| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This module was developed as part of a Rice University course CHEM496: Chemistry of Electronic Materials . This module was prepared with the assistance of Pui Yee Hung.
In 1990, electroluminescent (EL) from conjugated polymers was first reported by Burroughes et al. of Cambridge University. A layer of poly( para -phenylenevinylene) (PPV) was sandwiched between layers of indium tin oxide (ITO) and aluminum. When this device is under a 14 V dc bias, the PPV emits a yellowish-green light with a quantum efficiency of 0.05%. This report attracted a lot of attention, because the potential that polymer light emitting diodes (LEDs) could be inexpensively mass produced into large area display area. The processing steps in making polymer LEDs are readily scaleable. The industrial coating techniques is well developed to mass produce polymer layers of 100 nm thickness, and the device could be patterned onto large surface area by pixellation of metal.
Since the initial discovery, and increasing amount of researches has been performed, and significant progress has been made. In 1990 the polymer LED only emitted yellowish green color, now the emission color ranged from deep blue to near infra red. The efficiency of the multi-layer polymer LED even reached a quantum efficiency of>4% and the operating voltage has been reduced significantly. In term of efficiency, color selection and operating voltage, polymer LEDs have attained adequate levels for commercialization. But there are reliability problems that are symptomatic of any organic devices.
A schematic diagram of a polymer LED is shown in [link] . A polymer LED can be divided into three different components:
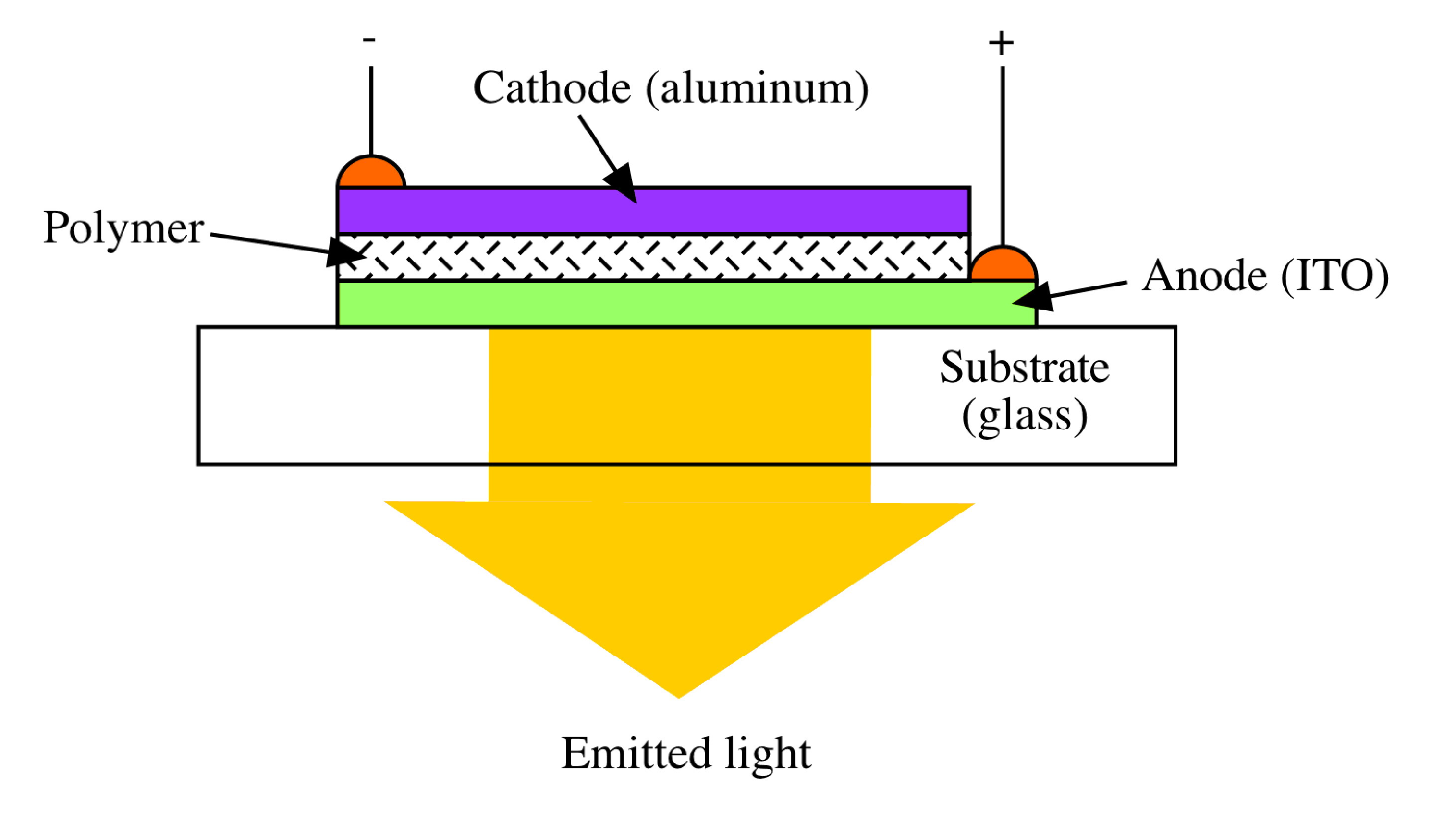
When a polymer LED is under a direct current (dc) bias, holes are injected from the anode (ITO) and electrons are injected from the cathode (aluminum). Under the influences of the electrical field, the electrons and holes will migrate toward each other. When they recombine in the conjugated polymer layer, a bound excited states (excitons) will be formed. Some of the excitons (singlets) then decays in the conjugated polymer layer to emit light through the transparent substrates (glass). The emission color will be depended on the energy gap of the polymers. There is energy gap in a conjugated polymer because the π electron are not completely delocalized over the entire polymer chain. Instead there are alternate region in the polymer chain that has a higher electron density ( [link] a). The chain length of this region is about 15-20 multiple bonds. The emission color can be controlled by tuning this energy band gap ( [link] b). It shows that bond alternation limits the extent of delocalization. [link] summarizes the structure and emission color of some common conjugated polymers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of electronic materials' conversation and receive update notifications?