| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
It is important that the "standard deviation" used must be appropriate for the parameter we are estimating, so in this section we need to use the standard deviation that applies to sample means, which is . The fraction , is commonly called the "standard error of the mean" in order to distinguish clearly the standard deviation for a mean from the population standard deviation σ .
To construct a confidence interval estimate for an unknown population mean, we need data from a random sample. The steps to construct and interpret the confidence interval are:
We will first examine each step in more detail, and then illustrate the process with some examples.
When we know the population standard deviation σ , we use a standard normal distribution to calculate the error bound EBM and construct the confidence interval. We need to find the value of z that puts an area equal to the confidence level (in decimal form) in the middle of the standard normal distribution Z ~ N (0, 1).
The confidence level, CL , is the area in the middle of the standard normal distribution. CL = 1 – α , so α is the area that is split equally between the two tails. Each of the tails contains an area equal to .
The z-score that has an area to the right of is denoted by .
For example, when CL = 0.95, α = 0.05 and = 0.025; we write = z 0.025 .
The area to the right of z 0.025 is 0.025 and the area to the left of z 0.025 is 1 – 0.025 = 0.975.
, using a calculator, computer or a standard normal probability table.
invNorm (0.975, 0, 1) = 1.96
Remember to use the area to the LEFT of ; in this chapter the last two inputs in the invNorm command are 0, 1, because you are using a standard normal distribution Z ~ N (0, 1).
The error bound formula for an unknown population mean μ when the population standard deviation σ is known is
The graph gives a picture of the entire situation.
CL + + = CL + α = 1.
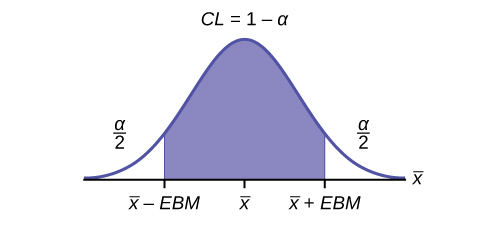
The interpretation should clearly state the confidence level ( CL ), explain what population parameter is being estimated (here, a population mean ), and state the confidence interval (both endpoints). "We estimate with ___% confidence that the true population mean (include the context of the problem) is between ___ and ___ (include appropriate units)."

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introductory statistics' conversation and receive update notifications?