| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As we can see, neither subtraction nor division is associative.
The distributive property states that the product of a factor times a sum is the sum of the factor times each term in the sum.
This property combines both addition and multiplication (and is the only property to do so). Let us consider an example.
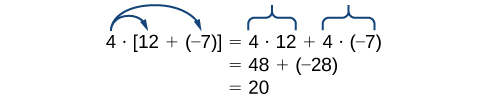
Note that 4 is outside the grouping symbols, so we distribute the 4 by multiplying it by 12, multiplying it by –7, and adding the products.
To be more precise when describing this property, we say that multiplication distributes over addition. The reverse is not true, as we can see in this example.
Multiplication does not distribute over subtraction, and division distributes over neither addition nor subtraction.
A special case of the distributive property occurs when a sum of terms is subtracted.
For example, consider the difference We can rewrite the difference of the two terms 12 and by turning the subtraction expression into addition of the opposite. So instead of subtracting we add the opposite.
Now, distribute and simplify the result.
This seems like a lot of trouble for a simple sum, but it illustrates a powerful result that will be useful once we introduce algebraic terms. To subtract a sum of terms, change the sign of each term and add the results. With this in mind, we can rewrite the last example.
The identity property of addition states that there is a unique number, called the additive identity (0) that, when added to a number, results in the original number.
The identity property of multiplication states that there is a unique number, called the multiplicative identity (1) that, when multiplied by a number, results in the original number.
For example, we have and There are no exceptions for these properties; they work for every real number, including 0 and 1.
The inverse property of addition states that, for every real number a , there is a unique number, called the additive inverse (or opposite), denoted− a , that, when added to the original number, results in the additive identity, 0.
For example, if the additive inverse is 8, since
The inverse property of multiplication holds for all real numbers except 0 because the reciprocal of 0 is not defined. The property states that, for every real number a , there is a unique number, called the multiplicative inverse (or reciprocal), denoted that, when multiplied by the original number, results in the multiplicative identity, 1.
For example, if the reciprocal, denoted is because
The following properties hold for real numbers a , b , and c .
| Addition | Multiplication | |
| Commutative Property | ||
| Associative Property | ||
| Distributive Property | ||
| Identity Property | There exists a unique real number called the additive identity, 0, such that, for any real number
a
|
There exists a unique real number called the multiplicative identity, 1, such that, for any real number
a
|
| Inverse Property | Every real number a has an additive inverse, or opposite, denoted
–a , such that
|
Every nonzero real number
a has a multiplicative inverse, or reciprocal, denoted
such that
|

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?