Regents of University of Michigan Medical School for the use of their extensive micrograph collection. Many of the UM micrographs that appear in Anatomy and Physiology are interactive WebScopes, which students can explore by zooming in and out.
We also wish to thank the Open Learning Initiative at Carnegie Mellon University, with whom we shared and exchanged resources during the development of Anatomy and Physiology .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?