| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In contrast, when a force exerted on the system has a component in the direction of motion, such as in [link] (d), work is done—energy is transferred to the briefcase. Finally, in [link] (e), energy is transferred from the briefcase to a generator. There are two good ways to interpret this energy transfer. One interpretation is that the briefcase’s weight does work on the generator, giving it energy. The other interpretation is that the generator does negative work on the briefcase, thus removing energy from it. The drawing shows the latter, with the force from the generator upward on the briefcase, and the displacement downward. This makes , and ; therefore, is negative.
Work and energy have the same units. From the definition of work, we see that those units are force times distance. Thus, in SI units, work and energy are measured in newton-meters . A newton-meter is given the special name joule (J), and . One joule is not a large amount of energy; it would lift a small 100-gram apple a distance of about 1 meter.
How much work is done on the lawn mower by the person in [link] (a) if he exerts a constant force of at an angle below the horizontal and pushes the mower on level ground? Convert the amount of work from joules to kilocalories and compare it with this person’s average daily intake of (about ) of food energy. One calorie (1 cal) of heat is the amount required to warm 1 g of water by , and is equivalent to , while one food calorie (1 kcal) is equivalent to .
Strategy
We can solve this problem by substituting the given values into the definition of work done on a system, stated in the equation . The force, angle, and displacement are given, so that only the work is unknown.
Solution
The equation for the work is
Substituting the known values gives
Converting the work in joules to kilocalories yields . The ratio of the work done to the daily consumption is
Discussion
This ratio is a tiny fraction of what the person consumes, but it is typical. Very little of the energy released in the consumption of food is used to do work. Even when we “work” all day long, less than 10% of our food energy intake is used to do work and more than 90% is converted to thermal energy or stored as chemical energy in fat.
Give an example of a situation in which there is a force and a displacement, but the force does no work. Explain why it does no work.
How much work does a supermarket checkout attendant do on a can of soup he pushes 0.600 m horizontally with a force of 5.00 N? Express your answer in joules and kilocalories.
A 75.0-kg person climbs stairs, gaining 2.50 meters in height. Find the work done to accomplish this task.
(a) Calculate the work done on a 1500-kg elevator car by its cable to lift it 40.0 m at constant speed, assuming friction averages 100 N. (b) What is the work done on the lift by the gravitational force in this process? (c) What is the total work done on the lift?
(a)
(b)
(c) The net force is zero.
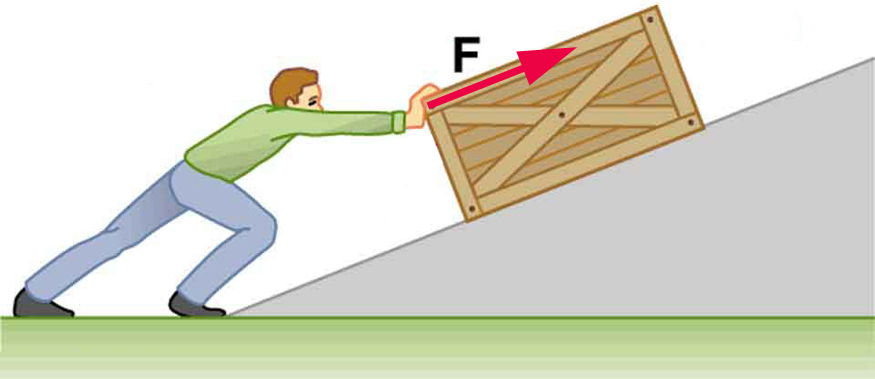
Calculate the work done by an 85.0-kg man who pushes a crate 4.00 m up along a ramp that makes an angle of with the horizontal. (See [link] .) He exerts a force of 500 N on the crate parallel to the ramp and moves at a constant speed. Be certain to include the work he does on the crate and on his body to get up the ramp.
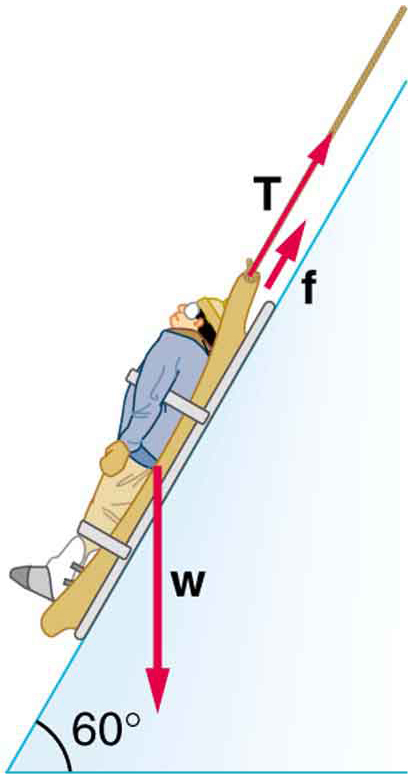
Suppose the ski patrol lowers a rescue sled and victim, having a total mass of 90.0 kg, down a slope at constant speed, as shown in [link] . The coefficient of friction between the sled and the snow is 0.100. (a) How much work is done by friction as the sled moves 30.0 m along the hill? (b) How much work is done by the rope on the sled in this distance? (c) What is the work done by the gravitational force on the sled? (d) What is the total work done?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Unit 5 - work and energy' conversation and receive update notifications?