| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Rather than solving the differential equation that arises in circuits containing capacitors and inductors, let's pretend thatall sources in the circuit are complex exponentials having the same frequency. Although this pretense can only be mathematically true, this fiction will greatly easesolving the circuit no matter what the source really is.
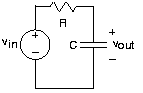
For the above example circuit ( [link] ), let . The complex amplitude determines the size of the source and its phase. The critical consequence of assuming that sources have this form is that all voltages and currents in the circuit are also complex exponentials, having amplitudes governed byKVL, KCL, and the v-i relations and the same frequency as the source. To appreciate why this should betrue, let's investigate how each circuit element behaves when either the voltage or current is a complex exponential. For theresistor, . When ; then . Thus, if the resistor's voltage is a complex exponential, so isthe current, with an amplitude (determined by the resistor's v-i relation) and a frequency the same as the voltage. Clearly, if the currentwere assumed to be a complex exponential, so would the voltage. For a capacitor, . Letting the voltage be a complex exponential, we have . The amplitude of this complex exponential is . Finally, for the inductor, where , assuming the current to be a complex exponential results in thevoltage having the form , making its complex amplitude .
The major consequence of assuming complex exponential voltage and currents is that the ratio for each element does not depend on time, but does depend on source frequency . This quantity is known as the element's impedance .
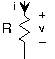
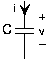
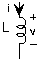
The impedance is, in general, a complex-valued, frequency-dependent quantity. For example, the magnitude of thecapacitor's impedance is inversely related to frequency, and has a phase of . This observation means that if the current is a complexexponential and has constant amplitude, the amplitude of the voltage decreases with frequency.
Let's consider Kirchoff's circuit laws. When voltages around aloop are all complex exponentials of the same frequency, we have
What we have discovered is that source(s) equaling a complex exponential of the same frequency forces all circuit variablesto be complex exponentials of the same frequency. Consequently, the ratio of voltage to current for each element equals theratio of their complex amplitudes, which depends only on the source's frequency and element values.
This situation occurs because the circuit elements are linearand time-invariant. For example, suppose we had a circuit element where the voltage equaled the square of the current: . If , , meaning that voltage and current no longer had the samefrequency and that their ratio was time-dependent.
Because for linear circuit elements the complex amplitude of voltage is proportional to the complex amplitude ofcurrent— — assuming complex exponential sources means circuitelements behave as if they were resistors, where instead of resistance, we use impedance. Because complex amplitudes for voltage and current also obey Kirchoff's laws, we can solvecircuits using voltage and current divider and the series and parallel combination rules by considering the elements to beimpedances.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?