| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Make waves with a dripping faucet, audio speaker, or laser! Add a second source or a pair of slits to create an interference pattern.

A guitar string has a number of frequencies at which it vibrates naturally. Which of the following is true in this context?
Explain the principle of superposition with figures that show the changes in the wave amplitude.
The student explains the principle of superposition and then shows two waves adding up to form a bigger wave when a crest adds with a crest and a trough with another trough. Also the student shows a wave getting cancelled out when a crest meets a trough and vice versa.
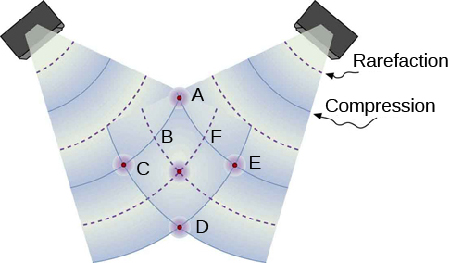
In this figure which points represent the points of constructive interference?
A string is fixed on both sides. It is snapped from both ends at the same time by applying an equal force. What happens to the shape of the waves generated in the string? Also, will you observe an overlap of waves?
The student must note that the shape of the wave remains the same and there is first an overlap and then receding of the waves.
In the preceding question, what would happen to the amplitude of the waves generated in this way? Also, consider another scenario where the string is snapped up from one end and down from the other end. What will happen in this situation?
Two sine waves travel in the same direction in a medium. The amplitude of each wave is A , and the phase difference between the two is 180°. What is the resultant amplitude?
(c)
Standing wave patterns consist of nodes and antinodes formed by repeated interference between two waves of the same frequency traveling in opposite directions. What are nodes and antinodes and how are they produced?
Speakers in stereo systems have two color-coded terminals to indicate how to hook up the wires. If the wires are reversed, the speaker moves in a direction opposite that of a properly connected speaker. Explain why it is important to have both speakers connected the same way.
A car has two horns, one emitting a frequency of 199 Hz and the other emitting a frequency of 203 Hz. What beat frequency do they produce?
The middle-C hammer of a piano hits two strings, producing beats of 1.50 Hz. One of the strings is tuned to 260.00 Hz. What frequencies could the other string have?
Two tuning forks having frequencies of 460 and 464 Hz are struck simultaneously. What average frequency will you hear, and what will the beat frequency be?
462 Hz,
4 Hz
Twin jet engines on an airplane are producing an average sound frequency of 4100 Hz with a beat frequency of 0.500 Hz. What are their individual frequencies?
A wave traveling on a Slinky® that is stretched to 4 m takes 2.4 s to travel the length of the Slinky and back again. (a) What is the speed of the wave? (b) Using the same Slinky stretched to the same length, a standing wave is created which consists of three antinodes and four nodes. At what frequency must the Slinky be oscillating?
(a) 3.33 m/s
(b) 1.25 Hz
Three adjacent keys on a piano (F, F-sharp, and G) are struck simultaneously, producing frequencies of 349, 370, and 392 Hz. What beat frequencies are produced by this discordant combination?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?