| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
All of these choices are theoretically possible, depending on Kimberly’s personal preferences as expressed through the total and marginal utility she would receive from consuming these two goods. When income rises, the most common reaction is to purchase more of both goods, like choice N, which is to the upper right relative to Kimberly’s original choice M, although exactly how much more of each good will vary according to personal taste. Conversely, when income falls, the most typical reaction is to purchase less of both goods. As defined in the chapter on Demand and Supply and again in the chapter on Elasticity , goods and services are called normal goods when a rise in income leads to a rise in the quantity consumed of that good and a fall in income leads to a fall in quantity consumed.
However, depending on Kimberly’s preferences, a rise in income could cause consumption of one good to increase while consumption of the other good declines. A choice like P means that a rise in income caused her quantity consumed of overnight stays to decline, while a choice like Q would mean that a rise in income caused her quantity of concerts to decline. Goods where demand declines as income rises (or conversely, where the demand rises as income falls) are called “inferior goods.” An inferior good occurs when people trim back on a good as income rises, because they can now afford the more expensive choices that they prefer. For example, a higher-income household might eat fewer hamburgers or be less likely to buy a used car, and instead eat more steak and buy a new car.
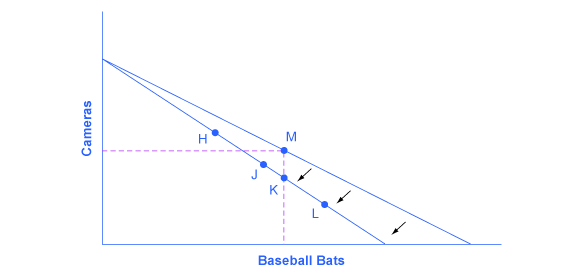
For analyzing the possible effect of a change in price on consumption, let’s again use a concrete example. [link] represents the consumer choice of Sergei, who chooses between purchasing baseball bats and cameras. A price increase for baseball bats would have no effect on the ability to purchase cameras, but it would reduce the number of bats Sergei could afford to buy. Thus a price increase for baseball bats, the good on the horizontal axis, causes the budget constraint to rotate inward, as if on a hinge, from the vertical axis. As in the previous section, the point labeled M represents the originally preferred point on the original budget constraint, which Sergei has chosen after contemplating his total utility and marginal utility and the tradeoffs involved along the budget constraint. In this example, the units along the horizontal and vertical axes are not numbered, so the discussion must focus on whether more or less of certain goods will be consumed, not on numerical amounts.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?