| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Atmospheric pressure is another example of pressure due to the weight of a fluid, in this case due to the weight of air above a given height. The atmospheric pressure at the Earth’s surface varies a little due to the large-scale flow of the atmosphere induced by the Earth’s rotation (this creates weather “highs” and “lows”). However, the average pressure at sea level is given by the standard atmospheric pressure , measured to be
This relationship means that, on average, at sea level, a column of air above of the Earth’s surface has a weight of , equivalent to . (See [link] .)
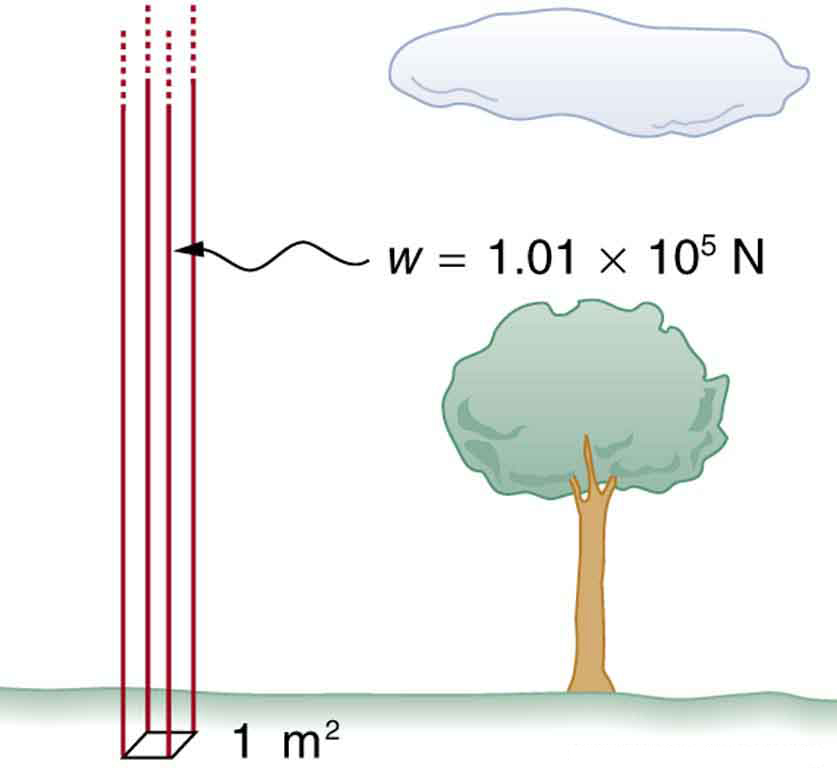
Calculate the average density of the atmosphere, given that it extends to an altitude of 120 km. Compare this density with that of air listed in [link] .
Strategy
If we solve for density, we see that
We then take to be atmospheric pressure, is given, and is known, and so we can use this to calculate .
Solution
Entering known values into the expression for yields
Discussion
This result is the average density of air between the Earth’s surface and the top of the Earth’s atmosphere, which essentially ends at 120 km. The density of air at sea level is given in [link] as —about 15 times its average value. Because air is so compressible, its density has its highest value near the Earth’s surface and declines rapidly with altitude.
Calculate the depth below the surface of water at which the pressure due to the weight of the water equals 1.00 atm.
Strategy
We begin by solving the equation for depth :
Then we take to be 1.00 atm and to be the density of the water that creates the pressure.
Solution
Entering the known values into the expression for gives
Discussion
Just 10.3 m of water creates the same pressure as 120 km of air. Since water is nearly incompressible, we can neglect any change in its density over this depth.
What do you suppose is the total pressure at a depth of 10.3 m in a swimming pool? Does the atmospheric pressure on the water’s surface affect the pressure below? The answer is yes. This seems only logical, since both the water’s weight and the atmosphere’s weight must be supported. So the total pressure at a depth of 10.3 m is 2 atm—half from the water above and half from the air above. We shall see in Pascal’s Principle that fluid pressures always add in this way.
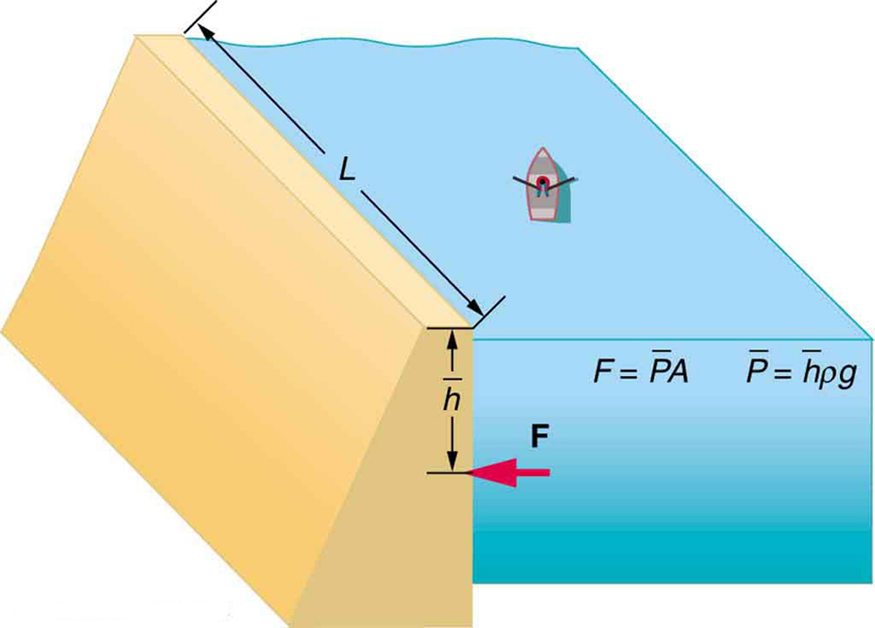
where is the pressure, is the height of the liquid, is the density of the liquid, and is the acceleration due to gravity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?