| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The pH of human blood normally ranges from 7.35 to 7.45, although it is typically identified as pH 7.4. At this slightly basic pH, blood can reduce the acidity resulting from the carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) constantly being released into the bloodstream by the trillions of cells in the body. Homeostatic mechanisms (along with exhaling CO 2 while breathing) normally keep the pH of blood within this narrow range. This is critical, because fluctuations—either too acidic or too alkaline—can lead to life-threatening disorders.
All cells of the body depend on homeostatic regulation of acid–base balance at a pH of approximately 7.4. The body therefore has several mechanisms for this regulation, involving breathing, the excretion of chemicals in urine, and the internal release of chemicals collectively called buffers into body fluids. A buffer is a solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base. A buffer can neutralize small amounts of acids or bases in body fluids. For example, if there is even a slight decrease below 7.35 in the pH of a bodily fluid, the buffer in the fluid—in this case, acting as a weak base—will bind the excess hydrogen ions. In contrast, if pH rises above 7.45, the buffer will act as a weak acid and contribute hydrogen ions.
In contrast, alkalosis is a condition in which the blood and other body fluids are too alkaline (basic). As with acidosis, respiratory disorders are a major cause; however, in respiratory alkalosis, carbon dioxide levels fall too low. Lung disease, aspirin overdose, shock, and ordinary anxiety can cause respiratory alkalosis, which reduces the normal concentration of H + .
Metabolic alkalosis often results from prolonged, severe vomiting, which causes a loss of hydrogen and chloride ions (as components of HCl). Medications also can prompt alkalosis. These include diuretics that cause the body to lose potassium ions, as well as antacids when taken in excessive amounts, for instance by someone with persistent heartburn or an ulcer.
Inorganic compounds essential to human functioning include water, salts, acids, and bases. These compounds are inorganic; that is, they do not contain both hydrogen and carbon. Water is a lubricant and cushion, a heat sink, a component of liquid mixtures, a byproduct of dehydration synthesis reactions, and a reactant in hydrolysis reactions. Salts are compounds that, when dissolved in water, dissociate into ions other than H + or OH – . In contrast, acids release H + in solution, making it more acidic. Bases accept H + , thereby making the solution more alkaline (caustic).
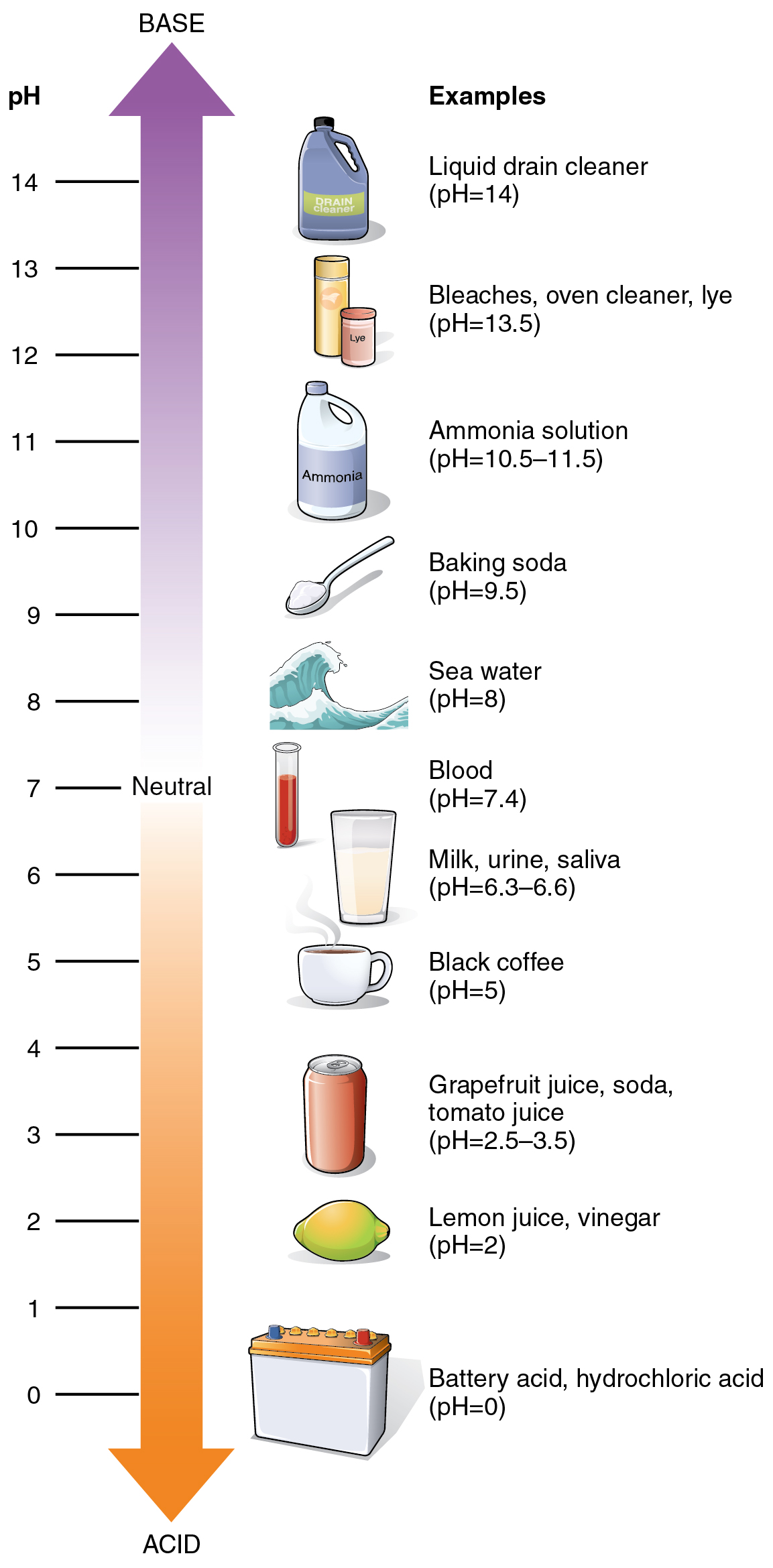
The pH of any solution is its relative concentration of H + . A solution with pH 7 is neutral. Solutions with pH below 7 are acids, and solutions with pH above 7 are bases. A change in a single digit on the pH scale (e.g., from 7 to 8) represents a ten-fold increase or decrease in the concentration of H + . In a healthy adult, the pH of blood ranges from 7.35 to 7.45. Homeostatic control mechanisms important for keeping blood in a healthy pH range include chemicals called buffers, weak acids and weak bases released when the pH of blood or other body fluids fluctuates in either direction outside of this normal range.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?