| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

| LO 1.1.1 | LO 2.10 | LO 3.2.2 | LO 3.3.1 |

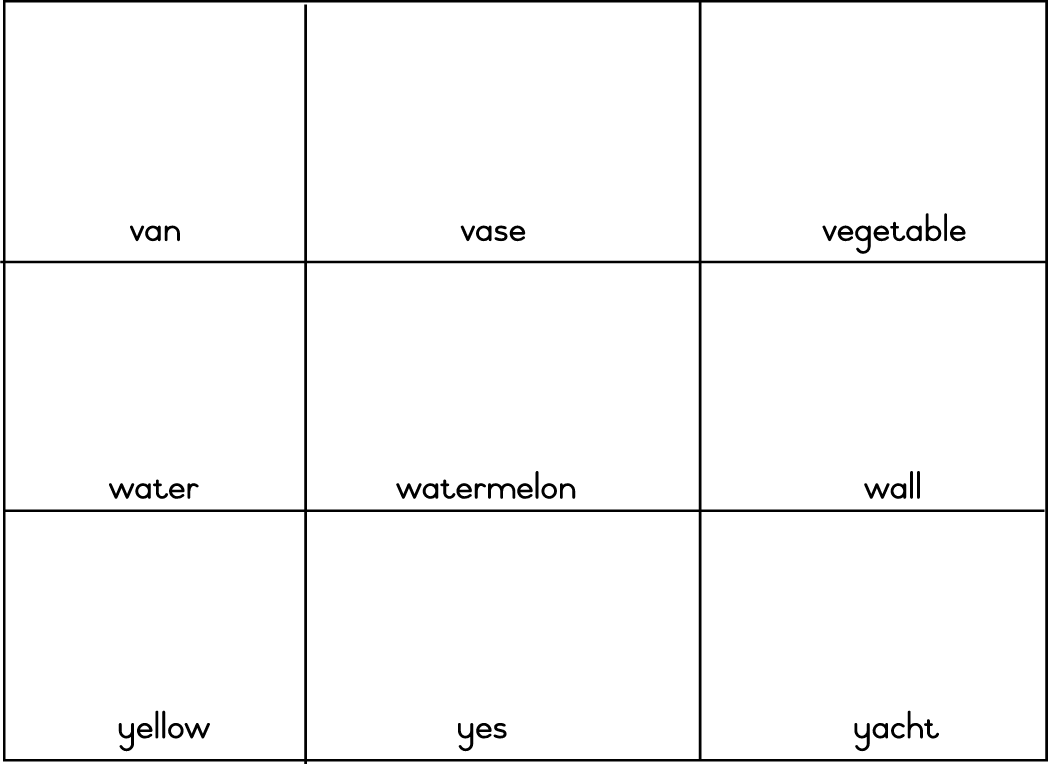
| LO 1.5.1 | LO 3.3 | LO 3.7.2 |
This went on for a long time.
The shoemaker and his wife were never hungry.
One night the shoemaker’s wife said, “Let’s sit up and find out who makes our shoes”.
And so they did.
When the clock struck twelve, three little elves ran into the room. They jumped onto the workbench.
They rapped and tapped and made all the shoes. Then they ran away.

-What are they?
-What do they look like?
-How big are they?
-Where do you think they live?
-Why did they help the shoemaker?
| LO 2.5 | LO 3.2.3 | LO 3.3.1 | LO 6.1 |
The kind shoemaker and his kind wife made some new clothes for the little elves.
That night they left the new clothes with the leather.
When the clock struck twelve, the three little elves came in to stitch the shoes.
They saw the beautiful clothes and put them on.
They rapped and tapped until all the shoes were made. Then they ran away and were never seen again.
The shoemaker and his wife were rich.
They made many pairs of shoes and sold them. They lived happily ever after.

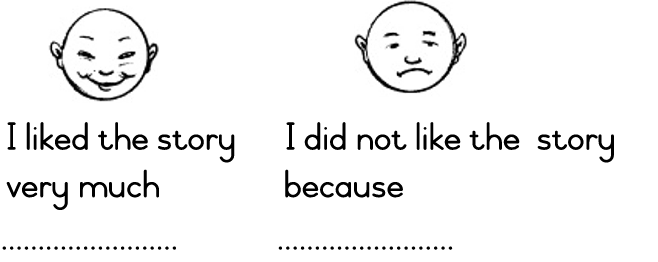
| LO 1.1.6 | LO 3.8.1 | LO 6.6 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING : The learner will be able to listen for information and enjoyment, and respond appropriately and critically in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.1: We know this when the learner shows understanding of stories:
1.1.1 predicts what the story will be about from the title;
1.1.4 recalls and retells parts of the story;
1.1.6 expresses feelings about the story;
1.1.7 discusses in own home language any social and ethical issues (e.g. whether something is fair);
Assessment Standard 1.5: We know this when the learner develops phonic awareness:
1.5.1 distinguishes between different vowel sounds that are important for reading and writing (e.g. ‘u’ and ‘ur’ in ‘hut’ and ‘hurt’);
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.1: We know this when the learner answers questions using words and phrases;
Assessment Standard 2.6: We know this when the learner attends to pronunciation as part of reading, for example;
Assessment Standard 2.10: We know this when the learner participates in a conversation on a familiar topic;
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment, and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts;
Assessment Standard 3.1: We know this when the learner uses visual cues to make meaning:
3.1.1 understands a picture story or comic strip by relating captions and speech bubbles to visual images;
Assessment Standard 3.2: We know this when the learner makes meaning of written text by reading with the teacher;
3.2.2 predicts what a book is about from the title;
3.2.3 answers literal questions about the story;
Assessment Standard 3.3: We know this when the learner recognises and makes meaning of letters and words:
3.3.1 recognises on sight an increasing number of high-frequency words;
Assessment Standard 3.7: We know this when the learner develops phonic awareness:
3.7.2 recognises some differences between sound/spelling relationships in home and additional language (e.g. ‘thatha’ and ‘thin’);
Assessment Standard 3.8: We know this when the learner develops phonic awareness:
Learning Outcome 6: GRAMMAR AND VOCABULARY : The learner knows and is able to use the sounds, vocabulary and grammar of the language to create and interpret texts.
Assessment Standard 6.1: We know this when the learner understands and uses a variety of question forms (e.g. ‘where…?’, ‘when…?’, ‘why…?’);
Assessment Standard 6.6: We know this when the learner understands some adjectives (e.g. bored, tired).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English first additional language grade 3' conversation and receive update notifications?