| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Samples for ESI-MS must be in a liquid state. This requirement provides the necessary medium to easily charge the macromolecules or proteins into a fine aerosol state that can be easily fragmented to provide the desired outcomes. The benefit to this technique is that solid proteins that were once difficult to analyze, like metallothionein, can dissolved in an appropriate solvent that will allow analysis through ESI-MS. Because the sample is being delivered into the system as a liquid, the capillary can easily charge the solution to begin fragmentation of the protein into smaller fractions Maximum charge of the capillary is approximately 4 kV. However, this amount of charge is not necessary for every macromolecule. The appropriate charge is dependent on the size and characteristic of the solvent and each individual macromolecule. This has allowed for the removal of the molecular weight limit that was once held true for simple mass spectrometry analysis of proteins. Large proteins and macromolecules can now easily be detected and analyzed through ESI-MS due to the facility with which the molecules can fragment.
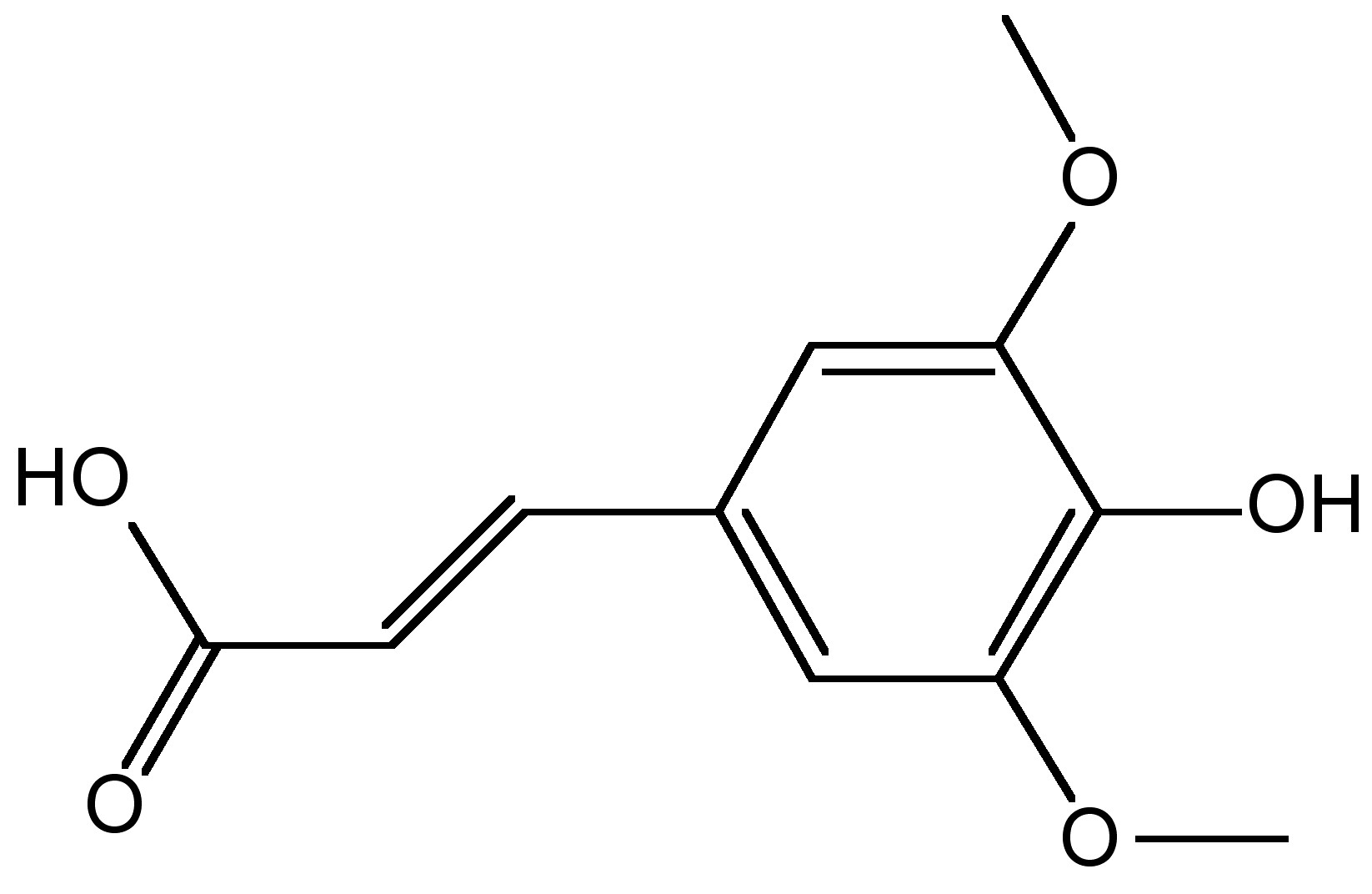
A related technique that was developed at approximately the same time as ESI-MS is matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS). This technique that was developed in the late 1980’s as wells, serves the same fundamental purpose; allowing analysis of large macromolecules via mass spectrometry through an alternative route of generating the necessary gas phase for analysis. In MALDI-MS, a matrix, usually comprised of crystallized 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid ( [link] ), water, and an organic solvent, is used to mix the analyte, and a laser is used to charge the matrix. The matrix then co-crystallizes the analyte and pulses of the laser are then used to cause desorption of the matrix and some of the analyte crystals with it, leading to ionization of the crystals and the phase change into the gaseous state. The analytes are then read by the tandem mass spectrometer. [link] directly compares some attributes between ESI-MS and MALDI-MS. It should be noted that there are several variations of both ESI-MS and MALDI-MS, with the methods of data collection varying and the piggy-backing of several other methods (liquid chromatography, capillary electrophoresis, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, etc.), yet all of them have the same fundamental principles as these basic two methods.
