| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Although gold is generally unreactive, you can watch a video of the complex mixture of compounds present in aqua regia dissolving it into solution.
Nitrates , salts of nitric acid, form when metals, oxides, hydroxides, or carbonates react with nitric acid. Most nitrates are soluble in water; indeed, one of the significant uses of nitric acid is to prepare soluble metal nitrates.
Nitric acid finds extensive use in the laboratory and in chemical industries as a strong acid and strong oxidizing agent. It is important in the manufacture of explosives, dyes, plastics, and drugs. Salts of nitric acid (nitrates) are valuable as fertilizers. Gunpowder is a mixture of potassium nitrate, sulfur, and charcoal.
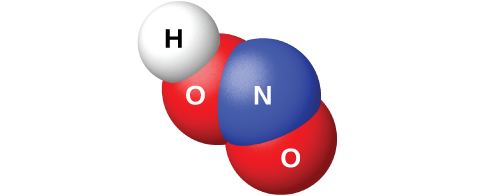
The reaction of N 2 O 3 with water gives a pale blue solution of nitrous acid, HNO 2 . However, HNO 2 (shown in [link] ) is easier to prepare by the addition of an acid to a solution of nitrite; nitrous acid is a weak acid, so the nitrite ion is basic in aqueous solution:
Nitrous acid is very unstable and exists only in solution. It disproportionates slowly at room temperature (rapidly when heated) into nitric acid and nitric oxide. Nitrous acid is an active oxidizing agent with strong reducing agents, and strong oxidizing agents oxidize it to nitric acid.
Sodium nitrite, NaNO 2 , is an additive to meats such as hot dogs and cold cuts. The nitrite ion has two functions. It limits the growth of bacteria that can cause food poisoning, and it prolongs the meat’s retention of its red color. The addition of sodium nitrite to meat products is controversial because nitrous acid reacts with certain organic compounds to form a class of compounds known as nitrosamines. Nitrosamines produce cancer in laboratory animals. This has prompted the FDA to limit the amount of NaNO 2 in foods.
The nitrites are much more stable than the acid, but nitrites, like nitrates, can explode. Nitrites, like nitrates, are also soluble in water (AgNO 2 is only slightly soluble).
Pure orthophosphoric acid, H 3 PO 4 (shown in [link] ), forms colorless, deliquescent crystals that melt at 42 °C. The common name of this compound is phosphoric acid, and is commercially available as a viscous 82% solution known as syrupy phosphoric acid. One use of phosphoric acid is as an additive to many soft drinks.
One commercial method of preparing orthophosphoric acid is to treat calcium phosphate rock with concentrated sulfuric acid:
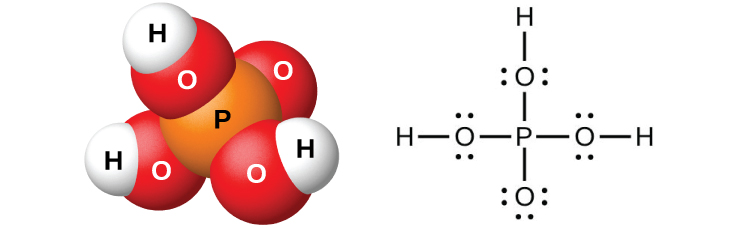
Dilution of the products with water, followed by filtration to remove calcium sulfate, gives a dilute acid solution contaminated with calcium dihydrogen phosphate, Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 , and other compounds associated with calcium phosphate rock. It is possible to prepare pure orthophosphoric acid by dissolving P 4 O 10 in water.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?