| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Watch this video to learn more about different knee injuries and diagnostic testing of the knee. What are the most common causes of anterior cruciate ligament injury?
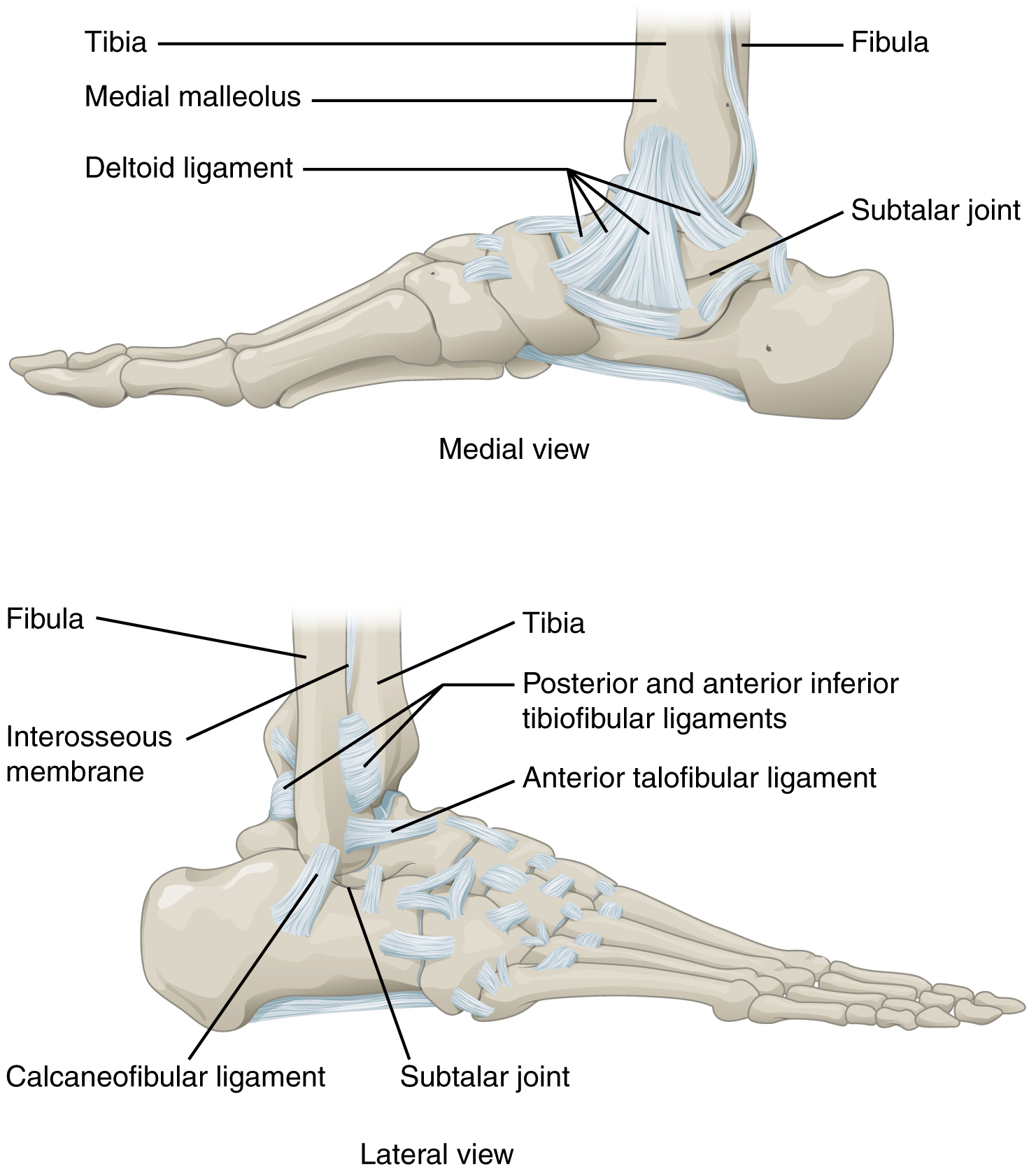
The ankle is formed by the talocrural joint ( [link] ). It consists of the articulations between the talus bone of the foot and the distal ends of the tibia and fibula of the leg (crural = “leg”). The superior aspect of the talus bone is square-shaped and has three areas of articulation. The top of the talus articulates with the inferior tibia. This is the portion of the ankle joint that carries the body weight between the leg and foot. The sides of the talus are firmly held in position by the articulations with the medial malleolus of the tibia and the lateral malleolus of the fibula, which prevent any side-to-side motion of the talus. The ankle is thus a uniaxial hinge joint that allows only for dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot.
Additional joints between the tarsal bones of the posterior foot allow for the movements of foot inversion and eversion. Most important for these movements is the subtalar joint , located between the talus and calcaneus bones. The joints between the talus and navicular bones and the calcaneus and cuboid bones are also important contributors to these movements. All of the joints between tarsal bones are plane joints. Together, the small motions that take place at these joints all contribute to the production of inversion and eversion foot motions.
Like the hinge joints of the elbow and knee, the talocrural joint of the ankle is supported by several strong ligaments located on the sides of the joint. These ligaments extend from the medial malleolus of the tibia or lateral malleolus of the fibula and anchor to the talus and calcaneus bones. Since they are located on the sides of the ankle joint, they allow for dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot. They also prevent abnormal side-to-side and twisting movements of the talus and calcaneus bones during eversion and inversion of the foot. On the medial side is the broad deltoid ligament . The deltoid ligament supports the ankle joint and also resists excessive eversion of the foot. The lateral side of the ankle has several smaller ligaments. These include the anterior talofibular ligament and the posterior talofibular ligament , both of which span between the talus bone and the lateral malleolus of the fibula, and the calcaneofibular ligament , located between the calcaneus bone and fibula. These ligaments support the ankle and also resist excess inversion of the foot.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?