| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As shown in [link] all the combinations of Group 13 element (M) and halogen (X) exist for the trihalides (MX 3 ), except thallium(III) iodide. It should be noted that while there is a compound with the general formula TlI 3 , it is actually a thallium(I) compound of I 3 - .
| Element | Mp (°C) | Bp (°C) |
| BF 3 | -126.8 | -100.3 |
| BCl 3 | -107.3 | 12.6 |
| BBr 3 | -46.3 | 91.3 |
| BI 3 | 49.9 | 210 |
| AlF 3 | 1291 | - |
| AlCl 3 | 192.4 (anhydrous), 0.0 (hexahydrate) | 120 (hexahydrate) |
| AlBr 3 | 97.8 | 265 |
| AlI 3 | 189.4 (anhydrous) 185 dec. (hexahydrate) | 300 subl. |
| GaF 3 | 800 | 1000 |
| GaCl 3 | 77.9 | 201 |
| GaBr 3 | 121.5 | 278.8 |
| GaI 3 | 212 | 345 |
| InF 3 | 1172 | - |
| InCl 3 | 586 | 800 |
| InBr 3 | 220 | - |
| InI 3 | 210 subl. | - |
| TlF 3 | 300 dec. | - |
| TlCl 3 | 40 dec. | - |
| TlBr 3 | 40 dec. | - |
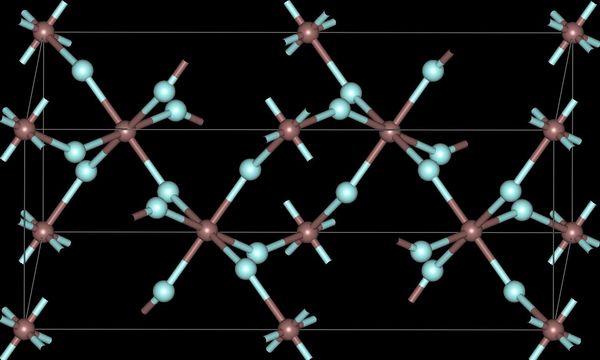
The trihalides of boron are all monomers with a coordination number of 3 ( [link] ), as evidence from their low melting points ( [link] ). In contrast, the fluorides and chlorides of the heavier Group 13 elements (except GaCl 3 ) are generally ionic or have a high ionic character, with a coordination number of 6 ( [link] , [link] and [link] ). The bromides and iodides (except InBr 3 ) are generally dimeric with a coordination number of 4 ( [link] ) and have molecular structures involving halide bridging ligands ( [link] and [link] ). AlCl 3 is unusual in that in the solid state it has an ionic structure, but it is readily sublimed, and in the vapor phase (and liquid phase) it has a dimeric structure ( [link] ).
| Element | Fluoride | Chloride | Bromide | Iodide |
| B | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Al | 6 | 6 (4) | 4 | 4 |
| Ga | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| In | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4 |
| Tl | 6 | 6 | 4 | - |
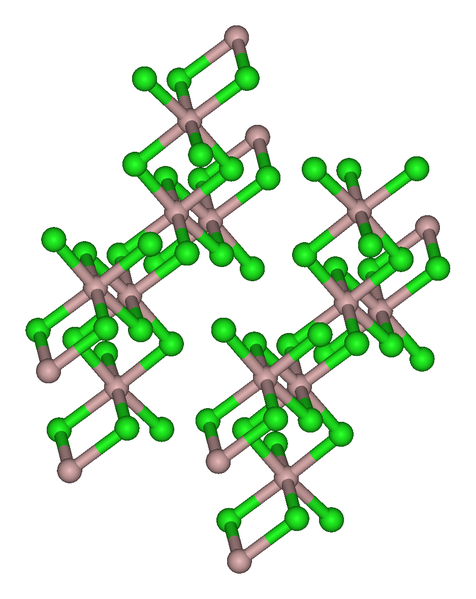
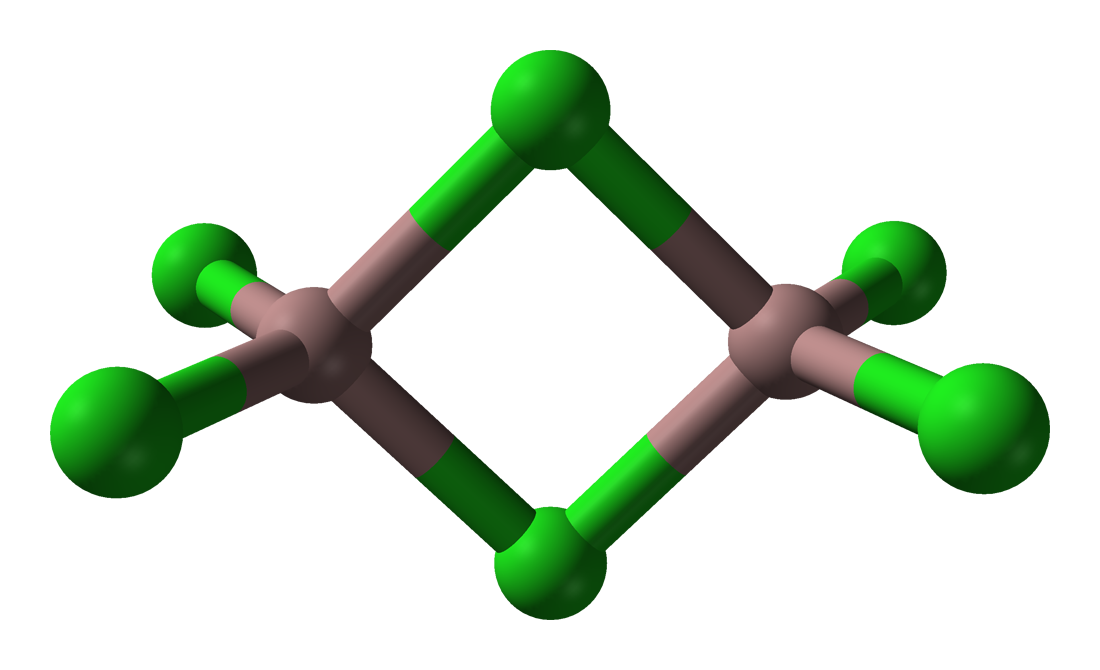
| Compound | M-X t (Å) a | M-X b (Å) a | X t -M-X t (°) a | X b -M-X b (°) a | M-X-M (°) |
| Al 2 Br 6 | 2.21 | 2.33 | 115 | 93 | 87 |
| In 2 I 6 | 2.64 | 2.84 | 125.1 | 93.7 | 86.3 |
Boron trifluoride (BF 3 ) is manufactured commercially by the reaction of boron oxides with hydrogen fluoride, [link] . The HF is produced in-situ from sulfuric acid and fluorite (CaF 2 ). On smaller scales, BF 3 is prepared by the thermal decomposition of diazonium salts, [link] .
Boron trichloride is also made from boron oxide, but in the presence of carbon, [link] .
Many of the trihalides are readily prepared by either the direct reaction of the metal with the appropriate halogen, [link] - [link] , or the acid, [link] and [link] . Thallium tribromide can be prepared in CH 3 CN by treating a solution of the monobromide with bromine gas, [link] .
The reaction chemistry of the Group 13 trihalides tends to fall into two categories:
There are, however, a number of reactions involving halide exchange reactions. Aluminum tribromide reacts with carbon tetrachloride at 100 °C to form carbon tetrabromide, [link] , and with phosgene yields carbonyl bromide and aluminum chlorobromide, [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of the main group elements' conversation and receive update notifications?