| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Angular momentum, like energy and linear momentum, is conserved. This universally applicable law is another sign of underlying unity in physical laws. Angular momentum is conserved when net external torque is zero, just as linear momentum is conserved when the net external force is zero.
We can now understand why Earth keeps on spinning. As we saw in the previous example, . This equation means that, to change angular momentum, a torque must act over some period of time. Because Earth has a large angular momentum, a large torque acting over a long time is needed to change its rate of spin. So what external torques are there? Tidal friction exerts torque that is slowing Earth's rotation, but tens of millions of years must pass before the change is very significant. Recent research indicates the length of the day was 18 h some 900 million years ago. Only the tides exert significant retarding torques on Earth, and so it will continue to spin, although ever more slowly, for many billions of years.
What we have here is, in fact, another conservation law. If the net torque is zero , then angular momentum is constant or conserved . We can see this rigorously by considering for the situation in which the net torque is zero. In that case,
implying that
If the change in angular momentum is zero, then the angular momentum is constant; thus,
or
These expressions are the law of conservation of angular momentum . Conservation laws are as scarce as they are important.
An example of conservation of angular momentum is seen in [link] , in which an ice skater is executing a spin. The net torque on her is very close to zero, because there is relatively little friction between her skates and the ice and because the friction is exerted very close to the pivot point. (Both and are small, and so is negligibly small.) Consequently, she can spin for quite some time. She can do something else, too. She can increase her rate of spin by pulling her arms and legs in. Why does pulling her arms and legs in increase her rate of spin? The answer is that her angular momentum is constant, so that
Expressing this equation in terms of the moment of inertia,
where the primed quantities refer to conditions after she has pulled in her arms and reduced her moment of inertia. Because is smaller, the angular velocity must increase to keep the angular momentum constant. The change can be dramatic, as the following example shows.
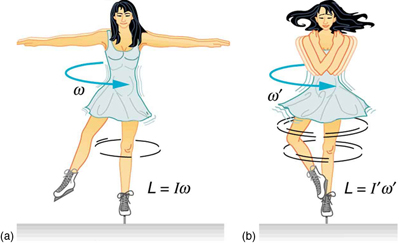
Suppose an ice skater, such as the one in [link] , is spinning at 0.800 rev/ s with her arms extended. She has a moment of inertia of with her arms extended and of with her arms close to her body. (These moments of inertia are based on reasonable assumptions about a 60.0-kg skater.) (a) What is her angular velocity in revolutions per second after she pulls in her arms? (b) What is her rotational kinetic energy before and after she does this?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?