| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Similar observations can be made using a meter stick held at different locations along its length.
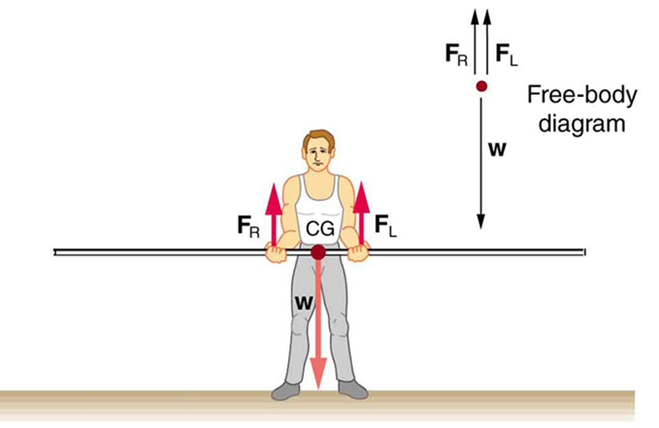
If the pole vaulter holds the pole as shown in [link] , the situation is not as simple. The total force he exerts is still equal to the weight of the pole, but it is not evenly divided between his hands. (If , then the torques about the cg would not be equal since the lever arms are different.) Logically, the right hand should support more weight, since it is closer to the cg. In fact, if the right hand is moved directly under the cg, it will support all the weight. This situation is exactly analogous to two people carrying a load; the one closer to the cg carries more of its weight. Finding the forces and is straightforward, as the next example shows.
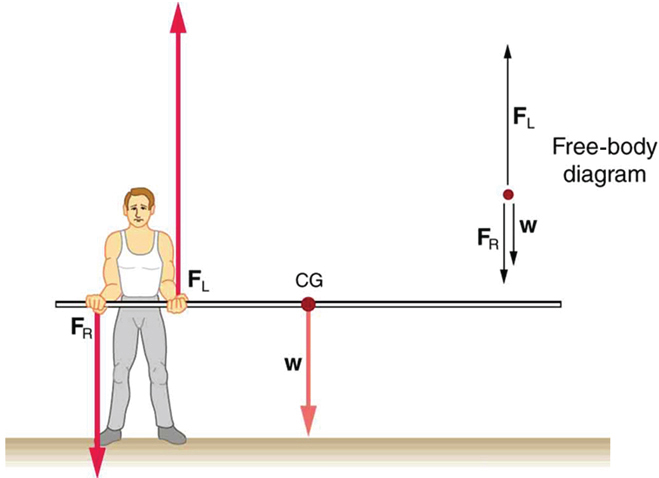
If the pole vaulter holds the pole from near the end of the pole ( [link] ), the direction of the force applied by the right hand of the vaulter reverses its direction.
For the situation shown in [link] , calculate: (a) , the force exerted by the right hand, and (b) , the force exerted by the left hand. The hands are 0.900 m apart, and the cg of the pole is 0.600 m from the left hand.
Strategy
[link] includes a free body diagram for the pole, the system of interest. There is not enough information to use the first condition for equilibrium ), since two of the three forces are unknown and the hand forces cannot be assumed to be equal in this case. There is enough information to use the second condition for equilibrium if the pivot point is chosen to be at either hand, thereby making the torque from that hand zero. We choose to locate the pivot at the left hand in this part of the problem, to eliminate the torque from the left hand.
Solution for (a)
There are now only two nonzero torques, those from the gravitational force ( ) and from the push or pull of the right hand ( ). Stating the second condition in terms of clockwise and counterclockwise torques,
or the algebraic sum of the torques is zero.
Here this is
since the weight of the pole creates a counterclockwise torque and the right hand counters with a clockwise torque. Using the definition of torque, , noting that , and substituting known values, we obtain
Thus,
Solution for (b)
The first condition for equilibrium is based on the free body diagram in the figure. This implies that by Newton’s second law:
From this we can conclude:
Solving for , we obtain
Discussion
is seen to be exactly half of , as we might have guessed, since is applied twice as far from the cg as .
If the pole vaulter holds the pole as he might at the start of a run, shown in [link] , the forces change again. Both are considerably greater, and one force reverses direction.
This is an experiment to perform while standing in a bus or a train. Stand facing sideways. How do you move your body to readjust the distribution of your mass as the bus accelerates and decelerates? Now stand facing forward. How do you move your body to readjust the distribution of your mass as the bus accelerates and decelerates? Why is it easier and safer to stand facing sideways rather than forward? Note: For your safety (and those around you), make sure you are holding onto something while you carry out this activity!
Play with objects on a teeter totter to learn about balance. Test what you've learned by trying the Balance Challenge game.

When visiting some countries, you may see a person balancing a load on the head. Explain why the center of mass of the load needs to be directly above the person’s neck vertebrae.
To get up on the roof, a person (mass 70.0 kg) places a 6.00-m aluminum ladder (mass 10.0 kg) against the house on a concrete pad with the base of the ladder 2.00 m from the house. The ladder rests against a plastic rain gutter, which we can assume to be frictionless. The center of mass of the ladder is 2 m from the bottom. The person is standing 3 m from the bottom. What are the magnitudes of the forces on the ladder at the top and bottom?
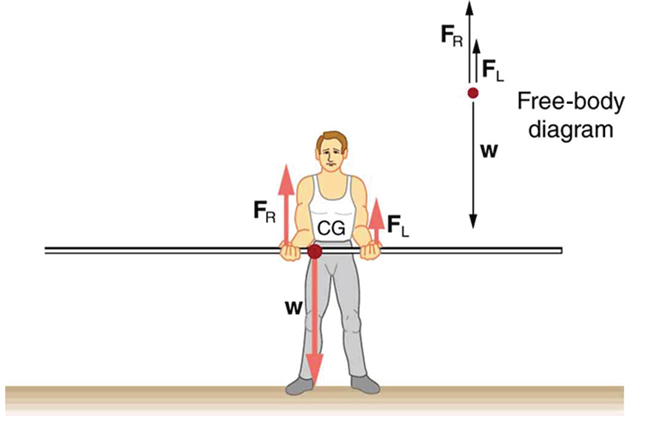
In [link] , the cg of the pole held by the pole vaulter is 2.00 m from the left hand, and the hands are 0.700 m apart. Calculate the force exerted by (a) his right hand and (b) his left hand. (c) If each hand supports half the weight of the pole in [link] , show that the second condition for equilibrium is satisfied for a pivot other than the one located at the center of gravity of the pole. Explicitly show how you follow the steps in the Problem-Solving Strategy for static equilibrium described above.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?