| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A first step in the study of psychological disorders is carefully and systematically discerning significant signs and symptoms. How do mental health professionals ascertain whether or not a person’s inner states and behaviors truly represent a psychological disorder? Arriving at a proper diagnosis —that is, appropriately identifying and labeling a set of defined symptoms—is absolutely crucial. This process enables professionals to use a common language with others in the field and aids in communication about the disorder with the patient, colleagues and the public. A proper diagnosis is an essential element to guide proper and successful treatment. For these reasons, classification systems that organize psychological disorders systematically are necessary.
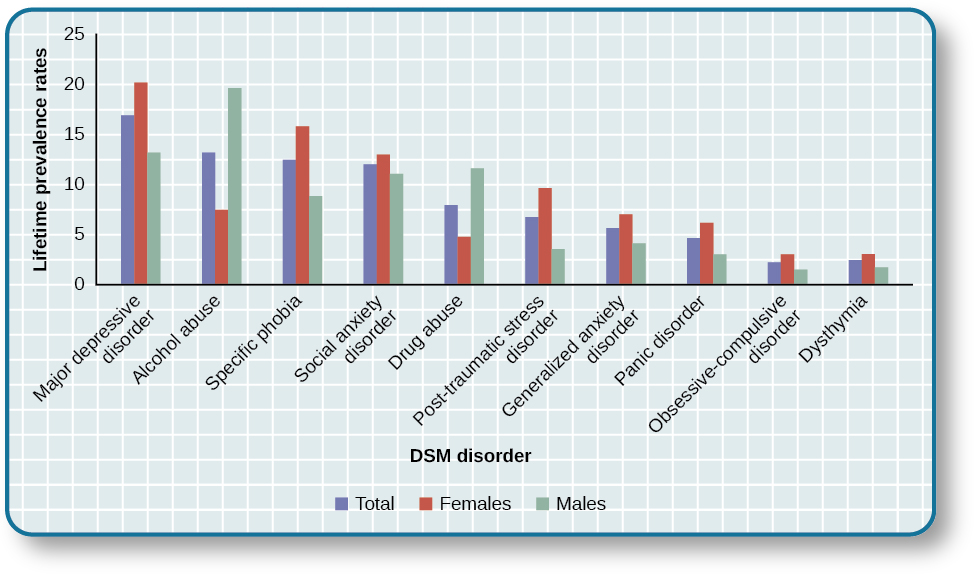
Although a number of classification systems have been developed over time, the one that is used by most mental health professionals in the United States is the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) , published by the American Psychiatric Association (2013). (Note that the American Psychiatric Association differs from the American Psychological Association; both are abbreviated APA.) The first edition of the DSM, published in 1952, classified psychological disorders according to a format developed by the U.S. Army during World War II (Clegg, 2012). In the years since, the DSM has undergone numerous revisions and editions. The most recent edition, published in 2013, is the DSM-5 (APA, 2013). The DSM-5 includes many categories of disorders (e.g., anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, and dissociative disorders). Each disorder is described in detail, including an overview of the disorder (diagnostic features), specific symptoms required for diagnosis (diagnostic criteria), prevalence information (what percent of the population is thought to be afflicted with the disorder), and risk factors associated with the disorder. [link] shows lifetime prevalence rates—the percentage of people in a population who develop a disorder in their lifetime—of various psychological disorders among U.S. adults. These data were based on a national sample of 9,282 U.S. residents (National Comorbidity Survey, 2007).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?