| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In order to maintain homeostasis in the cardiovascular system and provide adequate blood to the tissues, blood flow must be redirected continually to the tissues as they become more active. In a very real sense, the cardiovascular system engages in resource allocation, because there is not enough blood flow to distribute blood equally to all tissues simultaneously. For example, when an individual is exercising, more blood will be directed to skeletal muscles, the heart, and the lungs. Following a meal, more blood is directed to the digestive system. Only the brain receives a more or less constant supply of blood whether you are active, resting, thinking, or engaged in any other activity.
[link] provides the distribution of systemic blood at rest and during exercise. Although most of the data appears logical, the values for the distribution of blood to the integument may seem surprising. During exercise, the body distributes more blood to the body surface where it can dissipate the excess heat generated by increased activity into the environment.
| Systemic Blood Flow During Rest, Mild Exercise, and Maximal Exercise in a Healthy Young Individual | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Organ | Resting
(mL/min) |
Mild exercise
(mL/min) |
Maximal exercise
(mL/min) |
| Skeletal muscle | 1200 | 4500 | 12,500 |
| Heart | 250 | 350 | 750 |
| Brain | 750 | 750 | 750 |
| Integument | 500 | 1500 | 1900 |
| Kidney | 1100 | 900 | 600 |
| Gastrointestinal | 1400 | 1100 | 600 |
| Others
(i.e., liver, spleen) |
600 | 400 | 400 |
| Total | 5800 | 9500 | 17,500 |
Three homeostatic mechanisms ensure adequate blood flow, blood pressure, distribution, and ultimately perfusion: neural, endocrine, and autoregulatory mechanisms. They are summarized in [link] .
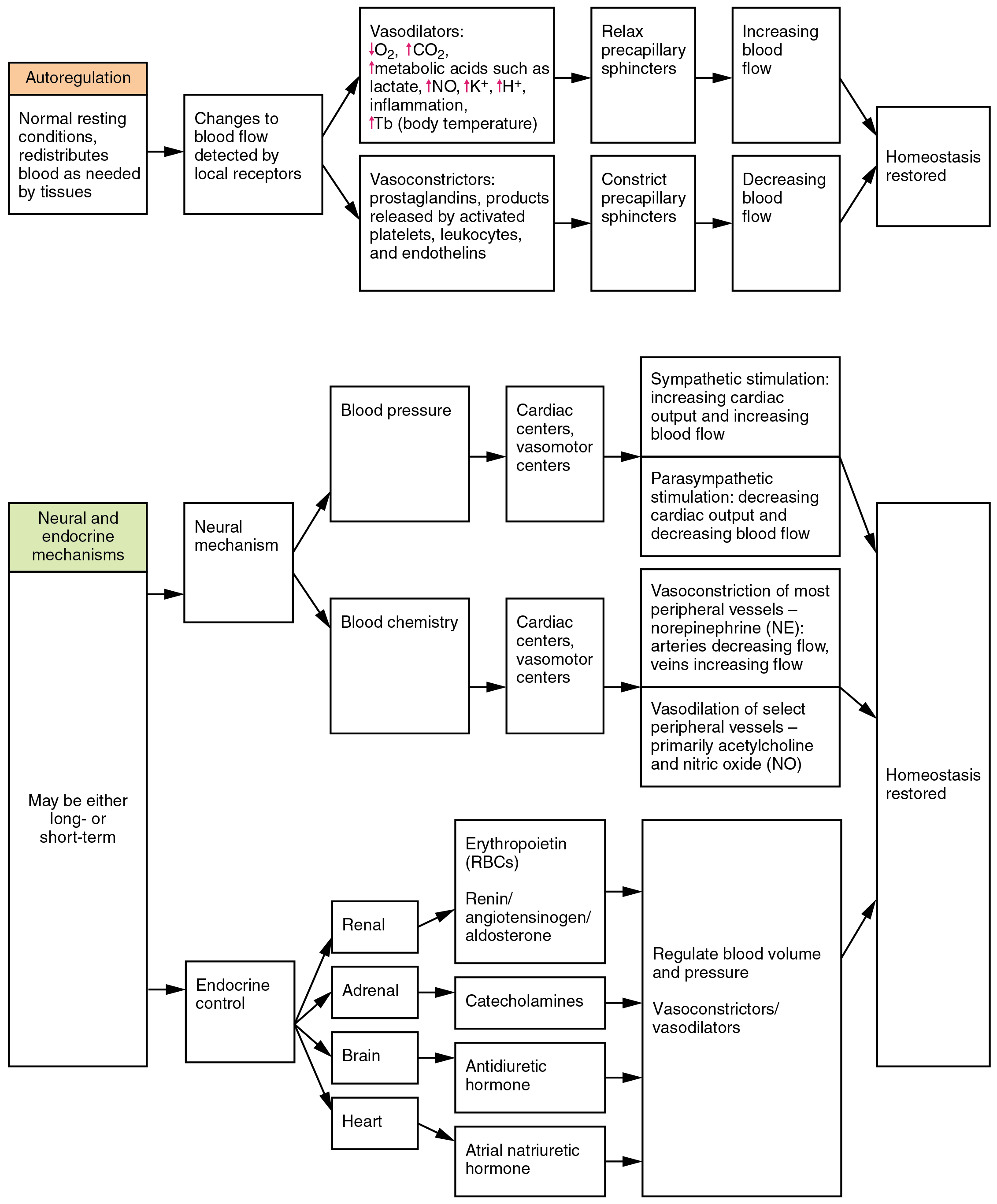
The nervous system plays a critical role in the regulation of vascular homeostasis. The primary regulatory sites include the cardiovascular centers in the brain that control both cardiac and vascular functions. In addition, more generalized neural responses from the limbic system and the autonomic nervous system are factors.
Neurological regulation of blood pressure and flow depends on the cardiovascular centers located in the medulla oblongata. This cluster of neurons responds to changes in blood pressure as well as blood concentrations of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen ions. The cardiovascular center contains three distinct paired components:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?