| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Mendel’s seminal publication makes no mention of linkage, and many researchers have questioned whether he encountered linkage but chose not to publish those crosses out of concern that they would invalidate his independent assortment postulate. The garden pea has seven chromosomes, and some have suggested that his choice of seven characteristics was not a coincidence. However, even if the genes he examined were not located on separate chromosomes, it is possible that he simply did not observe linkage because of the extensive shuffling effects of recombination.
Mendel’s studies in pea plants implied that the sum of an individual’s phenotype was controlled by genes (or as he called them, unit factors), such that every characteristic was distinctly and completely controlled by a single gene. In fact, single observable characteristics are almost always under the influence of multiple genes (each with two or more alleles) acting in unison. For example, at least eight genes contribute to eye color in humans.
Eye color in humans is determined by multiple alleles. Use the Eye Color Calculator to predict the eye color of children from parental eye color.
In some cases, several genes can contribute to aspects of a common phenotype without their gene products ever directly interacting. In the case of organ development, for instance, genes may be expressed sequentially, with each gene adding to the complexity and specificity of the organ. Genes may function in complementary or synergistic fashions, such that two or more genes expressed simultaneously affect a phenotype. An apparent example of this occurs with human skin color, which appears to involve the action of at least three (and probably more) genes. Cases in which inheritance for a characteristic like skin color or human height depend on the combined effects of numerous genes are called polygenic inheritance.
Genes may also oppose each other, with one gene suppressing the expression of another. In epistasis , the interaction between genes is antagonistic, such that one gene masks or interferes with the expression of another. “Epistasis” is a word composed of Greek roots meaning “standing upon.” The alleles that are being masked or silenced are said to be hypostatic to the epistatic alleles that are doing the masking. Often the biochemical basis of epistasis is a gene pathway in which expression of one gene is dependent on the function of a gene that precedes or follows it in the pathway.
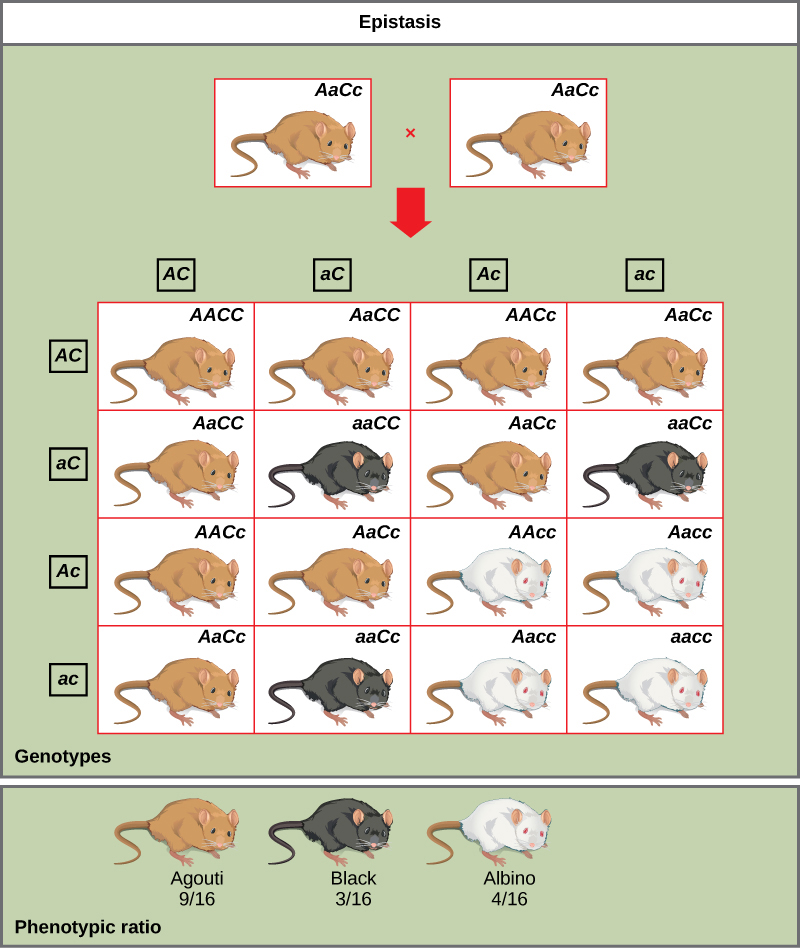
An example of epistasis is pigmentation in mice. The wild-type coat color, agouti (AA) is dominant to solid-colored fur (aa). However, a separate gene C, when present as the recessive homozygote (cc), negates any expression of pigment from the A gene and results in an albino mouse ( [link] ). Therefore, the genotypes AAcc , Aacc , and aacc all produce the same albino phenotype. A cross between heterozygotes for both genes ( AaCc x AaCc ) would generate offspring with a phenotypic ratio of 9 agouti:3 black:4 albino ( [link] ). In this case, the C gene is epistatic to the A gene.
Alleles do not always behave in dominant and recessive patterns. Incomplete dominance describes situations in which the heterozygote exhibits a phenotype that is intermediate between the homozygous phenotypes. Codominance describes the simultaneous expression of both of the alleles in the heterozygote. Although diploid organisms can only have two alleles for any given gene, it is common for more than two alleles for a gene to exist in a population. In humans, as in many animals and some plants, females have two X chromosomes and males have one X and one Y chromosome. Genes that are present on the X but not the Y chromosome are said to be X-linked, such that males only inherit one allele for the gene, and females inherit two.
According to Mendel’s law of independent assortment, genes sort independently of each other into gametes during meiosis. This occurs because chromosomes, on which the genes reside, assort independently during meiosis and crossovers cause most genes on the same chromosomes to also behave independently. When genes are located in close proximity on the same chromosome, their alleles tend to be inherited together. This results in offspring ratios that violate Mendel's law of independent assortment. However, recombination serves to exchange genetic material on homologous chromosomes such that maternal and paternal alleles may be recombined on the same chromosome. This is why alleles on a given chromosome are not always inherited together. Recombination is a random event occurring anywhere on a chromosome. Therefore, genes that are far apart on the same chromosome are likely to still assort independently because of recombination events that occurred in the intervening chromosomal space.
Whether or not they are sorting independently, genes may interact at the level of gene products, such that the expression of an allele for one gene masks or modifies the expression of an allele for a different gene. This is called epistasis.
[link] What ratio of offspring would result from a cross between a white-eyed male and a female that is heterozygous for red eye color?
[link] Half of the female offspring would be heterozygous (X W X w ) with red eyes, and half would be homozygous recessive (X w X w ) with white eyes. Half of the male offspring would be hemizygous dominant (X W Y) with red eyes, and half would be hemizygous recessive (X w Y) with white eyes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?