| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Lab A | Lab B | |
|---|---|---|
| Computers | 15 | 27 |
| Computer Tables | 16 | 34 |
| Chairs | 16 | 34 |
Converting the data to a matrix, we have
To calculate how much computer equipment will be needed, we multiply all entries in matrix by 0.15.
We must round up to the next integer, so the amount of new equipment needed is
Adding the two matrices as shown below, we see the new inventory amounts.
This means
Thus, Lab A will have 18 computers, 19 computer tables, and 19 chairs; Lab B will have 32 computers, 40 computer tables, and 40 chairs.
Scalar multiplication involves finding the product of a constant by each entry in the matrix. Given
the scalar multiple is
Scalar multiplication is distributive. For the matrices and with scalars and
Multiply matrix by the scalar 3.
Multiply each entry in by the scalar 3.
Find the sum
First, find
then
Now, add
In addition to multiplying a matrix by a scalar, we can multiply two matrices. Finding the product of two matrices is only possible when the inner dimensions are the same, meaning that the number of columns of the first matrix is equal to the number of rows of the second matrix. If is an matrix and is an matrix, then the product matrix is an matrix. For example, the product is possible because the number of columns in is the same as the number of rows in If the inner dimensions do not match, the product is not defined.
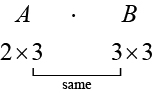
We multiply entries of with entries of according to a specific pattern as outlined below. The process of matrix multiplication becomes clearer when working a problem with real numbers.
To obtain the entries in row of we multiply the entries in row of by column in and add. For example, given matrices and where the dimensions of are and the dimensions of are the product of will be a matrix.
Multiply and add as follows to obtain the first entry of the product matrix

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?