| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The point is on the unit circle, as shown in [link] . Find and
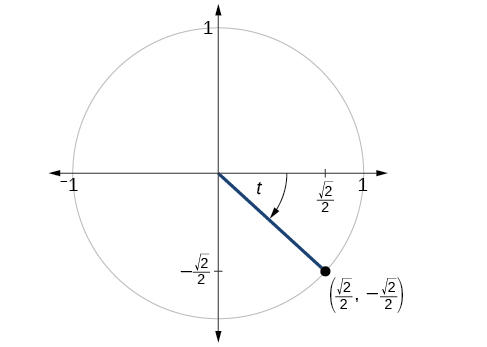
Find and when
We have previously used the properties of equilateral triangles to demonstrate that and We can use these values and the definitions of tangent, secant, cosecant, and cotangent as functions of sine and cosine to find the remaining function values.
Because we know the sine and cosine values for the common first-quadrant angles, we can find the other function values for those angles as well by setting equal to the cosine and equal to the sine and then using the definitions of tangent, secant, cosecant, and cotangent. The results are shown in [link] .
| Angle | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cosine | 1 | 0 | |||
| Sine | 0 | 1 | |||
| Tangent | 0 | 1 | Undefined | ||
| Secant | 1 | 2 | Undefined | ||
| Cosecant | Undefined | 2 | 1 | ||
| Cotangent | Undefined | 1 | 0 |
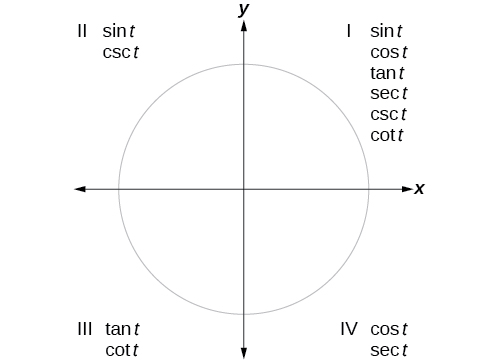
We can evaluate trigonometric functions of angles outside the first quadrant using reference angles as we have already done with the sine and cosine functions. The procedure is the same: Find the reference angle formed by the terminal side of the given angle with the horizontal axis. The trigonometric function values for the original angle will be the same as those for the reference angle, except for the positive or negative sign, which is determined by x - and y -values in the original quadrant. [link] shows which functions are positive in which quadrant.
To help remember which of the six trigonometric functions are positive in each quadrant, we can use the mnemonic phrase “A Smart Trig Class.” Each of the four words in the phrase corresponds to one of the four quadrants, starting with quadrant I and rotating counterclockwise. In quadrant I, which is “ A ,” a ll of the six trigonometric functions are positive. In quadrant II, “ S mart,” only s ine and its reciprocal function, cosecant, are positive. In quadrant III, “ T rig,” only t angent and its reciprocal function, cotangent, are positive. Finally, in quadrant IV, “ C lass,” only c osine and its reciprocal function, secant, are positive.
Given an angle not in the first quadrant, use reference angles to find all six trigonometric functions.
Use reference angles to find all six trigonometric functions of
The angle between this angle’s terminal side and the x -axis is so that is the reference angle. Since is in the third quadrant, where both and are negative, cosine, sine, secant, and cosecant will be negative, while tangent and cotangent will be positive.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?