| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This module will explain norms, a mathematical concept that provides a notion of the size of a vector. Specifically, the general definition of a norm will be discussed and discrete time signal norms will be presented.
The norm of a vector is a real number that represents the "size" of the vector.
In , we can define a norm to be a vectors geometric length.
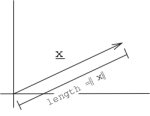
, norm
Mathematically, a norm is just a function (taking a vector and returning a real number) that satisfies three rules.
To be a norm, must satisfy:
A vector space with a well defined norm is called a normed vector space or normed linear space .
(or ), , , with this norm is called .
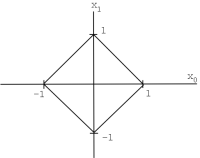
(or ), with norm , is called (the usual "Euclidean"norm).
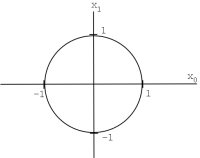
We can define similar norms for spaces of sequences and functions.
Discrete time signals = sequences of numbers
For continuous time functions:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Signals and systems' conversation and receive update notifications?