| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
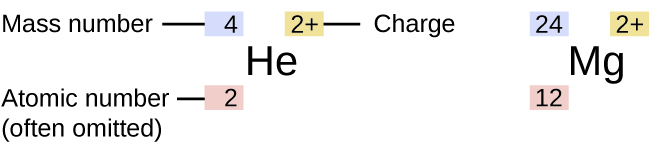
Information about the naturally occurring isotopes of elements with atomic numbers 1 through 10 is given in [link] . Note that in addition to standard names and symbols, the isotopes of hydrogen are often referred to using common names and accompanying symbols. Hydrogen-2, symbolized 2 H, is also called deuterium and sometimes symbolized D. Hydrogen-3, symbolized 3 H, is also called tritium and sometimes symbolized T.
| Nuclear Compositions of Atoms of the Very Light Elements | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Number of Protons | Number of Neutrons | Mass (amu) | % Natural Abundance |
| hydrogen |
(protium) |
1 | 1 | 0 | 1.0078 | 99.989 |
|
(deuterium) |
1 | 1 | 1 | 2.0141 | 0.0115 | |
|
(tritium) |
1 | 1 | 2 | 3.01605 | — (trace) | |
| helium | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3.01603 | 0.00013 | |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 4.0026 | 100 | ||
| lithium | 3 | 3 | 3 | 6.0151 | 7.59 | |
| 3 | 3 | 4 | 7.0160 | 92.41 | ||
| beryllium | 4 | 4 | 5 | 9.0122 | 100 | |
| boron | 5 | 5 | 5 | 10.0129 | 19.9 | |
| 5 | 5 | 6 | 11.0093 | 80.1 | ||
| carbon | 6 | 6 | 6 | 12.0000 | 98.89 | |
| 6 | 6 | 7 | 13.0034 | 1.11 | ||
| 6 | 6 | 8 | 14.0032 | — (trace) | ||
| nitrogen | 7 | 7 | 7 | 14.0031 | 99.63 | |
| 7 | 7 | 8 | 15.0001 | 0.37 | ||
| oxygen | 8 | 8 | 8 | 15.9949 | 99.757 | |
| 8 | 8 | 9 | 16.9991 | 0.038 | ||
| 8 | 8 | 10 | 17.9992 | 0.205 | ||
| fluorine | 9 | 9 | 10 | 18.9984 | 100 | |
| neon | 10 | 10 | 10 | 19.9924 | 90.48 | |
| 10 | 10 | 11 | 20.9938 | 0.27 | ||
| 10 | 10 | 12 | 21.9914 | 9.25 |
Use this Build an Atom simulator to build atoms of the first 10 elements, see which isotopes exist, check nuclear stability, and gain experience with isotope symbols.
Because each proton and each neutron contribute approximately one amu to the mass of an atom, and each electron contributes far less, the atomic mass of a single atom is approximately equal to its mass number (a whole number). However, the average masses of atoms of most elements are not whole numbers because most elements exist naturally as mixtures of two or more isotopes.
The mass of an element shown in a periodic table or listed in a table of atomic masses is a weighted, average mass of all the isotopes present in a naturally occurring sample of that element. This is equal to the sum of each individual isotope’s mass multiplied by its fractional abundance.
For example, the element boron is composed of two isotopes: About 19.9% of all boron atoms are 10 B with a mass of 10.0129 amu, and the remaining 80.1% are 11 B with a mass of 11.0093 amu. The average atomic mass for boron is calculated to be:
It is important to understand that no single boron atom weighs exactly 10.8 amu; 10.8 amu is the average mass of all boron atoms, and individual boron atoms weigh either approximately 10 amu or 11 amu.
The average mass of a neon atom in the solar wind is 20.15 amu. (The average mass of a terrestrial neon atom is 20.1796 amu. This result demonstrates that we may find slight differences in the natural abundance of isotopes, depending on their origin.)
24.31 amu

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?