| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
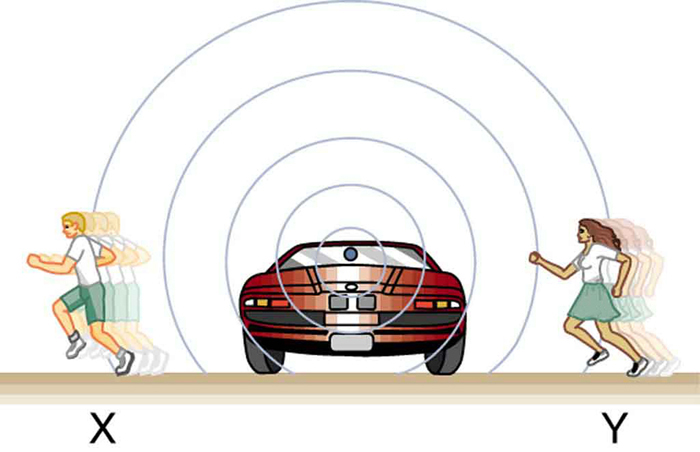
We know that wavelength and frequency are related by , where is the fixed speed of sound. The sound moves in a medium and has the same speed in that medium whether the source is moving or not. Thus multiplied by is a constant. Because the observer on the right in [link] receives a shorter wavelength, the frequency she receives must be higher. Similarly, the observer on the left receives a longer wavelength, and hence he hears a lower frequency. The same thing happens in [link] . A higher frequency is received by the observer moving toward the source, and a lower frequency is received by an observer moving away from the source. In general, then, relative motion of source and observer toward one another increases the received frequency. Relative motion apart decreases frequency. The greater the relative speed is, the greater the effect.
The Doppler effect occurs not only for sound but for any wave when there is relative motion between the observer and the source. There are Doppler shifts in the frequency of sound, light, and water waves, for example. Doppler shifts can be used to determine velocity, such as when ultrasound is reflected from blood in a medical diagnostic. The recession of galaxies is determined by the shift in the frequencies of light received from them and has implied much about the origins of the universe. Modern physics has been profoundly affected by observations of Doppler shifts.
For a stationary observer and a moving source, the frequency f obs received by the observer can be shown to be
where is the frequency of the source, is the speed of the source along a line joining the source and observer, and is the speed of sound. The minus sign is used for motion toward the observer and the plus sign for motion away from the observer, producing the appropriate shifts up and down in frequency. Note that the greater the speed of the source, the greater the effect. Similarly, for a stationary source and moving observer, the frequency received by the observer is given by
where is the speed of the observer along a line joining the source and observer. Here the plus sign is for motion toward the source, and the minus is for motion away from the source.
Suppose a train that has a 150-Hz horn is moving at 35.0 m/s in still air on a day when the speed of sound is 340 m/s.
(a) What frequencies are observed by a stationary person at the side of the tracks as the train approaches and after it passes?
(b) What frequency is observed by the train’s engineer traveling on the train?
Strategy
To find the observed frequency in (a), must be used because the source is moving. The minus sign is used for the approaching train, and the plus sign for the receding train. In (b), there are two Doppler shifts—one for a moving source and the other for a moving observer.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?