| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Doppler-shifted radar echoes are used to measure wind velocities in storms as well as aircraft and automobile speeds. The principle is the same as for Doppler-shifted ultrasound. There is evidence that bats and dolphins may also sense the velocity of an object (such as prey) reflecting their ultrasound signals by observing its Doppler shift.
Ultrasound that has a frequency of 2.50 MHz is sent toward blood in an artery that is moving toward the source at 20.0 cm/s, as illustrated in [link] . Use the speed of sound in human tissue as 1540 m/s. (Assume that the frequency of 2.50 MHz is accurate to seven significant figures.)
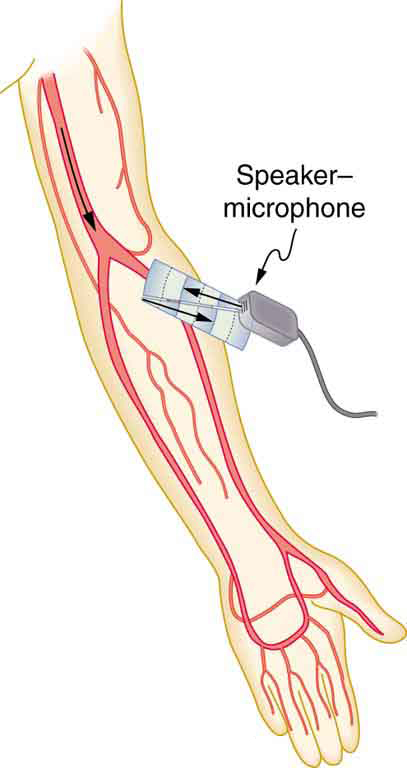
Strategy
The first two questions can be answered using and for the Doppler shift. The last question asks for beat frequency, which is the difference between the original and returning frequencies.
Solution for (a)
(1) Identify knowns:
(2) Enter the given values into the equation.
(3) Calculate to find the frequency: 2,500,325 Hz.
Solution for (b)
(1) Identify knowns:
is the frequency received by the speaker-microphone.
The minus sign is used because the motion is toward the observer.
(2) Enter the given values into the equation:
(3) Calculate to find the frequency returning to the source: 2,500,649 Hz.
Solution for (c)
(1) Identify knowns:
(2) Substitute known values:
(3) Calculate to find the beat frequency: 649 Hz.
Discussion
The Doppler shifts are quite small compared with the original frequency of 2.50 MHz. It is far easier to measure the beat frequency than it is to measure the echo frequency with an accuracy great enough to see shifts of a few hundred hertz out of a couple of megahertz. Furthermore, variations in the source frequency do not greatly affect the beat frequency, because both and would increase or decrease. Those changes subtract out in

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?