| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
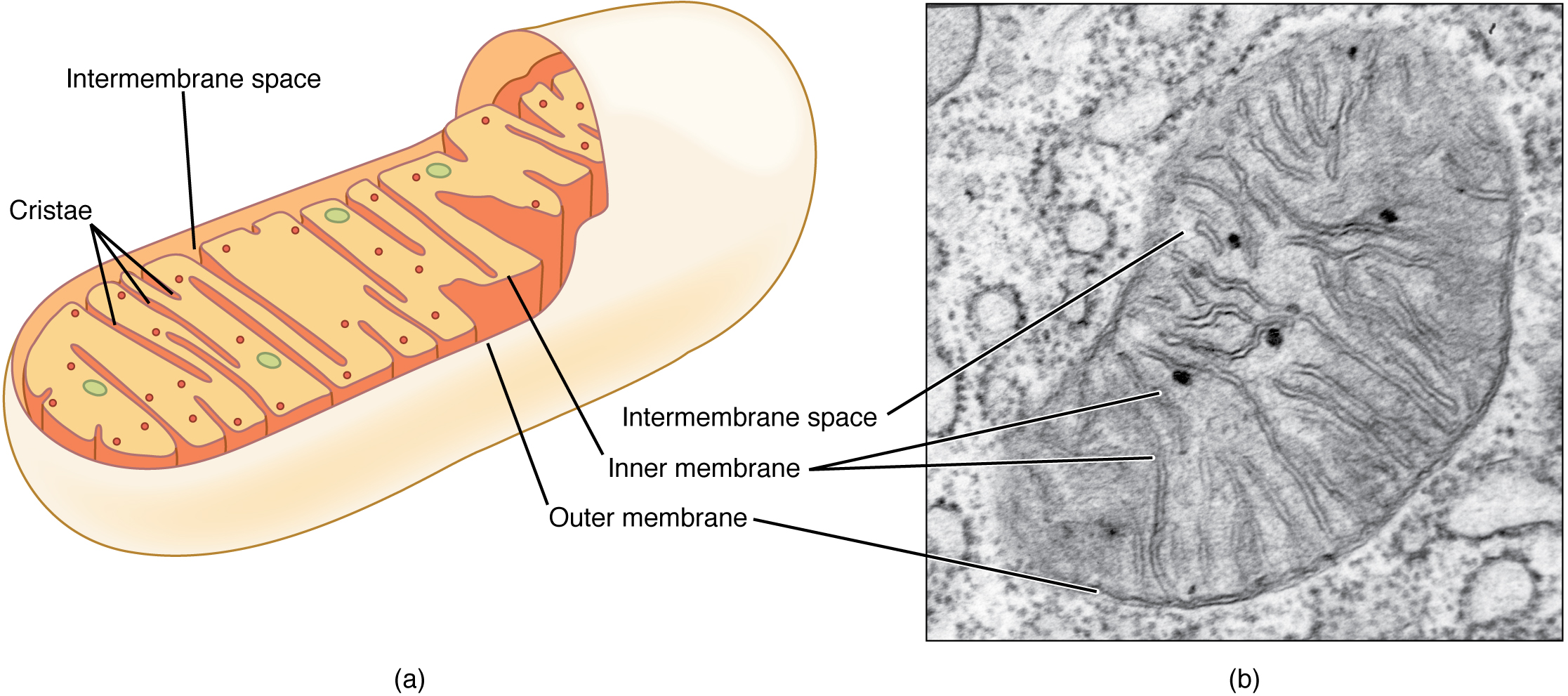
Like lysosomes, a peroxisome is a membrane-bound cellular organelle that contains mostly enzymes ( [link] ). Peroxisomes perform a couple of different functions, including lipid metabolism and chemical detoxification. In contrast to the digestive enzymes found in lysosomes, the enzymes within peroxisomes serve to transfer hydrogen atoms from various molecules to oxygen, producing hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ). In this way, peroxisomes neutralize poisons such as alcohol. In order to appreciate the importance of peroxisomes, it is necessary to understand the concept of reactive oxygen species.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as peroxides and free radicals are the highly reactive products of many normal cellular processes, including the mitochondrial reactions that produce ATP and oxygen metabolism. Examples of ROS include the hydroxyl radical OH, H 2 O 2 , and superoxide ( ). Some ROS are important for certain cellular functions, such as cell signaling processes and immune responses against foreign substances. Free radicals are reactive because they contain free unpaired electrons; they can easily oxidize other molecules throughout the cell, causing cellular damage and even cell death. Free radicals are thought to play a role in many destructive processes in the body, from cancer to coronary artery disease.
Peroxisomes, on the other hand, oversee reactions that neutralize free radicals. Peroxisomes produce large amounts of the toxic H 2 O 2 in the process, but peroxisomes contain enzymes that convert H 2 O 2 into water and oxygen. These byproducts are safely released into the cytoplasm. Like miniature sewage treatment plants, peroxisomes neutralize harmful toxins so that they do not wreak havoc in the cells. The liver is the organ primarily responsible for detoxifying the blood before it travels throughout the body, and liver cells contain an exceptionally high number of peroxisomes.
Defense mechanisms such as detoxification within the peroxisome and certain cellular antioxidants serve to neutralize many of these molecules. Some vitamins and other substances, found primarily in fruits and vegetables, have antioxidant properties. Antioxidants work by being oxidized themselves, halting the destructive reaction cascades initiated by the free radicals. Sometimes though, ROS accumulate beyond the capacity of such defenses.
Oxidative stress is the term used to describe damage to cellular components caused by ROS. Due to their characteristic unpaired electrons, ROS can set off chain reactions where they remove electrons from other molecules, which then become oxidized and reactive, and do the same to other molecules, causing a chain reaction. ROS can cause permanent damage to cellular lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Damaged DNA can lead to genetic mutations and even cancer. A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence in a gene within a cell’s DNA, potentially altering the protein coded by that gene. Other diseases believed to be triggered or exacerbated by ROS include Alzheimer’s disease, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, arthritis, Huntington’s disease, and schizophrenia, among many others. It is noteworthy that these diseases are largely age-related. Many scientists believe that oxidative stress is a major contributor to the aging process.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?