| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
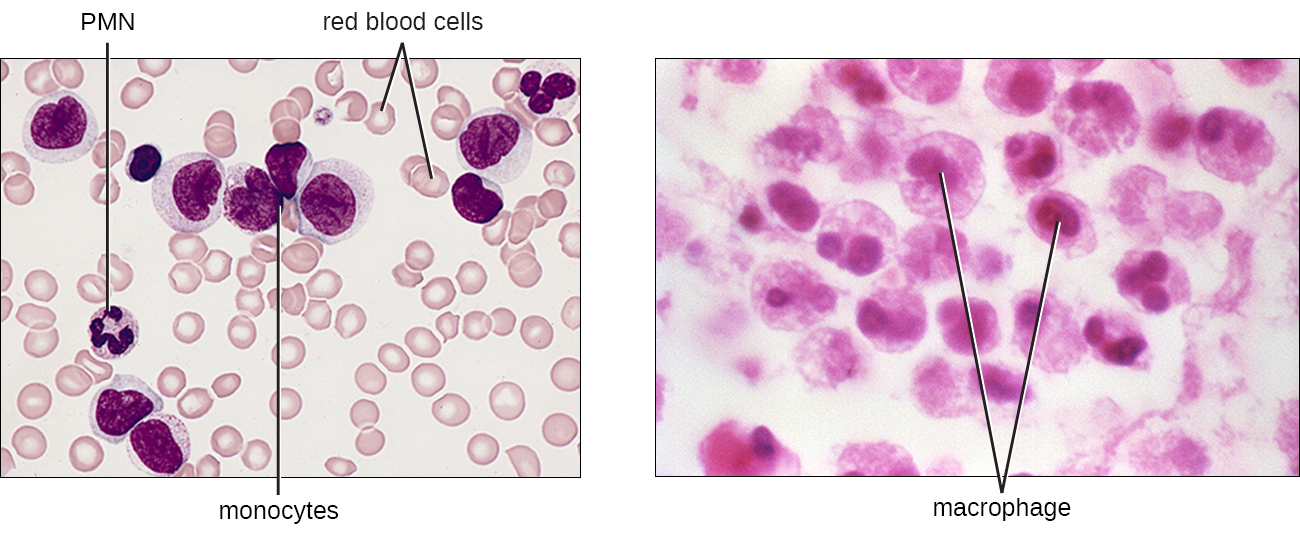
The largest of the white blood cells, monocytes have a nucleus that lacks lobes, and they also lack granules in the cytoplasm ( [link] ). Nevertheless, they are effective phagocytes, engulfing pathogens and apoptotic cells to help fight infection.
When monocytes leave the bloodstream and enter a specific body tissue, they differentiate into tissue-specific phagocytes called macrophages and dendritic cells . They are particularly important residents of lymphoid tissue, as well as nonlymphoid sites and organs. Macrophages and dendritic cells can reside in body tissues for significant lengths of time. Macrophages in specific body tissues develop characteristics suited to the particular tissue. Not only do they provide immune protection for the tissue in which they reside but they also support normal function of their neighboring tissue cells through the production of cytokines. Macrophages are given tissue-specific names, and a few examples of tissue-specific macrophages are listed in [link] . Dendritic cells are important sentinels residing in the skin and mucous membranes, which are portals of entry for many pathogens. Monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells are all highly phagocytic and important promoters of the immune response through their production and release of cytokines. These cells provide an essential bridge between innate and adaptive immune responses, as discussed in the next section as well as the next chapter.
| Macrophages Found in Various Body Tissues | |
|---|---|
| Tissue | Macrophage |
| Brain and central nervous system | Microglial cells |
| Liver | Kupffer cells |
| Lungs | Alveolar macrophages (dust cells) |
| Peritoneal cavity | Peritoneal macrophages |
Match each cell type with its description.
| ___natural killer cell | A. stains with basic dye methylene blue, has large amounts of histamine in granules, and facilitates allergic responses and inflammation |
| ___basophil | B. stains with acidic dye eosin, has histamine and major basic protein in granules, and facilitates responses to protozoa and helminths |
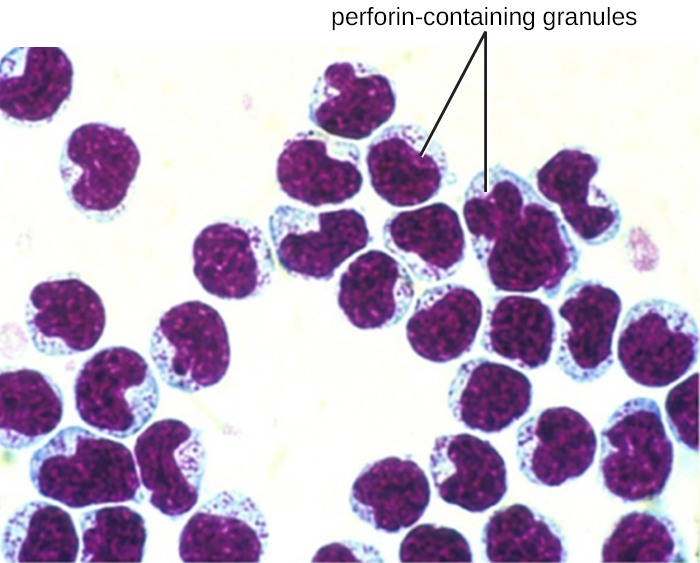
| ___macrophage | C. recognizes abnormal cells, binds to them, and releases perforin and granzyme molecules, which induce apoptosis |
| ___eosinophil | D. large agranular phagocyte that resides in tissues such as the brain and lungs |
C, A, D, B
Match each cellular defense with the infection it would most likely target.
| ___natural killer cell | A. virus-infected cell |
| ___neutrophil | B. tapeworm in the intestines |
| ___eosinophil | C. bacteria in a skin lesion |
A, C, B
The cell in the bone marrow that gives rise to all other blood cell types is the ________.
pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell (HSC)
Kupffer cells residing in the liver are a type of ________.
macrophage
_____________ are similar to basophils, but reside in tissues rather than circulating in the blood.
mast cells
Explain the difference between plasma and the formed elements of the blood.
List three ways that a neutrophil can destroy an infectious bacterium.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?