| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Current in a conductor consists of moving charges. Therefore, a current carrying coil in a magnetic field will also feel the Lorentz force. For a straight current carrying wire which is not moving:
where
is the force (in newtons, N)
is the current in the wire (in amperes, A)
is the length of the wire which is in the magnetic field (in m) and
is the magnetic field strength (in teslas, T).
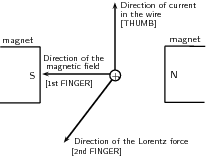
The direction of the Lorentz force is perpendicular to both the direction of the flow of current and the magnetic field and can be found using the Right Hand Rule as shown in the picture below. Use your right hand ; your thumb points in the direction of the current, your first finger in the direction of the magnetic field and your third finger will then point in the direction of the force.
Both motors and generators can be explained in terms of a coil that rotates in a magnetic field. In a generator the coil is attached to an external circuit that is turned, resulting in a changing flux that induces an emf. In a motor, a current-carrying coil in a magnetic field experiences a force on both sides of the coil, creating a twisting force (called a torque , pronounce like 'talk') which makes it turn.
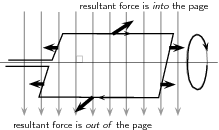
Any coil carrying current can feel a force in a magnetic field. The force is the Lorentz force on the moving charges in the conductor. The force on opposite sides of the coil will be in opposite directions because the charges are moving in opposite directions. This means the coil will rotate, see the picture below:
Instead of rotating the loops through a magnetic field to create electricity, a current is sent through the wires, creating electromagnets. The outer magnets will then repel the electromagnets and rotate the shaft as an electric motor. If the current is AC, the two slip rings are required to create an AC motor. An AC motor is shown in [link]

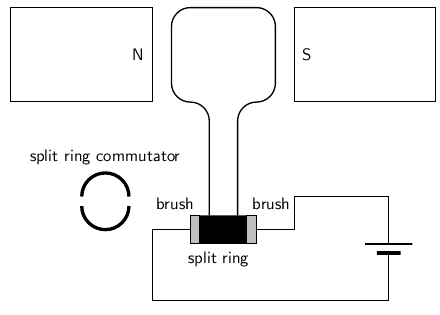
If the current is DC, split-ring commutators are required to create a DC motor. This is shown in [link] .
A car contains an alternator that charges its battery and powers the car's electric system when its engine is running. Alternators have the great advantage over direct-current generators of not using a commutator, which makes them simpler, lighter, less costly, and more rugged than a DC generator.
Try to find out the different ampere values produced by alternators for different types of machines. Compare these to understand what numbers make sense in the real world. You will find different numbers for cars, trucks, buses, boats etc. Try to find out what other machines might have alternators.
A car also contains a DC electric motor, the starter motor, to turn over the engine to start it. A starter motor consists of the very powerful DC electric motor and starter solenoid that is attached to the motor.A starter motor requires a very high current to crank the engine, that's why it's connected to the battery with large cables.
AC generators are mainly used in the real-world to generate electricity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?