| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the space shuttle, gravity acts on each of the atoms constituting our body and this gravity itself is the provider of centripetal force. There is no push on the body as in the case of car. The body experiences the "feeling" of weightlessness as both space shuttle and the person are continuously falling towards center of Earth. The person is not able to push other bodies. Importantly, gravitational pull or weight of the person is equal to mg’ and not equal to zero.
Horizontal rotor holds an object against the wall of a rotating cylinder at a certain angular speed. The object (which could be a person in a fun game arrangement) is held by friction between the surfaces of the object and the cylinder's inside wall. For a given weight of the object, there is a threshold minimum velocity of the rotor (cylinder); otherwise the object will fall down.
The object has a tendency to move straight. As the object is forced to move in a circle, it tends to move away from the center. This means that the object presses the wall of the rotor. The rotor, in turn, applies normal force on the object towards the center of circular path.
Since friction is linearly related to normal force for a given pair of surfaces ( ), it is possible to adjust speed of the rotor such that maximum friction is equal to the weight of the object. In the vertical direction, we have :
Horizontal circular motion in a rotor
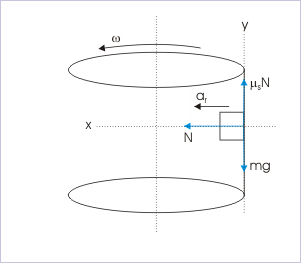
Combining two equations, we have :
This is threshold value of speed for the person to remain stuck with the rotor.
We note following points about the horizontal rotor :
Motion in vertical loop involves non-uniform circular motion. To illustrate the force analysis, we consider the motion of a cyclist, who makes circular rounds in vertical plane within a cylindrical surface by maintaining a certain speed.
In the vertical loop within a hallow cylindrical surface, the cyclist tends to move straight in accordance with its natural tendency. The curvature of cylinder, however, forces the cyclist to move along circular path (by changing direction). As such, the body has the tendency to press the surface of the cylindrical surface. In turn, cylindrical surface presses the body towards the center of the circular path.
Vertical circular motion
The free body diagram of the cyclist at an angle “θ” is shown in the figure. We see that the resultant of normal force and component of weight in the radial direction meets the requirement of centripetal force in radial direction,
Vertical circular motion
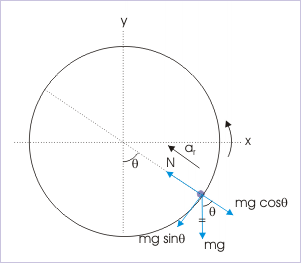
The distinguishing aspects of circular motion in vertical plane are listed here :
The cyclist is required to maintain a minimum speed to avoid free fall. The possibility of free fall is most stringent at the highest point of the loop. We, therefore, analyze the motion at the highest point with the help of the free body diagram as shown in the figure.
Vertical circular motion
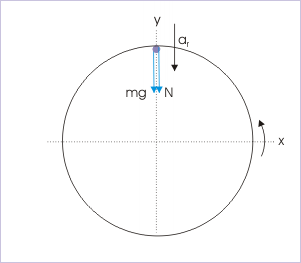
Th minimum speed of the cyclist corresponds to the situation when normal force is zero. For this condition,
This motion is same as discussed above. Only difference is that tension of the string replaces normal force in this case. The force at the highest point is given as :
Also, the minimum speed for the string not to slack at the highest point (T = 0),
The complete analysis of circular motion in vertical plane involves considering forces on the body at different positions. However, external forces depend on the position of the body in the circular trajectory. The forces are not constant forces as in the case of circular motion in horizontal plane.
We shall learn subsequently that situation involving variable force is best analyzed in terms of energy concept. As such, we will revisit vertical circular motion again after studying different forms of mechanical energy.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?