| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In pure rotational motion, the constituent particles of a rigid body rotate about a fixed axis in a circular trajectory. The particles, composing the rigid body, are always at a constant perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation as their internal distances within the rigid body is locked. Farther the particle from the axis of rotation, greater is the speed of rotation of the particle. Clearly, rotation of a rigid body comprises of circular motion of individual particles.
Rotation of a rigid body about a fixed axis
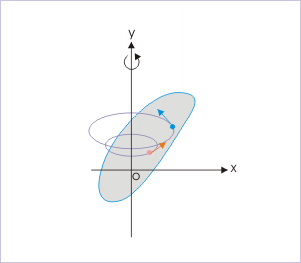
We shall study these and other details about the rotational motion of rigid bodies at a later stage. For now, we confine ourselves to the aspects of rotational motion, which are connected to the circular motion as executed by a particle. In this background, we can say that uniform circular motion (UCM) represents the basic form of circular motion and circular motion, in turn, constitutes rotational motion of a rigid body.
The description of a circular and hence that of rotational motion is best suited to corresponding angular quantities as against linear quantities that we have so far used to describe translational motion. In this module, we shall introduce these angular quantities and prepare the ground work to enable us apply the concepts of angular quantities to “circular motion” in general and “uniform circulation motion” in particular.
Most important aspect of angular description as against linear description is that there exists one to one correspondence of quantities describing motion : angular displacement (linear displacement), angular velocity (linear velocity) and angular acceleration (linear acceleration).
In this section, we discuss some of the defining quantities, which are used to study uniform circular motion of a particle and rotational motion of rigid bodies. These quantities are angular position, angular displacement and angular velocity. They possess directional properties. Their measurement in counter clockwise direction is considered positive, whereas quantities measured in clockwise direction is considered negative. This gives us a simplified scheme to represent an angular vector by a simple variable, whose sign indicates its direction.
Notably, we shall not discuss angular acceleration in this module. It will be discussed as a part of non-uniform circular motion in a separate module.
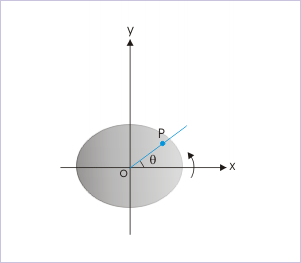
We need two straight lines to measure an angle. In rotational motion, one of them represents fixed direction, while another represents the rotating arm containing the particle. Both these lines are perpendicular to the rotating axis. The rotating arm, additionally, passes through the position of the particle.
Angular position (θ)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?