| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This learning unit tells the incredible history of the development of road transport.
1
2
3
4

5
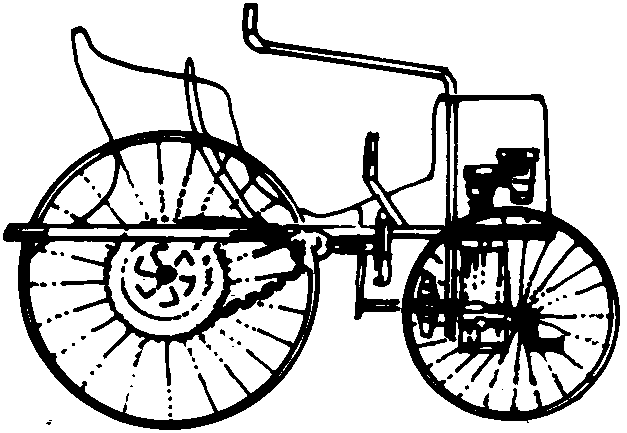
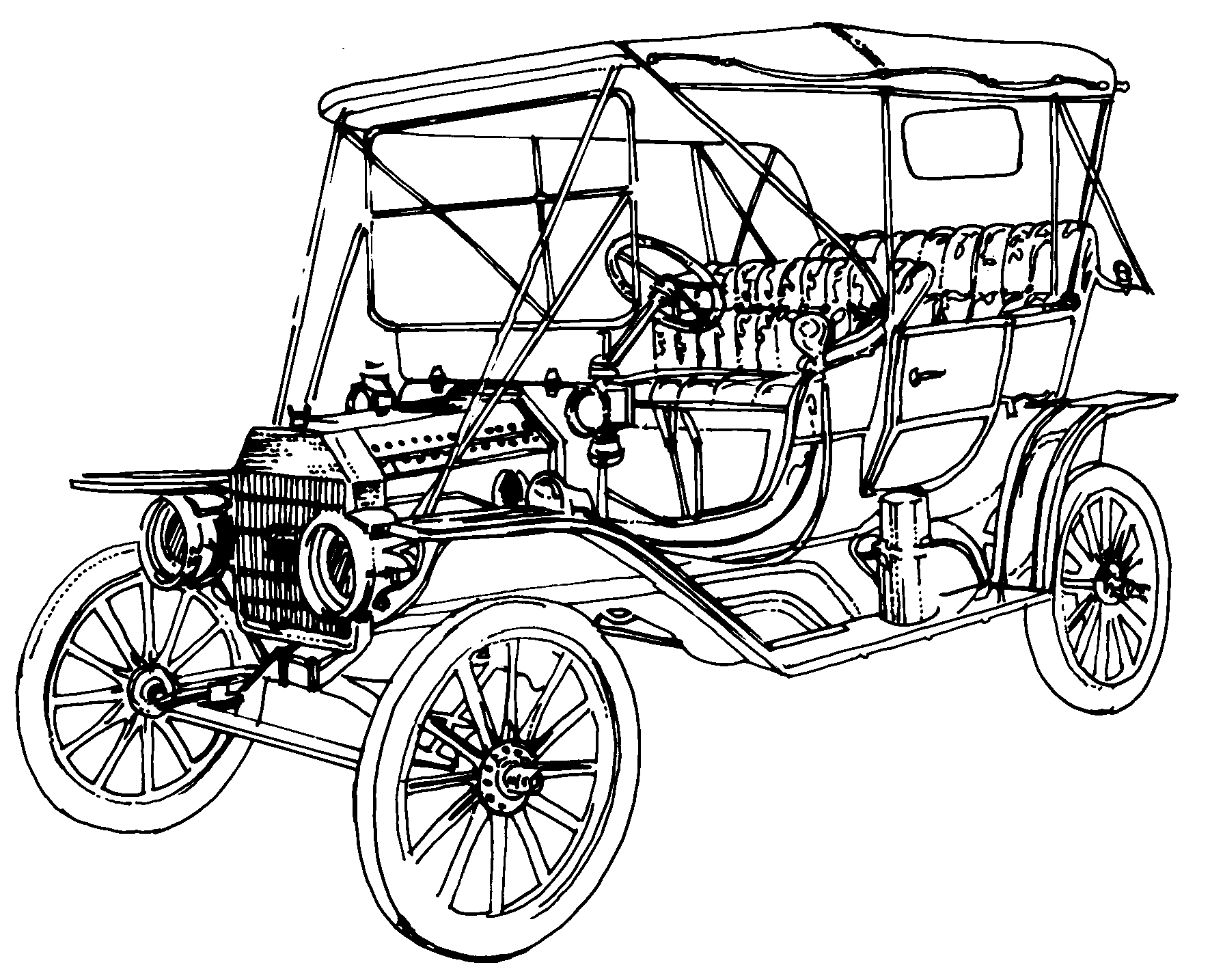
First motorcar with gears
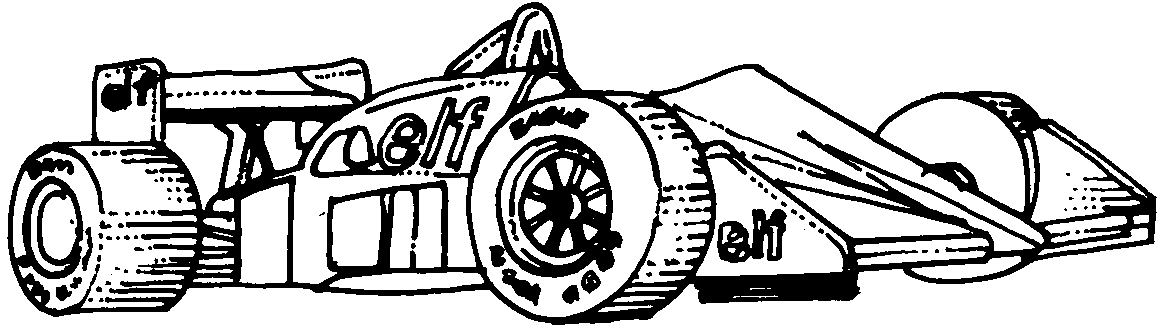
Formula One racing car
We'll be doing more exercises that involve time later in the module.
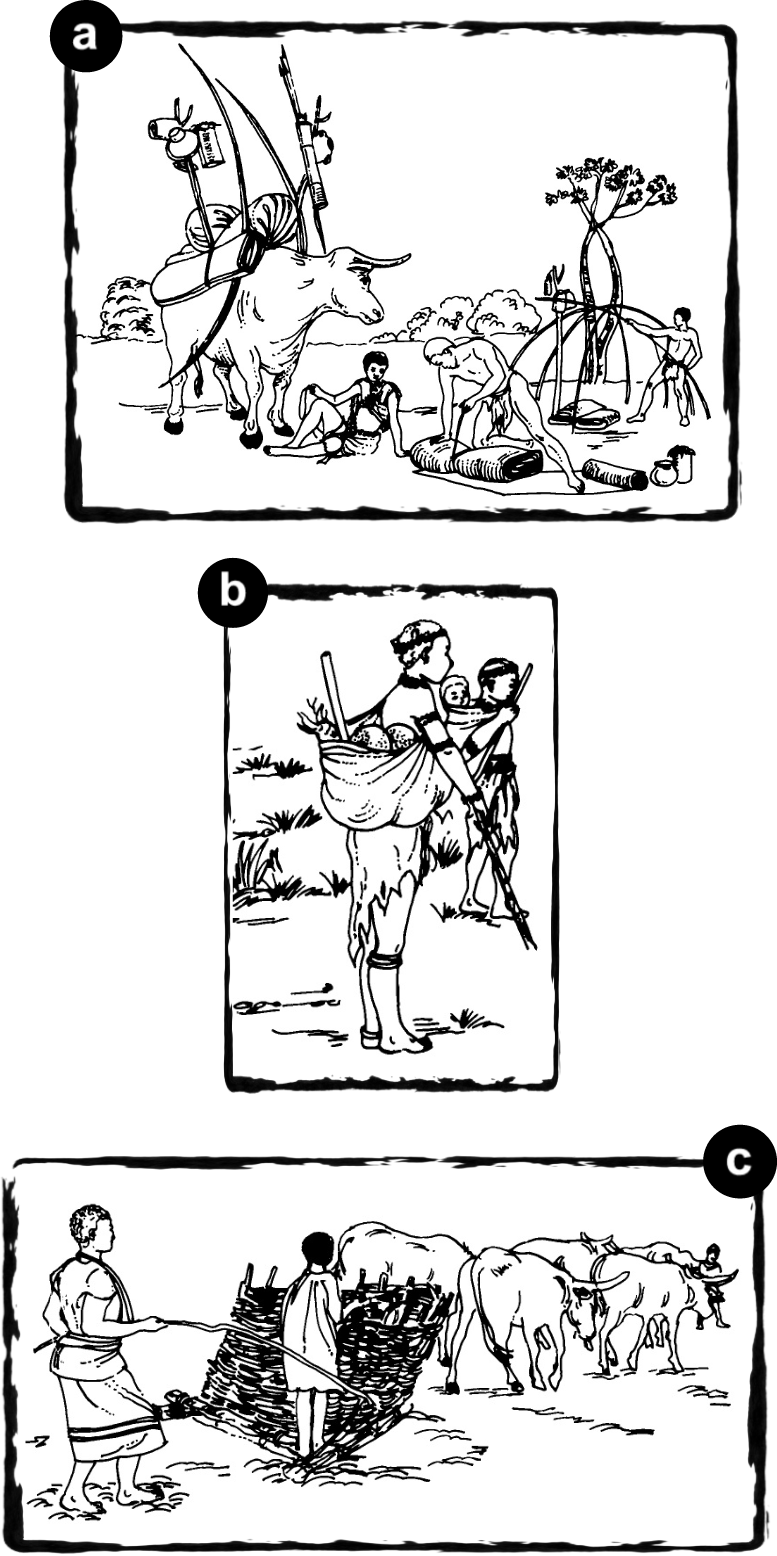
The San, Khoina and Bantu-speaking peoples lived in our country many years ago.
