| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this learning unit you are going to research pop-up cards (1.1), design (1.2), make (1.3) and evaluate (1.4) them.

A What is The Need?
First you have to determine the need, submit a design proposal and analyse the problem further, and then compile the final specifications.
B Make a proposal that you will design
I’m going to design a ……………………………………….. (type of card) for
…………………………………………………………..(user) to use in or at the
………………………………………… (place) for ……………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………..(use of).
C Analyse the problem further
The following W-questions will help a lot. Ask your own questions as well.
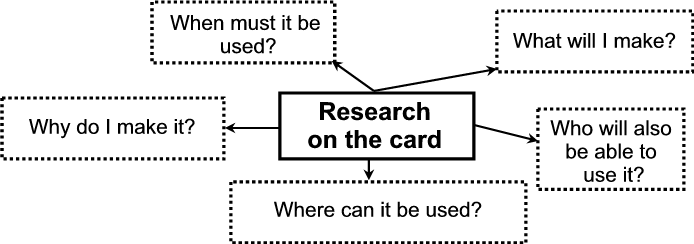
D Compile a list of specifications
Consider the following:
Now you can begin to design the card!

A Discuss your ideas again.
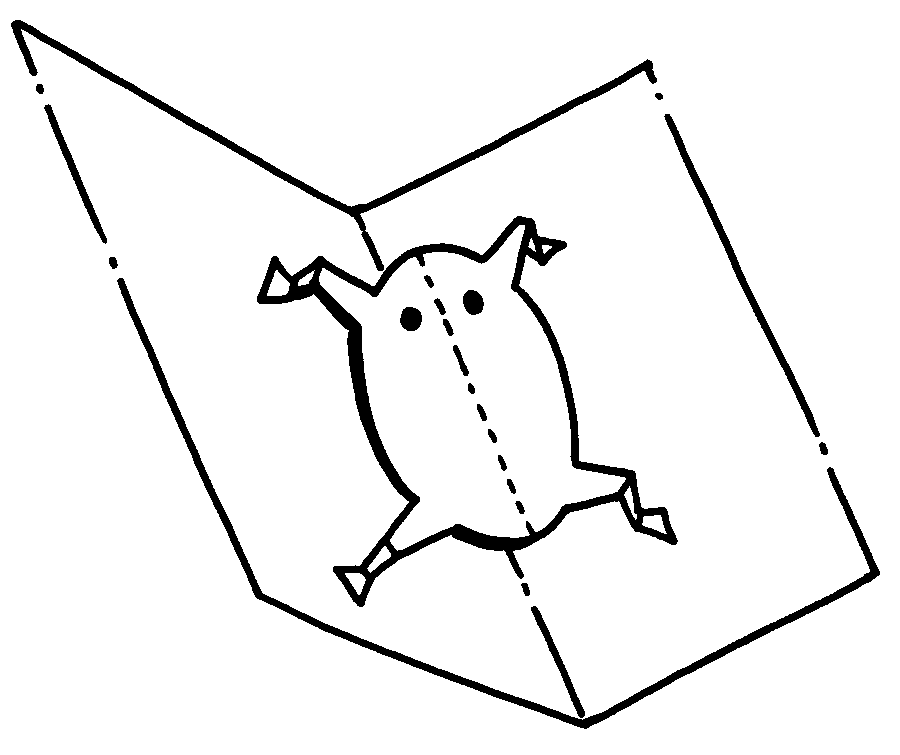
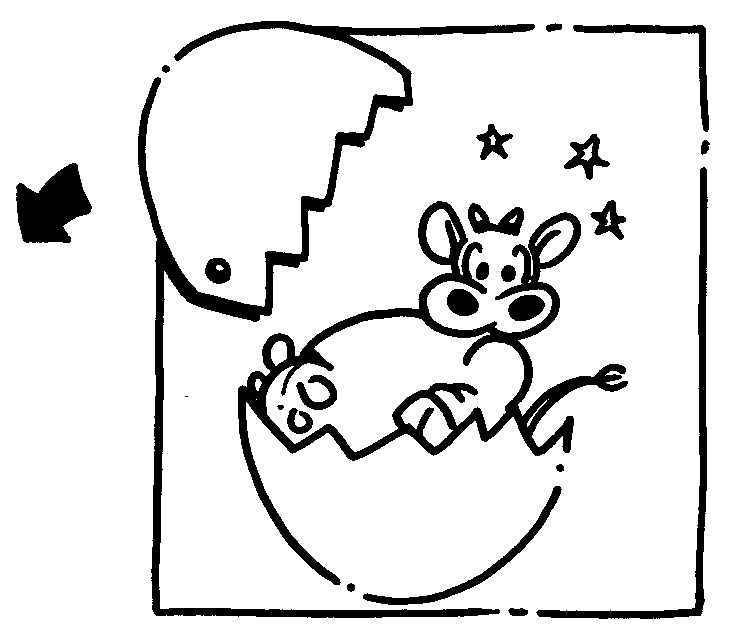
B Decide on your best idea!
Hints
Ask critical questions while you draw:
Make neat final drawings and decorate them in colour. You may use drawing tools.

