| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

In addition to clinical scales, the tests also have validity and reliability scales. (Recall the concepts of reliability and validity from your study of psychological research.) One of the validity scales, the Lie Scale (or “L” Scale), consists of 15 items and is used to ascertain whether the respondent is “faking good” (underreporting psychological problems to appear healthier). For example, if someone responds “yes” to a number of unrealistically positive items such as “I have never told a lie,” they may be trying to “fake good” or appear better than they actually are.
Reliability scales test an instrument’s consistency over time, assuring that if you take the MMPI-2-RF today and then again 5 years later, your two scores will be similar. Beutler, Nussbaum, and Meredith (1988) gave the MMPI to newly recruited police officers and then to the same police officers 2 years later. After 2 years on the job, police officers’ responses indicated an increased vulnerability to alcoholism, somatic symptoms (vague, unexplained physical complaints), and anxiety. When the test was given an additional 2 years later (4 years after starting on the job), the results suggested high risk for alcohol-related difficulties.
Another method for assessment of personality is projective testing . This kind of test relies on one of the defense mechanisms proposed by Freud—projection—as a way to assess unconscious processes. During this type of testing, a series of ambiguous cards is shown to the person being tested, who then is encouraged to project his feelings, impulses, and desires onto the cards—by telling a story, interpreting an image, or completing a sentence. Many projective tests have undergone standardization procedures (for example, Exner, 2002) and can be used to access whether someone has unusual thoughts or a high level of anxiety, or is likely to become volatile. Some examples of projective tests are the Rorschach Inkblot Test, the Thematic Apperception Test (TAT), the Contemporized-Themes Concerning Blacks test, the TEMAS (Tell-Me-A-Story), and the Rotter Incomplete Sentence Blank (RISB).
The Rorschach Inkblot Test was developed in 1921 by a Swiss psychologist named Hermann Rorschach (pronounced “ROAR-shock”). It is a series of symmetrical inkblot cards that are presented to a client by a psychologist. Upon presentation of each card, the psychologist asks the client, “What might this be?” What the test-taker sees reveals unconscious feelings and struggles (Piotrowski, 1987; Weiner, 2003). The Rorschach has been standardized using the Exner system and is effective in measuring depression, psychosis, and anxiety.
A second projective test is the Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) , created in the 1930s by Henry Murray, an American psychologist, and a psychoanalyst named Christiana Morgan. A person taking the TAT is shown 8–12 ambiguous pictures and is asked to tell a story about each picture. The stories give insight into their social world, revealing hopes, fears, interests, and goals. The storytelling format helps to lower a person’s resistance divulging unconscious personal details (Cramer, 2004). The TAT has been used in clinical settings to evaluate psychological disorders; more recently, it has been used in counseling settings to help clients gain a better understanding of themselves and achieve personal growth. Standardization of test administration is virtually nonexistent among clinicians, and the test tends to be modest to low on validity and reliability (Aronow, Weiss,&Rezinkoff, 2001; Lilienfeld, Wood,&Garb, 2000). Despite these shortcomings, the TAT has been one of the most widely used projective tests.
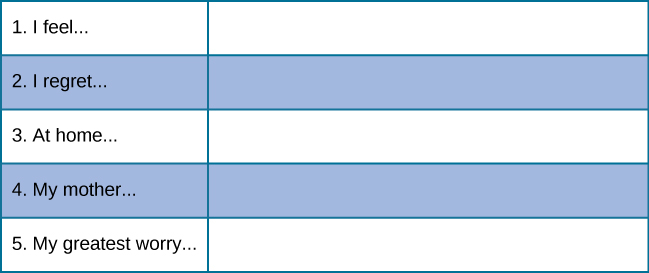
A third projective test is the Rotter Incomplete Sentence Blank (RISB) developed by Julian Rotter in 1950 (recall his theory of locus of control, covered earlier in this chapter). There are three forms of this test for use with different age groups: the school form, the college form, and the adult form. The tests include 40 incomplete sentences that people are asked to complete as quickly as possible ( [link] ). The average time for completing the test is approximately 20 minutes, as responses are only 1–2 words in length. This test is similar to a word association test, and like other types of projective tests, it is presumed that responses will reveal desires, fears, and struggles. The RISB is used in screening college students for adjustment problems and in career counseling (Holaday, Smith,&Sherry, 2010; Rotter&Rafferty 1950).
For many decades, these traditional projective tests have been used in cross-cultural personality assessments. However, it was found that test bias limited their usefulness (Hoy-Watkins&Jenkins-Moore, 2008). It is difficult to assess the personalities and lifestyles of members of widely divergent ethnic/cultural groups using personality instruments based on data from a single culture or race (Hoy-Watkins&Jenkins-Moore, 2008). For example, when the TAT was used with African-American test takers, the result was often shorter story length and low levels of cultural identification (Duzant, 2005). Therefore, it was vital to develop other personality assessments that explored factors such as race, language, and level of acculturation (Hoy-Watkins&Jenkins-Moore, 2008). To address this need, Robert Williams developed the first culturally specific projective test designed to reflect the everyday life experiences of African Americans (Hoy-Watkins&Jenkins-Moore, 2008). The updated version of the instrument is the Contemporized-Themes Concerning Blacks Test (C-TCB) (Williams, 1972). The C-TCB contains 20 color images that show scenes of African-American lifestyles. When the C-TCB was compared with the TAT for African Americans, it was found that use of the C-TCB led to increased story length, higher degrees of positive feelings, and stronger identification with the C-TCB (Hoy, 1997; Hoy-Watkins&Jenkins-Moore, 2008).
The TEMAS Multicultural Thematic Apperception Test is another tool designed to be culturally relevant to minority groups, especially Hispanic youths. TEMAS—standing for “Tell Me a Story” but also a play on the Spanish word temas (themes)—uses images and storytelling cues that relate to minority culture (Constantino, 1982).
Personality tests are techniques designed to measure one’s personality. They are used to diagnose psychological problems as well as to screen candidates for college and employment. There are two types of personality tests: self-report inventories and projective tests. The MMPI is one of the most common self-report inventories. It asks a series of true/false questions that are designed to provide a clinical profile of an individual. Projective tests use ambiguous images or other ambiguous stimuli to assess an individual’s unconscious fears, desires, and challenges. The Rorschach Inkblot Test, the TAT, the RISB, and the C-TCB are all forms of projective tests.
How objective do you think you can be about yourself in answering questions on self-report personality assessment measures? What implications might this have for the validity of the personality test?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?