The San walked to find water for drinking, plants for eating and animals to hunt. They therefore usually carried their possessions with them.
The Khoina and the Bantu-speaking peoples kept cattle. Sometimes they used the animals for transportation. They also used the cattle for trading.
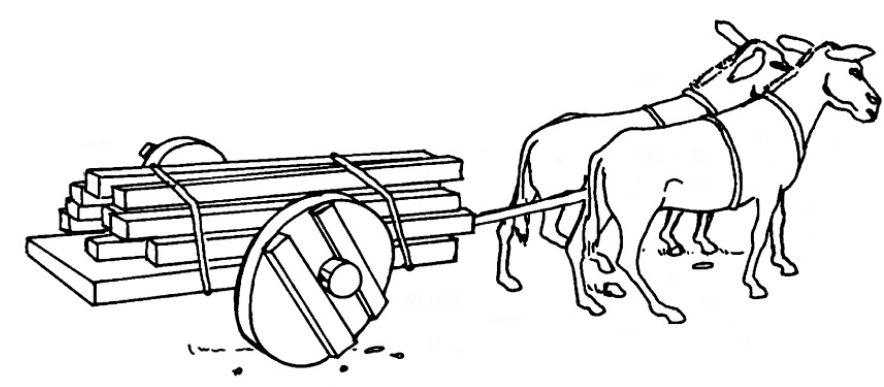
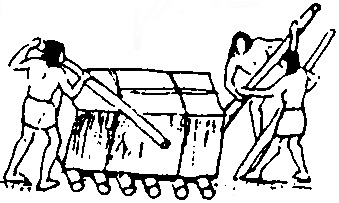
c)1. Name the different kinds of transportation shown in (a), (b) and (c). Decide on a caption for each picture.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………….
2. What is carried or transported by the people in each of the pictures?
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
3. How do you think each of these groups would cross a river?
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
4. Who is able to transport:
5. What was used to make the means of transport that is illustrated in (c)?
.………………………………………………………………………………….