| Experimental details | ESI-MS | MALDI-MS |
| Starting analyte state | Liquid | Liquid/solid |
| Method of ionization | Charged capillary needle | Matrix laser desorption |
| Final analyte state | Gas | Gas |
| Quantity of protein needed | 1 μL | 1 μL |
| Spectrum method | Mass spectrometry | Mass spectrometry |
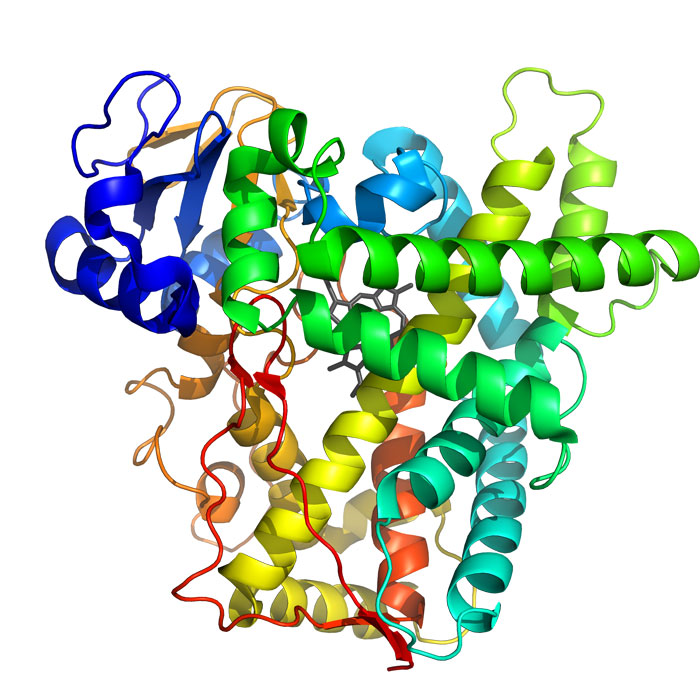
ESI-MS has proven to be useful in determination of tertiary structure and molecular weight calculations of large macromolecules. However, there are still several problems incorporated with the technique and macromolecule analysis. One problem is the isolation of the desired protein for analysis. If the protein is unable to be extracted from the cell, this is usually done through gel electrophoresis, there is a limiting factor in what proteins can be analyzed. Cytochrome c ( [link] ) is an example of a protein that can be isolated and analyzed, but provides an interesting limitation on how the analytical technique does not function for a completely effective protein analysis. The problem with cytochrome c is that even if the protein is in its native confirmation, it can still show different charge distribution. This occurs due to the availability of basic sites for protonation that are consistently exposed to the solvent. Any slight change to the native conformation may cause basic sites, such as in cytochrome c to be blocked causing different m / z ratios to be seen. Another interesting limitation is seen when inorganic elements, such as in metallothioneins proteins that contain zinc, are analyzed using ESI-MS. Metallothioneins have several isoforms that show no consistent trend in ESI-MS data between the varied isoforms. The marked differences occur due to the metallation of each isoform being different, which causes the electrospraying and as a result protonation of the protein to be different. Thus, incorporation of metal atoms in proteins can have various effects on ESI-MS data due to the unexpected interactions between the metal center and the protein itself.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?