| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The constant acceleration is a special case of accelerated motion. There are vast instances of motions, which can be approximated to be under constant force and hence constant acceleration. Two of the most important forces controlling motions in our daily life are force due to gravity and friction force. Incidentally, these two forces are constant in the range of motions of bodies in which we are interested. For example, force due to gravity is given by :
where "G" is the universal constant, "M" is the mass of earth, "m" is the mass of the body and "r" is the distance between center of earth and the body.
The resulting acceleration due to gravity, g, is a constant in the immediate neighborhood of the earth surface and is given by :
The only variable for a given mass is "r", which changes with the position of the body. The distance "r", however, is equal to Earth's radius for all practical purposes as any difference arising from the position of body on earth can be ignored. Therefore, acceleration due to gravity can safely be considered to be constant for motions close to the surface of the earth. Significantly acceleration due to gravity is a constant irrespective of the mass "m" of the body.
A ball kicked from a height
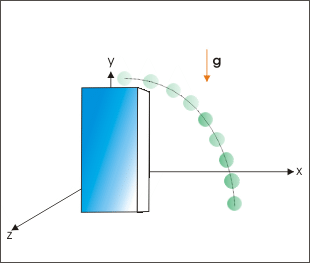
The figure above shows the motion of a ball kicked from the top of a tower. The ball moves under constant acceleration of gravity during its flight to the ground. The constant acceleration, therefore, assumes significance in relation to the motion that takes place under the influence of gravity. In the same manner, motion on a rough plane is acted upon by the force of friction in the direction opposite to the motion. The force of friction is a constant force for the moving body and characteristic of the surfaces in contact. As a result, the object slows down at a constant rate.
Motion influenced by friction force
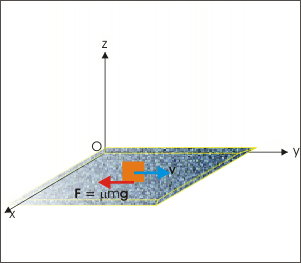
The constant acceleration means that the acceleration is independent of time and is equal to a constant value. The implication of a constant acceleration is discussed here as under :
1: As acceleration is same at all instants during the motion, it follows that average acceleration is equal to instantaneous acceleration during the motion. Mathematically,
2: When Δt = 1 second, then
This means that initial velocity , on an average, is changed by the acceleration vector after every second.
Problem : The position of a particle, in meters, moving in the coordinate space is described by the following functions in time.
Find the velocity and acceleration at t = 2 seconds from the start of motion. Also, calculate average acceleration in the first four seconds.
Solution : The component velocities in three directions are :
and the velocity is given by :
Thus, velocity at t = 2 seconds,
Acceleration of the particle along three axes are given as :
The resultant acceleration is given by :
which is a constant and is independent of time. The accelerations at all time instants are, therefore, same. We know that the average and instantaneous accelerations are equal when acceleration is constant. Hence, . We can check the result calculating average acceleration for the first four seconds as :

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?