How to make a pop-up mechanism
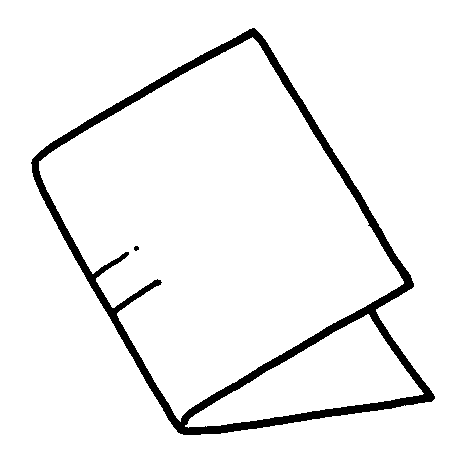
TIME is very important - therefore we must plan properly.
So many things need to be done at the same time, therefore you will have to organise your work in such a way that you won't waste any time and energy. We will set up a scheme so that you will utilise your time effectively. It makes your work easier. Good planning saves time and ensures a better product.
Actions Materials Tools
Tick off as soon as it is completed.
| make certain parts | glue | |||||
| finishing touches | round off | |||||
| paint | test |
Evaluate and compare the different materials that you will use with regard to:
(iii) Which tools will I use?
B Work safely!
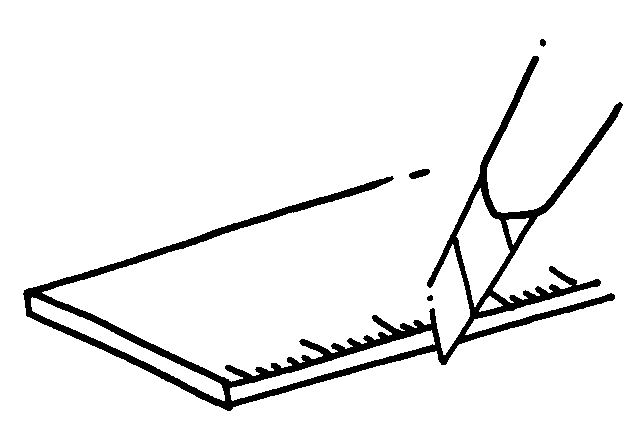
Safety knife
Be very careful when you cut paper or cardboard. Use a safety ruler with the safety knife.
1.4 Evaluate your products and work
Be honest about your mistakes. Learn through it.
A First discuss the questionnaire with your partner:
Did I do good research and planning ?
……………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………
The learner will be able to apply technological processes and skills ethically and responsibly using appropriate information and communication technologies.
We know this when the learner:
1.1 finds out, with assistance, about the background context (e.g. people, environment) when given a problem, need or opportunity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Technology grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?