| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
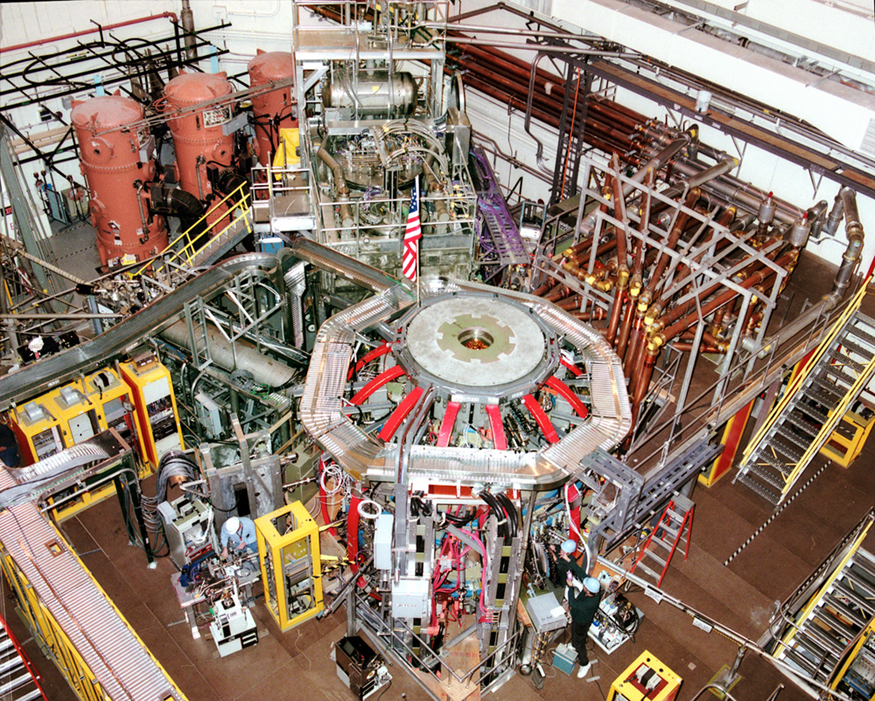
A tokamak is a form of experimental fusion reactor, which can change mass to energy. Accomplishing this requires an understanding of relativistic energy. Nuclear reactors are proof of the conservation of relativistic energy.
Conservation of energy is one of the most important laws in physics. Not only does energy have many important forms, but each form can be converted to any other. We know that classically the total amount of energy in a system remains constant. Relativistically, energy is still conserved, provided its definition is altered to include the possibility of mass changing to energy, as in the reactions that occur within a nuclear reactor. Relativistic energy is intentionally defined so that it will be conserved in all inertial frames, just as is the case for relativistic momentum. As a consequence, we learn that several fundamental quantities are related in ways not known in classical physics. All of these relationships are verified by experiment and have fundamental consequences. The altered definition of energy contains some of the most fundamental and spectacular new insights into nature found in recent history.
The first postulate of relativity states that the laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames. Einstein showed that the law of conservation of energy is valid relativistically, if we define energy to include a relativistic factor.
Total energy is defined to be
where is mass, is the speed of light, , and is the velocity of the mass relative to an observer. There are many aspects of the total energy that we will discuss—among them are how kinetic and potential energies are included in , and how is related to relativistic momentum. But first, note that at rest, total energy is not zero. Rather, when , we have , and an object has rest energy.
Rest energy is
This is the correct form of Einstein’s most famous equation, which for the first time showed that energy is related to the mass of an object at rest. For example, if energy is stored in the object, its rest mass increases. This also implies that mass can be destroyed to release energy. The implications of these first two equations regarding relativistic energy are so broad that they were not completely recognized for some years after Einstein published them in 1907, nor was the experimental proof that they are correct widely recognized at first. Einstein, it should be noted, did understand and describe the meanings and implications of his theory.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?