| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Perspiration (sweat) provides some moisture to the epidermis, which can increase the potential for microbial growth. For this reason, more microbes are found on the regions of the skin that produce the most sweat, such as the skin of the underarms and groin. However, in addition to water, sweat also contains substances that inhibit microbial growth, such as salts, lysozyme , and antimicrobial peptides . Sebum also serves to protect the skin and reduce water loss. Although some of the lipids and fatty acids in sebum inhibit microbial growth, sebum contains compounds that provide nutrition for certain microbes.
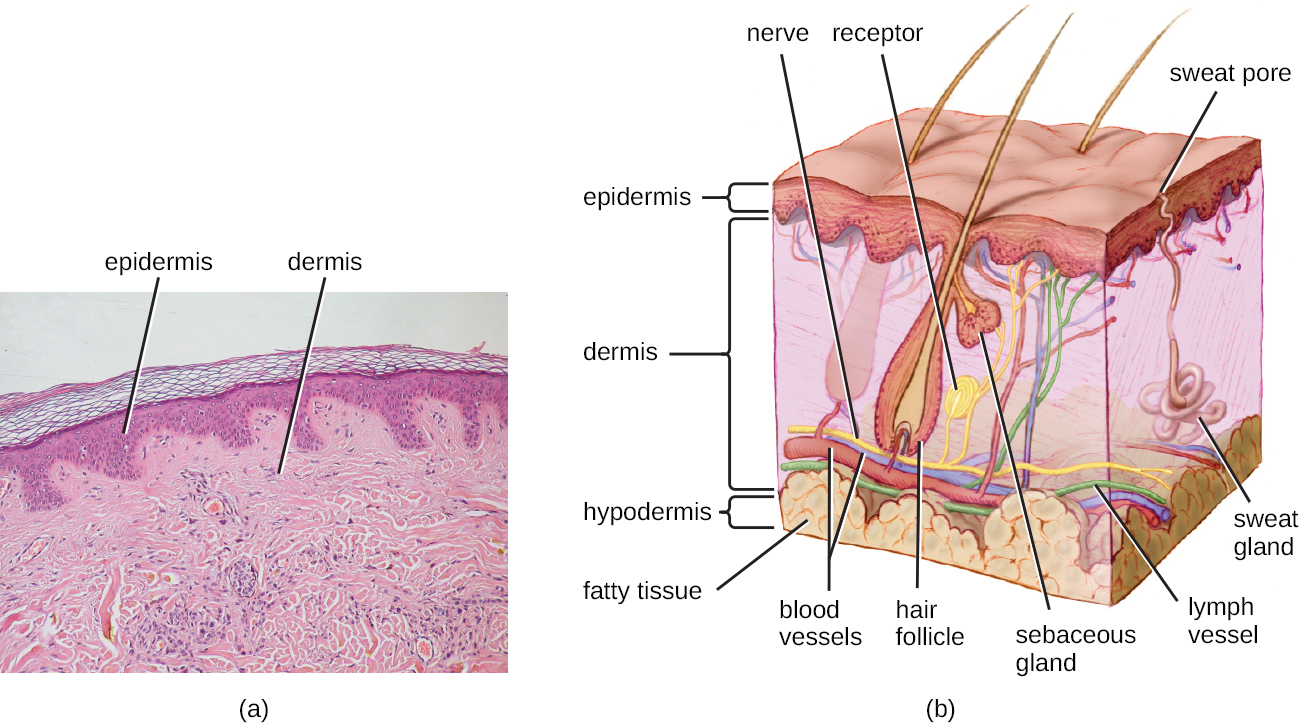
The skin is home to a wide variety of normal microbiota, consisting of commensal organisms that derive nutrition from skin cells and secretions such as sweat and sebum. The normal microbiota of skin tends to inhibit transient-microbe colonization by producing antimicrobial substances and outcompeting other microbes that land on the surface of the skin. This helps to protect the skin from pathogenic infection.
The skin’s properties differ from one region of the body to another, as does the composition of the skin’s microbiota. The availability of nutrients and moisture partly dictates which microorganisms will thrive in a particular region of the skin. Relatively moist skin, such as that of the nares (nostrils) and underarms, has a much different microbiota than the dryer skin on the arms, legs, hands, and top of the feet. Some areas of the skin have higher densities of sebaceous glands . These sebum -rich areas, which include the back, the folds at the side of the nose, and the back of the neck, harbor distinct microbial communities that are less diverse than those found on other parts of the body.
Different types of bacteria dominate the dry, moist, and sebum-rich regions of the skin. The most abundant microbes typically found in the dry and sebaceous regions are Betaproteobacteria and Propionibacteria , respectively. In the moist regions, Corynebacterium and Staphylococcus are most commonly found ( [link] ). Viruses and fungi are also found on the skin, with Malassezia being the most common type of fungus found as part of the normal microbiota. The role and populations of viruses in the microbiota, known as viromes , are still not well understood, and there are limitations to the techniques used to identify them. However, Circoviridae , Papillomaviridae , and Polyomaviridae appear to be the most common residents in the healthy skin virome. Belkaid, Y., and J.A. Segre. “Dialogue Between Skin Microbiota and Immunity,” Science 346 (2014) 6212:954–959. Foulongne, Vincent, et al. “Human Skin Microbiota: High Diversity of DNA Viruses Identified on the Human Skin by High Throughput Sequencing.” PLoS ONE (2012) 7(6): e38499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038499. Robinson, C.M., and J.K. Pfeiffer. “Viruses and the Microbiota.” Annual Review of Virology (2014) 1:55–59. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-031413-085550.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?