| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Mycoplasma grow very slowly when cultured. Therefore, penicillin and thallium acetate are added to agar to prevent the overgrowth by faster-growing potential contaminants. Since M. pneumoniae does not have a cell wall, it is resistant to these substances. Without a cell wall, the microbial cells appear pleomorphic. M. pneumoniae infections tend to be self-limiting but may also respond well to macrolide antibiotic therapy. β-lactams, which target cell wall synthesis, are not indicated for treatment of infections with this pathogen.
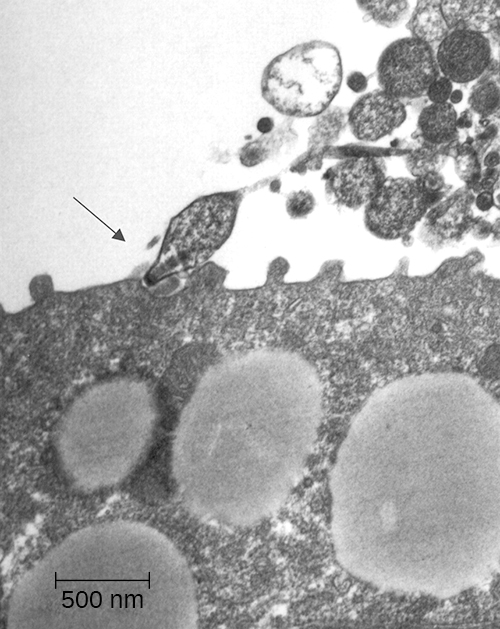
Chlamydial pneumonia can be caused by three different species of bacteria: Chlamydophila pneumoniae (formerly known as Chlamydia pneumoniae ), Chlamydophila psittaci (formerly known as Chlamydia psittaci ), and Chlamydia trachomatis . All three are obligate intracellular pathogens and cause mild to severe pneumonia and bronchitis. Of the three, Chlamydophila pneumoniae is the most common and is transmitted via respiratory droplets or aerosols. C. psittaci causes psittacosis , a zoonotic disease that primarily affects domesticated birds such as parakeets, turkeys, and ducks, but can be transmitted from birds to humans. Psittacosis is a relatively rare infection and is typically found in people who work with birds. Chlamydia trachomatis, the causative agent of the sexually transmitted disease chlamydia, can cause pneumonia in infants when the infection is passed from mother to baby during birth.
Diagnosis of chlamydia by culturing tends to be difficult and slow. Because they are intracellular pathogens, they require multiple passages through tissue culture. Recently, a variety of PCR- and serologically based tests have been developed to enable easier identification of these pathogens. Tetracycline and macrolide antibiotics are typically prescribed for treatment.
A variety of opportunistic bacteria that do not typically cause respiratory disease in healthy individuals are common causes of health care-associated pneumonia. These include Klebsiella pneumoniae , Staphylococcus aureus , and proteobacteria such as species of Escherichia , Proteus , and Serratia . Patients at risk include the elderly, those who have other preexisting lung conditions, and those who are immunocompromised. In addition, patients receiving supportive therapies such as intubation, antibiotics, and immunomodulatory drugs may also be at risk because these interventions disrupt the mucociliary escalator and other pulmonary defenses. Invasive medical devices such as catheters, medical implants, and ventilators can also introduce opportunistic pneumonia-causing pathogens into the body. SM Koenig et al. “Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention.” Clinical Microbiology Reviews 19 no. 4 (2006):637–657.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?