| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
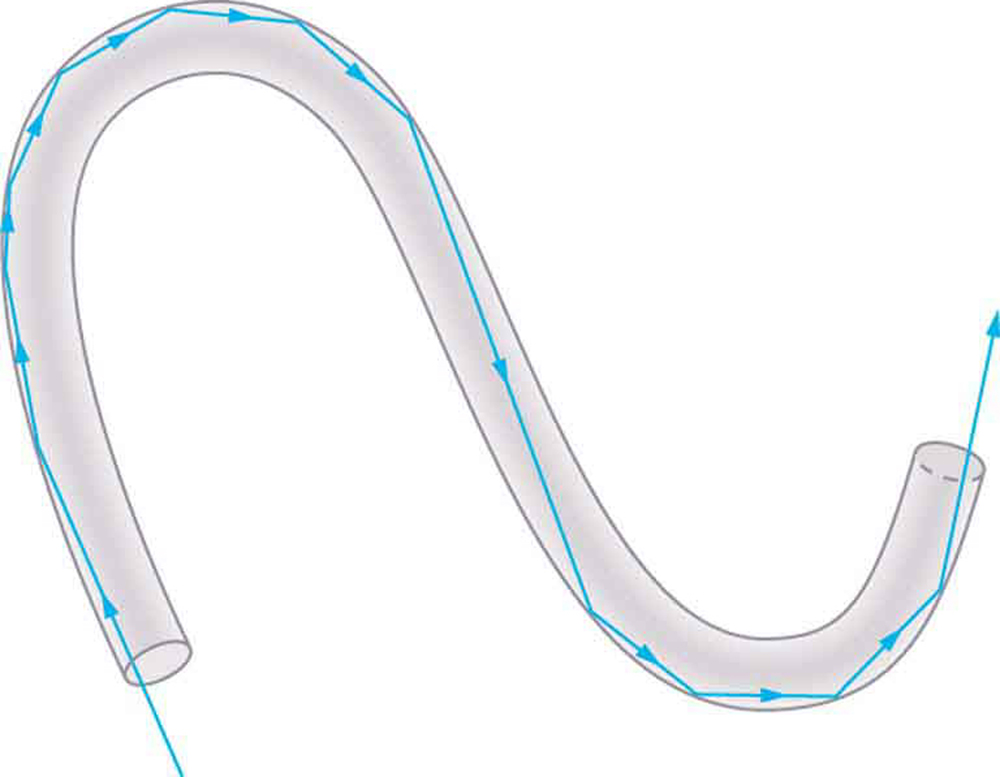
Fiber optics is one application of total internal reflection that is in wide use. In communications, it is used to transmit telephone, internet, and cable TV signals. Fiber optics employs the transmission of light down fibers of plastic or glass. Because the fibers are thin, light entering one is likely to strike the inside surface at an angle greater than the critical angle and, thus, be totally reflected (See [link] .) The index of refraction outside the fiber must be smaller than inside, a condition that is easily satisfied by coating the outside of the fiber with a material having an appropriate refractive index. In fact, most fibers have a varying refractive index to allow more light to be guided along the fiber through total internal refraction. Rays are reflected around corners as shown, making the fibers into tiny light pipes.
Bundles of fibers can be used to transmit an image without a lens, as illustrated in [link] . The output of a device called an endoscope is shown in [link] (b). Endoscopes are used to explore the body through various orifices or minor incisions. Light is transmitted down one fiber bundle to illuminate internal parts, and the reflected light is transmitted back out through another to be observed. Surgery can be performed, such as arthroscopic surgery on the knee joint, employing cutting tools attached to and observed with the endoscope. Samples can also be obtained, such as by lassoing an intestinal polyp for external examination.
Fiber optics has revolutionized surgical techniques and observations within the body. There are a host of medical diagnostic and therapeutic uses. The flexibility of the fiber optic bundle allows it to navigate around difficult and small regions in the body, such as the intestines, the heart, blood vessels, and joints. Transmission of an intense laser beam to burn away obstructing plaques in major arteries as well as delivering light to activate chemotherapy drugs are becoming commonplace. Optical fibers have in fact enabled microsurgery and remote surgery where the incisions are small and the surgeon’s fingers do not need to touch the diseased tissue.
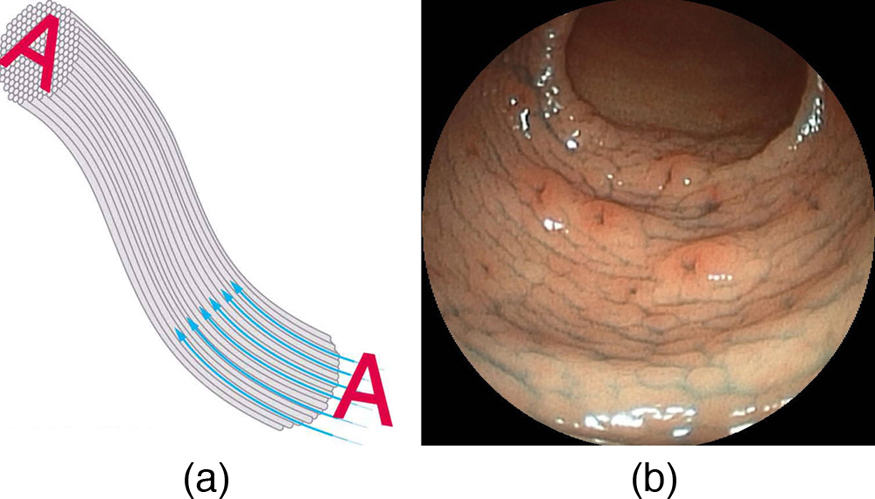
Fibers in bundles are surrounded by a cladding material that has a lower index of refraction than the core. (See [link] .) The cladding prevents light from being transmitted between fibers in a bundle. Without cladding, light could pass between fibers in contact, since their indices of refraction are identical. Since no light gets into the cladding (there is total internal reflection back into the core), none can be transmitted between clad fibers that are in contact with one another. The cladding prevents light from escaping out of the fiber; instead most of the light is propagated along the length of the fiber, minimizing the loss of signal and ensuring that a quality image is formed at the other end. The cladding and an additional protective layer make optical fibers flexible and durable.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?