| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Dilution is the process whereby the concentration of a solution is lessened by the addition of solvent. For example, we might say that a glass of iced tea becomes increasingly diluted as the ice melts. The water from the melting ice increases the volume of the solvent (water) and the overall volume of the solution (iced tea), thereby reducing the relative concentrations of the solutes that give the beverage its taste ( [link] ).
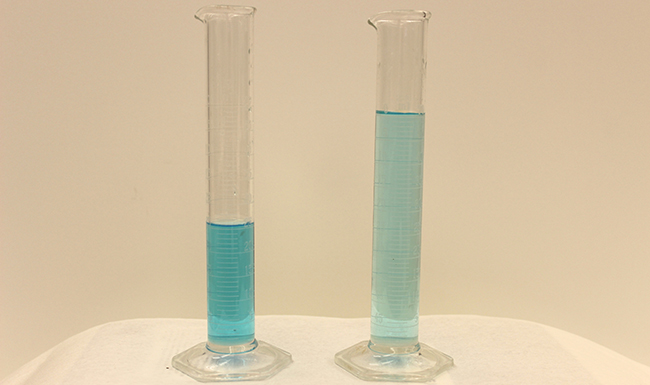
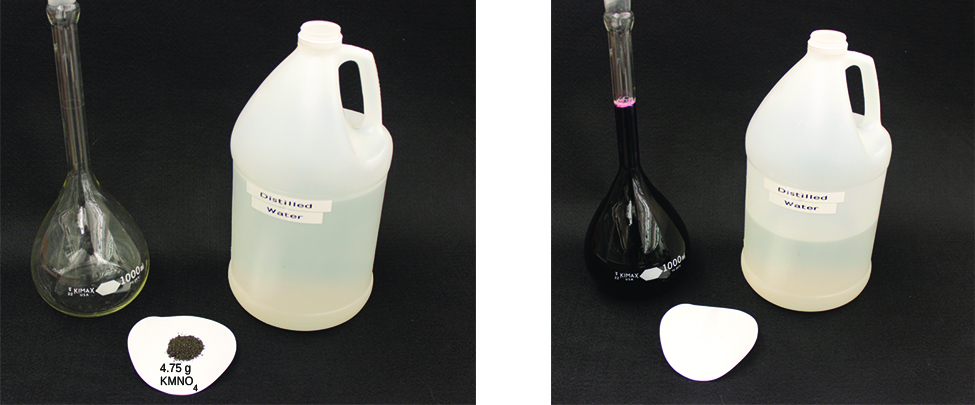
Dilution is also a common means of preparing solutions of a desired concentration. By adding solvent to a measured portion of a more concentrated stock solution , we can achieve a particular concentration. For example, commercial pesticides are typically sold as solutions in which the active ingredients are far more concentrated than is appropriate for their application. Before they can be used on crops, the pesticides must be diluted. This is also a very common practice for the preparation of a number of common laboratory reagents ( [link] ).

A simple mathematical relationship can be used to relate the volumes and concentrations of a solution before and after the dilution process. According to the definition of molarity, the molar amount of solute in a solution is equal to the product of the solution’s molarity and its volume in liters:
Expressions like these may be written for a solution before and after it is diluted:
where the subscripts “1” and “2” refer to the solution before and after the dilution, respectively. Since the dilution process does not change the amount of solute in the solution, n 1 = n 2 . Thus, these two equations may be set equal to one another:
This relation is commonly referred to as the dilution equation. Although we derived this equation using molarity as the unit of concentration and liters as the unit of volume, other units of concentration and volume may be used, so long as the units properly cancel per the factor-label method. Reflecting this versatility, the dilution equation is often written in the more general form:
where C and V are concentration and volume, respectively.
Use the simulation to explore the relations between solute amount, solution volume, and concentration and to confirm the dilution equation.
Since the stock solution is being diluted by more than two-fold (volume is increased from 0.85 L to 1.80 L), we would expect the diluted solution’s concentration to be less than one-half 5 M . We will compare this ballpark estimate to the calculated result to check for any gross errors in computation (for example, such as an improper substitution of the given quantities). Substituting the given values for the terms on the right side of this equation yields:
This result compares well to our ballpark estimate (it’s a bit less than one-half the stock concentration, 5 M ).
0.102 M CH 3 OH

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?