| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
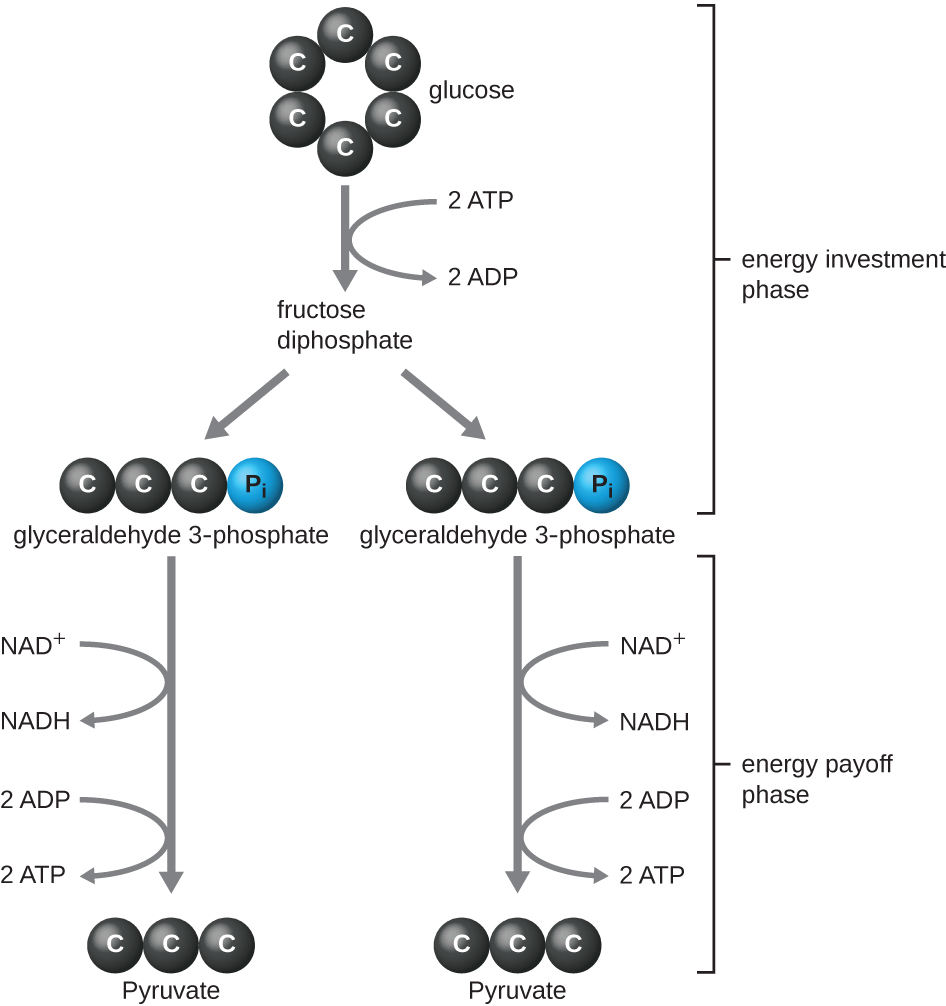
The type of glycolysis found in animals and that is most common in microbes is the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas (EMP) pathway , named after Gustav Embden (1874–1933), Otto Meyerhof (1884–1951), and Jakub Parnas (1884–1949). Glycolysis using the EMP pathway consists of two distinct phases ( [link] ). The first part of the pathway, called the energy investment phase, uses energy from two ATP molecules to modify a glucose molecule so that the six-carbon sugar molecule can be split evenly into two phosphorylated three-carbon molecules called glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). The second part of the pathway, called the energy payoff phase, extracts energy by oxidizing G3P to pyruvate, producing four ATP molecules and reducing two molecules of NAD + to two molecules of NADH, using electrons that originated from glucose. (A discussion and illustration of the full EMP pathway with chemical structures and enzyme names appear in Appendix C .)
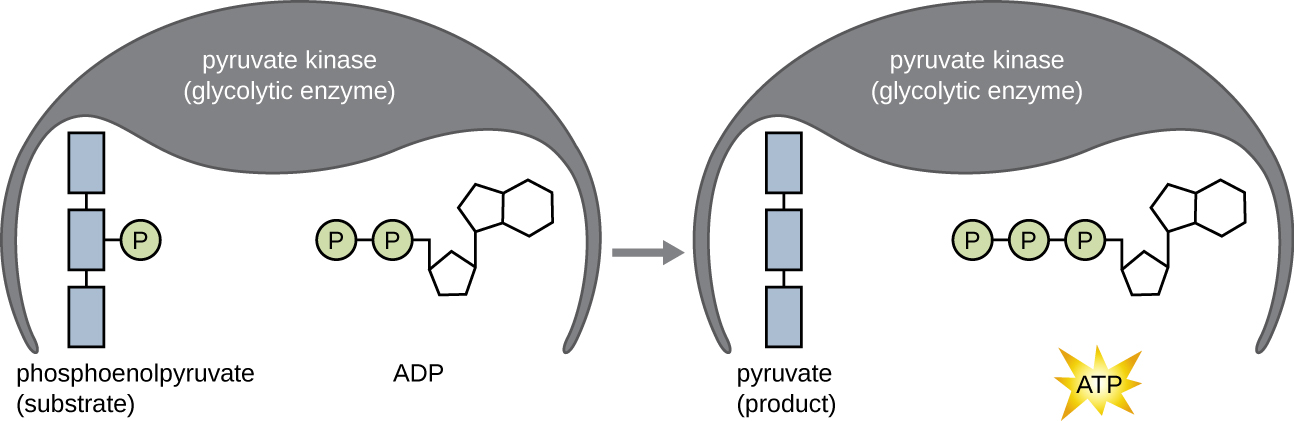
The ATP molecules produced during the energy payoff phase of glycolysis are formed by substrate-level phosphorylation ( [link] ), one of two mechanisms for producing ATP. In substrate-level phosphorylation, a phosphate group is removed from an organic molecule and is directly transferred to an available ADP molecule, producing ATP. During glycolysis, high-energy phosphate groups from the intermediate molecules are added to ADP to make ATP.
Overall, in this process of glycolysis, the net gain from the breakdown of a single glucose molecule is:
When we refer to glycolysis, unless otherwise indicated, we are referring to the EMP pathway used by animals and many bacteria. However, some prokaryotes use alternative glycolytic pathways. One important alternative is the Entner-Doudoroff (ED) pathway , named after its discoverers Nathan Entner and Michael Doudoroff (1911–1975). Although some bacteria, including the opportunistic gram-negative pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa , contain only the ED pathway for glycolysis, other bacteria, like E. coli , have the ability to use either the ED pathway or the EMP pathway.
A third type of glycolytic pathway that occurs in all cells, which is quite different from the previous two pathways, is the pentose phosphate pathway ( PPP ) also called the phosphogluconate pathway or the hexose monophosphate shunt . Evidence suggests that the PPP may be the most ancient universal glycolytic pathway. The intermediates from the PPP are used for the biosynthesis of nucleotides and amino acids. Therefore, this glycolytic pathway may be favored when the cell has need for nucleic acid and/or protein synthesis, respectively. A discussion and illustration of the complete ED pathway and PPP with chemical structures and enzyme names appear in Appendix C .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?