| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
The great Danish physicist Niels Bohr (1885–1962) made immediate use of Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom. ( [link] ). Bohr became convinced of its validity and spent part of 1912 at Rutherford’s laboratory. In 1913, after returning to Copenhagen, he began publishing his theory of the simplest atom, hydrogen, based on the planetary model of the atom. For decades, many questions had been asked about atomic characteristics. From their sizes to their spectra, much was known about atoms, but little had been explained in terms of the laws of physics. Bohr’s theory explained the atomic spectrum of hydrogen and established new and broadly applicable principles in quantum mechanics.

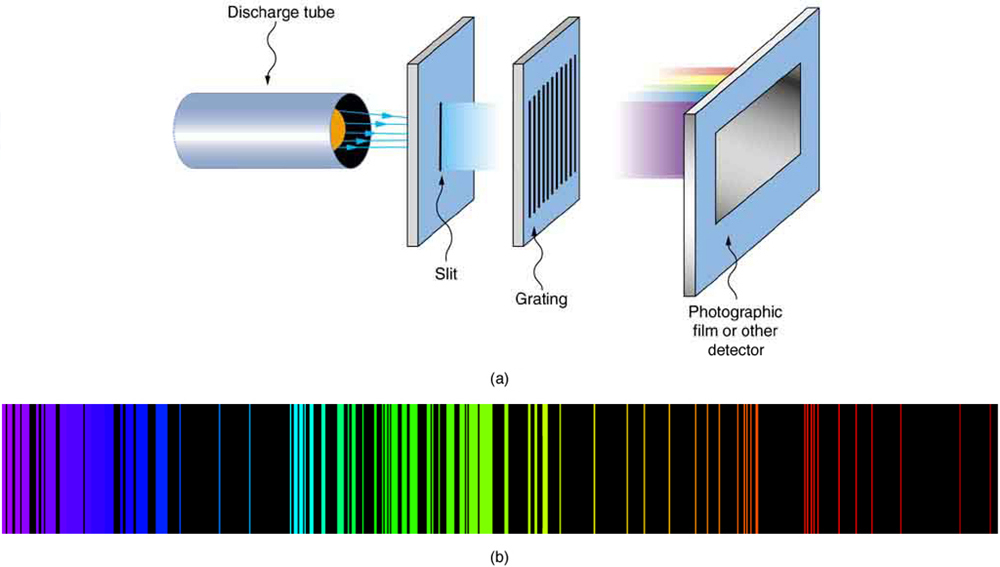
As noted in Quantization of Energy , the energies of some small systems are quantized. Atomic and molecular emission and absorption spectra have been known for over a century to be discrete (or quantized). (See [link] .) Maxwell and others had realized that there must be a connection between the spectrum of an atom and its structure, something like the resonant frequencies of musical instruments. But, in spite of years of efforts by many great minds, no one had a workable theory. (It was a running joke that any theory of atomic and molecular spectra could be destroyed by throwing a book of data at it, so complex were the spectra.) Following Einstein’s proposal of photons with quantized energies directly proportional to their wavelengths, it became even more evident that electrons in atoms can exist only in discrete orbits.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?