6. Which of these means of transport are still in use?……………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………..
People from the Netherlands who came to our country later brought very different means of transport with them. Horses, carts, wagons and slaves were common in the villages of the time. Cattle farmers in particular also used ox wagons.
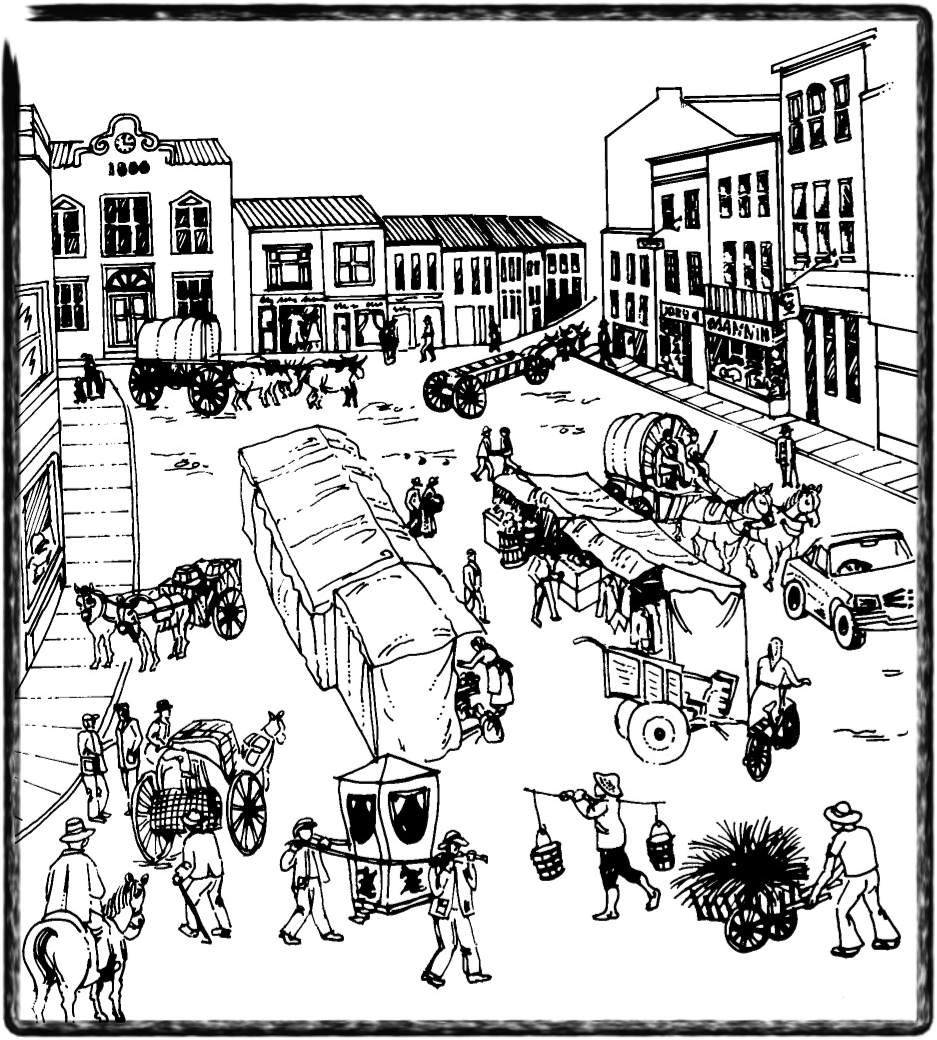

The town square in Dogsville towards 1800.

LEARNING OUTCOME 1: HISTORICAL ENQUIRY The learner will be able to use enquiry skills to investigate the past and present.
We know this when the learner:
1.2 answers questions: uses information from sources to answer questions.
The learner will be able to interpret aspects of history.
We know this when the learner:
needs a driver, etc.
Differences: streamlining, speed, power, etc.
c) 1. ox walk/carry sleigh of branches
2. Own answers.
3. Own answers.
4. Most: c Least: b
5. Wood.
6. Probably all three.
d) 1. Causes: comfort, speed.
Results: Buses, cars, bicycles, roller skates, gears, occupations, roads, etc.
.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'History grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?