| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Use reference angles to find all six trigonometric functions of
To be able to use our six trigonometric functions freely with both positive and negative angle inputs, we should examine how each function treats a negative input. As it turns out, there is an important difference among the functions in this regard.
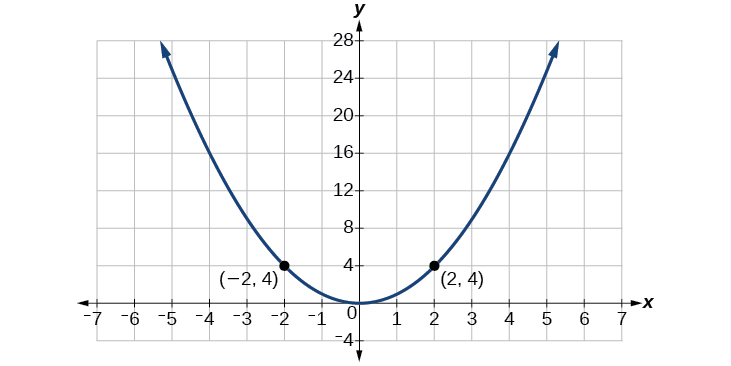
Consider the function shown in [link] . The graph of the function is symmetrical about the y -axis. All along the curve, any two points with opposite x -values have the same function value. This matches the result of calculation: and so on. So is an even function, a function such that two inputs that are opposites have the same output. That means
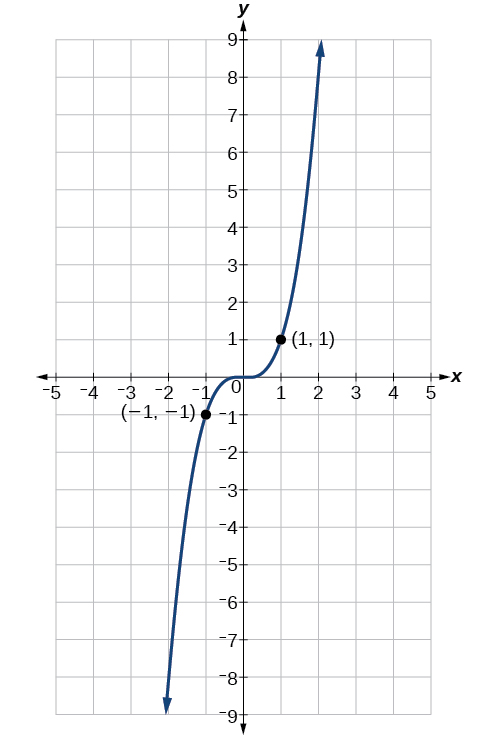
Now consider the function shown in [link] . The graph is not symmetrical about the y -axis. All along the graph, any two points with opposite x -values also have opposite y -values. So is an odd function, one such that two inputs that are opposites have outputs that are also opposites. That means
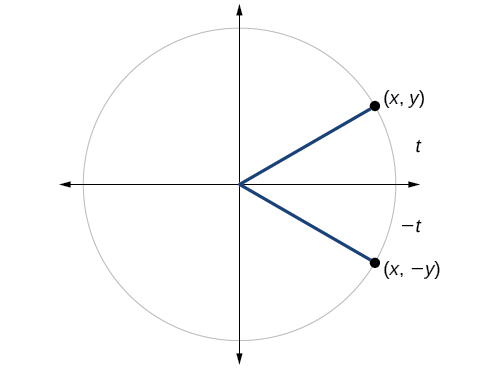
We can test whether a trigonometric function is even or odd by drawing a unit circle with a positive and a negative angle, as in [link] . The sine of the positive angle is The sine of the negative angle is The sine function, then, is an odd function. We can test each of the six trigonometric functions in this fashion. The results are shown in [link] .
An even function is one in which
An odd function is one in which
Cosine and secant are even:
Sine, tangent, cosecant, and cotangent are odd:
If the secant of angle is 2, what is the secant of
Secant is an even function. The secant of an angle is the same as the secant of its opposite. So if the secant of angle is 2, the secant of is also 2.
We have explored a number of properties of trigonometric functions. Now, we can take the relationships a step further, and derive some fundamental identities. Identities are statements that are true for all values of the input on which they are defined. Usually, identities can be derived from definitions and relationships we already know. For example, the Pythagorean Identity we learned earlier was derived from the Pythagorean Theorem and the definitions of sine and cosine.
We can derive some useful identities from the six trigonometric functions. The other four trigonometric functions can be related back to the sine and cosine functions using these basic relationships:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?