| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
If you have ever spun a bike wheel or pushed a merry-go-round, you know that force is needed to change angular velocity as seen in [link] . In fact, your intuition is reliable in predicting many of the factors that are involved. For example, we know that a door opens slowly if we push too close to its hinges. Furthermore, we know that the more massive the door, the more slowly it opens. The first example implies that the farther the force is applied from the pivot, the greater the angular acceleration; another implication is that angular acceleration is inversely proportional to mass. These relationships should seem very similar to the familiar relationships among force, mass, and acceleration embodied in Newton's second law of motion. There are, in fact, precise rotational analogs to both force and mass.
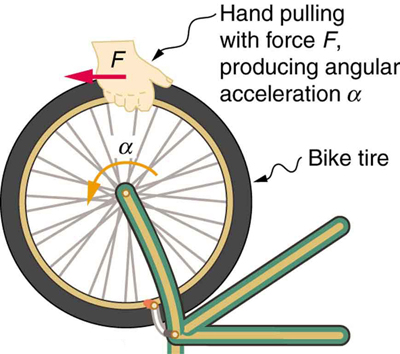
To develop the precise relationship among force, mass, radius, and angular acceleration, consider what happens if we exert a force on a point mass that is at a distance from a pivot point, as shown in [link] . Because the force is perpendicular to , an acceleration is obtained in the direction of . We can rearrange this equation such that and then look for ways to relate this expression to expressions for rotational quantities. We note that , and we substitute this expression into , yielding
Recall that torque is the turning effectiveness of a force. In this case, because is perpendicular to , torque is simply . So, if we multiply both sides of the equation above by , we get torque on the left-hand side. That is,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?