
1.1 An introduction to the human body Read Online
1.2 The chemical level of organization Read Online
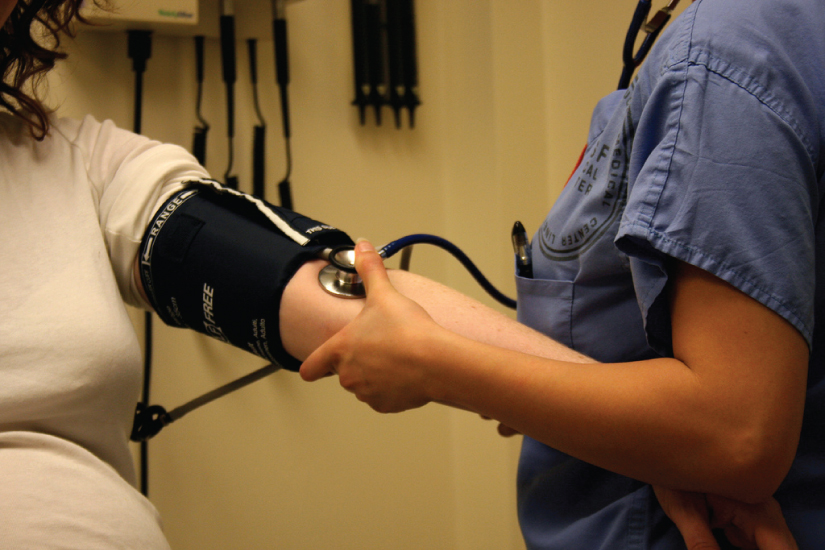
After studying this chapter, you will be able to:
Though you may approach a course in anatomy and physiology strictly as a requirement for your field of study, the knowledge you gain in this course will serve you well in many aspects of your life. An understanding of anatomy and physiology is not only fundamental to any career in the health professions, but it can also benefit your own health. Familiarity with the human body can help you make healthful choices and prompt you to take appropriate action when signs of illness arise. Your knowledge in this field will help you understand news about nutrition, medications, medical devices, and procedures and help you understand genetic or infectious diseases. At some point, everyone will have a problem with some aspect of his or her body and your knowledge can help you to be a better parent, spouse, partner, friend, colleague, or caregiver.
This chapter begins with an overview of anatomy and physiology and a preview of the body regions and functions. It then covers the characteristics of life and how the body works to maintain stable conditions. It introduces a set of standard terms for body structures and for planes and positions in the body that will serve as a foundation for more comprehensive information covered later in the text. It ends with examples of medical imaging used to see inside the living body.
Question: The function of the T tubules in muscle contraction is to
Choices:
make and store glycogen
release Ca2+ into the cell interior an then pick it up again
transmit the action potential deep into the muscle cells
form proteins
Question: The connective tissue covering that encloses the sarcolemma of an individual muscle fiber is called the
Choices:
epimysium
perimysium
endomysium
periosteum
Question: Characteristics of isometric contractions include all but
Choices:
shortening
increased muscle tension throughout the contraction phase
absence of shortening
used in resistance training
Question: A smooth sustained contraction resulting from very rapid stimulation of the muscle, in which no evidence of relaxation is seen, is called
Choices:
twitch
wave summation
multiple motor unit summation
fused tetanus
Question: The sites where the motor nerve impulse is transmitted from the nerve endings to the skeletal muscle cell membranes are
Choices:
neuromuscular junctions
sacromeres
myofilaments
z discs
Question: During muscle contraction, which provides ATP fastest?
Choices:
A coupled reaction of creatine phosphate with ADP
Aerobic respiration of glucose
Anaerobic glycolysis
Question: Contraction elicited by a single brief stimulus is called
Choices:
twitch
wave summation
multiple motor unit summation
fused tetanus
Question: During muscle contraction, Which provides the highest yield of ATP per glucose molecule?
Choices:
A coupled reaction of creatine phosphate with ADP
Aerobic respiration of glucose
Anaerobic glycolysis
Question: A fascicle is a
Choices:
muscle
bundle of muscle fibers enclosed by a connective tissue sheath
bundle of myofibrils
group of myofilaments
Question: A myofilament that contains actin is
Choices:
thin
thick
Question: During muscle contraction, Which does not require that oxygen be available?
Choices:
A coupled reaction of creatine phosphate with ADP
Aerobic respiration of glucose
Anaerobic glycolysis
A coupled reaction of creatine phosphate with ADP & Anaerobic glycolysis
Aerobic respiration of glucose & A coupled reaction of creatine phosphate with ADP