| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Which of the following statements about the heart is false?
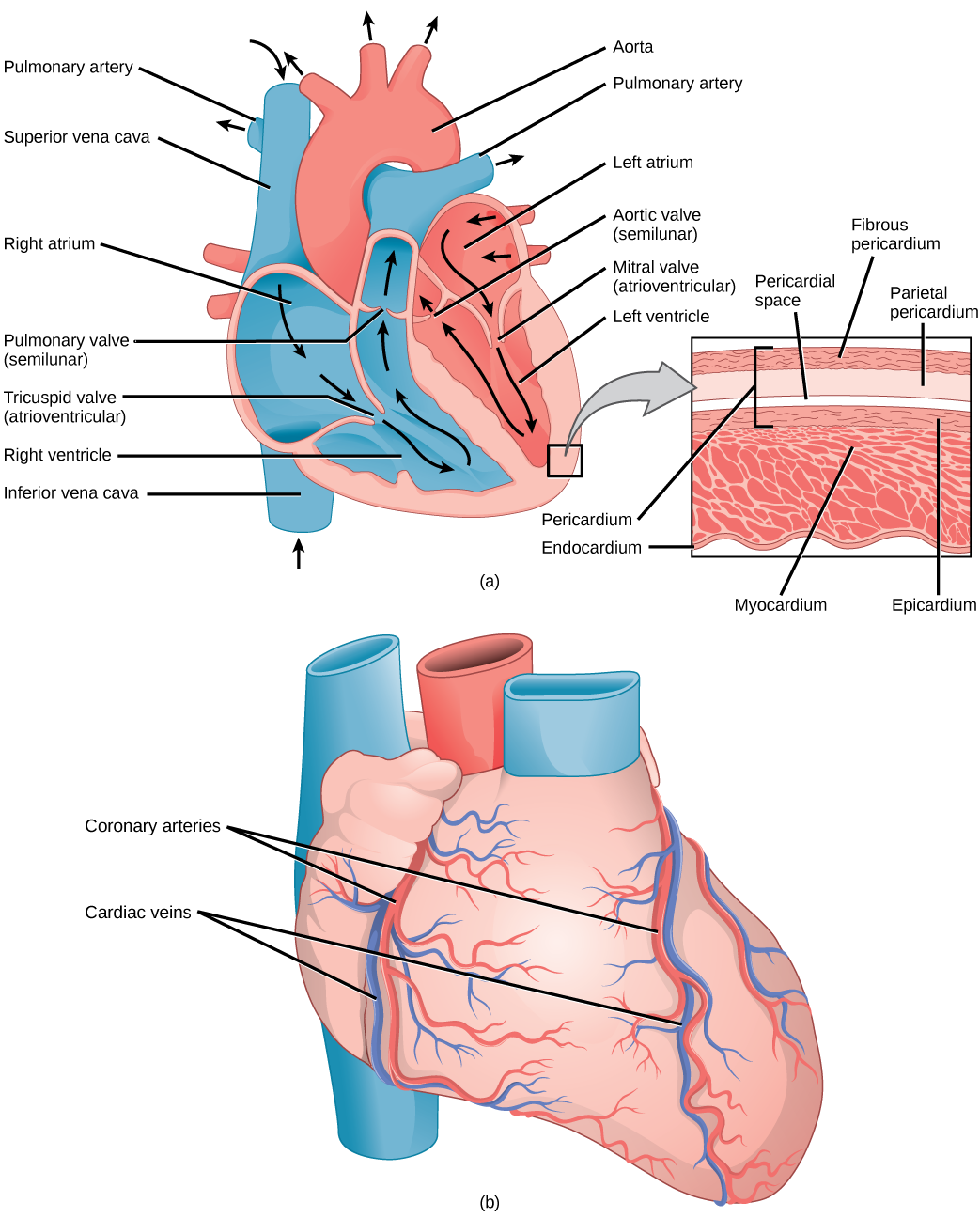
The heart is composed of three layers; the epicardium, the myocardium, and the endocardium, illustrated in [link] . The inner wall of the heart has a lining called the endocardium . The myocardium consists of the heart muscle cells that make up the middle layer and the bulk of the heart wall. The outer layer of cells is called the epicardium , of which the second layer is a membranous layered structure called the pericardium that surrounds and protects the heart; it allows enough room for vigorous pumping but also keeps the heart in place to reduce friction between the heart and other structures.
The heart has its own blood vessels that supply the heart muscle with blood. The coronary arteries branch from the aorta and surround the outer surface of the heart like a crown. They diverge into capillaries where the heart muscle is supplied with oxygen before converging again into the coronary veins to take the deoxygenated blood back to the right atrium where the blood will be re-oxygenated through the pulmonary circuit. The heart muscle will die without a steady supply of blood. Atherosclerosis is the blockage of an artery by the buildup of fatty plaques. Because of the size (narrow) of the coronary arteries and their function in serving the heart itself, atherosclerosis can be deadly in these arteries. The slowdown of blood flow and subsequent oxygen deprivation that results from atherosclerosis causes severe pain, known as angina , and complete blockage of the arteries will cause myocardial infarction : the death of cardiac muscle tissue, commonly known as a heart attack.
The main purpose of the heart is to pump blood through the body; it does so in a repeating sequence called the cardiac cycle. The cardiac cycle is the coordination of the filling and emptying of the heart of blood by electrical signals that cause the heart muscles to contract and relax. The human heart beats over 100,000 times per day. In each cardiac cycle, the heart contracts ( systole ), pushing out the blood and pumping it through the body; this is followed by a relaxation phase ( diastole ), where the heart fills with blood, as illustrated in [link] . The atria contract at the same time, forcing blood through the atrioventricular valves into the ventricles. Closing of the atrioventricular valves produces a monosyllabic “lup” sound. Following a brief delay, the ventricles contract at the same time forcing blood through the semilunar valves into the aorta and the artery transporting blood to the lungs (via the pulmonary artery). Closing of the semilunar valves produces a monosyllabic “dup” sound.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?